标签:with present pop user The 可变 不可 erro plain
包含的主要功能如下
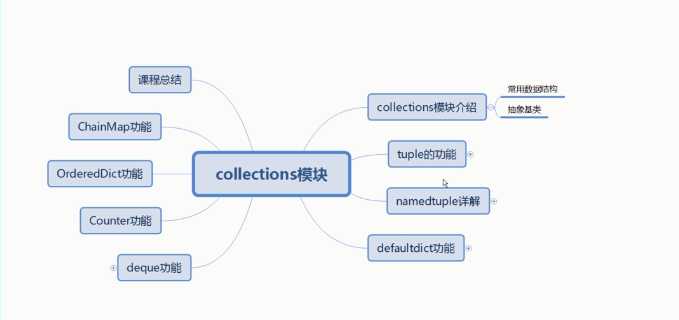
查看collections 的源码我们可以看到其为我们封装了以下的数据结果供我们调用
__all__ = [‘deque‘, ‘defaultdict‘, ‘namedtuple‘, ‘UserDict‘, ‘UserList‘,
‘UserString‘, ‘Counter‘, ‘OrderedDict‘, ‘ChainMap‘]
测试代码如下
name_tuple = (‘zhangbiao‘,18,[‘beijing‘])
name, *other = name_tuple
# 拆包
print(name,other)
# tuple 不可变不是绝对的
name_tuple[2].append(‘haha‘)
print(name_tuple)
# 可以作为字典的key
user_tuple = (‘zhangbiao‘,18,175)
dict = {}
dict[user_tuple] = ‘zhangbiao‘
print(dict)
输出结果如下

namedtuple适用于创建一个简单的对象
from collections import namedtuple User = namedtuple(‘user‘,[‘name‘,‘age‘,‘height‘]) user_tuple = (‘zhangbiao‘, 29, 175) user = User(*user_tuple) print(user.age, user.name, user.height)
打印结果如下
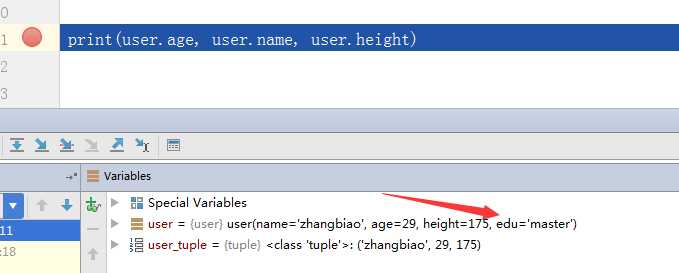
使用namedtuple的好处,比如我们通过查询数据库(MySQLClient和pymysql)返回给我们的就是一个元祖,我们想要给前端返回的数据是name,age,height 和edu ,而我们的数据库中没有edu这个字段,这时候我们就可以利用namedtuple很轻松的处理这种情况
from collections import namedtuple User = namedtuple(‘user‘,[‘name‘,‘age‘,‘height‘,‘edu‘]) # 假如是数据库中查询出来的数据 user_tuple = (‘zhangbiao‘, 29, 175) # 添加edu的字段 user = User(*user_tuple ,edu=‘master‘) print(user.age, user.name, user.height)
测试结果如下
namedtuple中的_make()和 _asdict() 方法
查看nametuple的源码我们可以看到其封装了以下的方法
class {typename}(tuple): ‘{typename}({arg_list})‘ __slots__ = () _fields = {field_names!r} def __new__(_cls, {arg_list}): ‘Create new instance of {typename}({arg_list})‘ return _tuple.__new__(_cls, ({arg_list})) @classmethod def _make(cls, iterable, new=tuple.__new__, len=len): ‘Make a new {typename} object from a sequence or iterable‘ result = new(cls, iterable) if len(result) != {num_fields:d}: raise TypeError(‘Expected {num_fields:d} arguments, got %d‘ % len(result)) return result def _replace(_self, **kwds): ‘Return a new {typename} object replacing specified fields with new values‘ result = _self._make(map(kwds.pop, {field_names!r}, _self)) if kwds: raise ValueError(‘Got unexpected field names: %r‘ % list(kwds)) return result def __repr__(self): ‘Return a nicely formatted representation string‘ return self.__class__.__name__ + ‘({repr_fmt})‘ % self def _asdict(self): ‘Return a new OrderedDict which maps field names to their values.‘ return OrderedDict(zip(self._fields, self)) def __getnewargs__(self): ‘Return self as a plain tuple. Used by copy and pickle.‘ return tuple(self) {field_defs} """
这里面最常用的的是_make 和 _asdict 方法
_make方法的使用是在我们创建 namedtuple的时候可以传入一个可迭代的对象
from collections import namedtuple
User = namedtuple(‘user‘,[‘name‘,‘age‘,‘height‘])
user_tuple = (‘zhangbiao‘, 29, 175)
user_list = [‘zhangbiao‘, 29, 175]
user_dict = {
"name": "zhangbiao",
"age": 29,
"height": 175,
}
user = User._make(user_dict)
user1 = User._make(user_list)
# 拆包
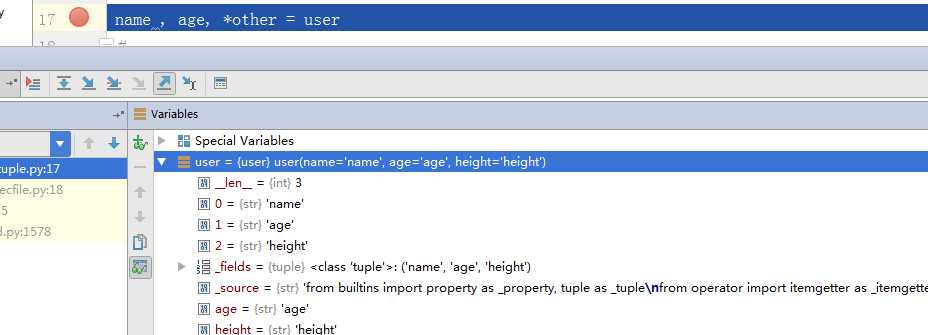
name , age, *other = user
打印结果如下
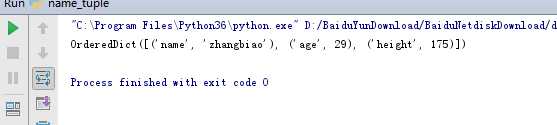
_asdict 方法就是把namedtulple转化成一个OrderedDict
from collections import namedtuple User = namedtuple(‘user‘,[‘name‘,‘age‘,‘height‘]) user_tuple = (‘zhangbiao‘, 29, 175) user = User._make(user_tuple) user_info_dict = user._asdict() print(user_info_dict)
打印结果如下
sdad
标签:with present pop user The 可变 不可 erro plain
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/crazymagic/p/10039980.html