标签:output java入门 index 对象 alt tle 笔记 get 用户输入


java文件编程--常用io流
常用io流--文件字节流
1、案例[Io02.java]:读取文件(文件字节输入流使用,目的:FileInputStream类)把用/** * File类的基本用法 * io流--文件字节流 * FileInputStream类的使用 */import java.io.*;public class Io02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //得到一个文件对象,f指向e:\ff\hsp.txt文件 File f=new File("e:\\ff\\hsp.txt"); FileInputStream fis=null; try { //因为File没有读写的能力,所以需要使用InputStream类 fis=new FileInputStream(f); //定义一个字节数组,相当于缓存 byte []bytes=new byte[1024]; int n=0;//得到实际读取到的字节数 //循环读取 while((n=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ //把字节转成String String s=new String(bytes,0,n); System.out.println(s); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //关闭文件流必需放在finally语句块中 try { fis.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }}2、案例[Io03.java]:从键盘接收用户输入内容,并保存到文件中(文件字节输出流,目的:FileOutputStream类)
x
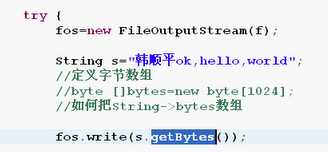
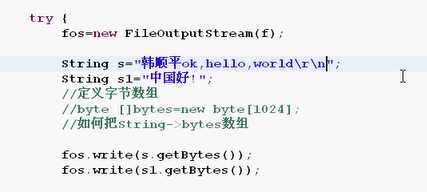
/** * File类的基本用法 * io流--文件字节流 * FileOutputStream类的使用 */import java.io.*;public class Io03 { public static void main(String[] args) { File f=new File("e:\\ff\\ss.txt");//直接覆盖写同一个文件 //字节输出流 FileOutputStream fos=null; if(f.exists()){ System.out.println("文件已存在"); }else{ try { fos=new FileOutputStream(f); String s="hello,world!\r\n"; String s1="中国人"; fos.write(s.getBytes()); fos.write(s1.getBytes()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { fos.close(); } catch (Exception e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } } } }}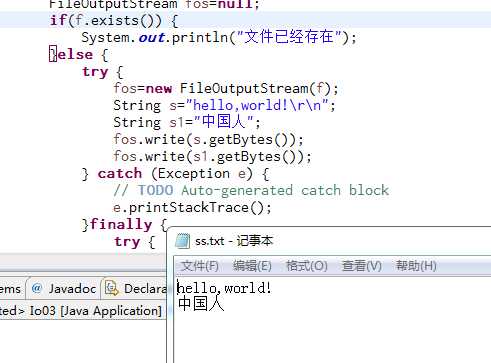
标签:output java入门 index 对象 alt tle 笔记 get 用户输入
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuxaut-558/p/10045771.html