目录
基本
--新建表: create table table1( id varchar(300) primary key, name varchar(200) not null); --插入数据 insert into table1 (id,name) values (‘aa‘,‘bb‘); --更新数据 update table1 set id = ‘bb‘ where id=‘cc‘; --删除数据 delete from table1 where id =‘cc‘; --删除表 drop table table1; --修改表名: alter table table1 rename to table2; --表数据复制: insert into table1 (select * from table2); --复制表结构: create table table1 select * from table2 where 1>1; --复制表结构和数据: create table table1 select * from table2; --复制指定字段: create table table1 as select id, name from table2 where 1>1; --条件查询: select id,name (case gender when 0 then ‘男‘ when 1 then ‘女’ end ) gender from table1
数学函数
--绝对值:abs() select abs(-2) value from dual; --(2) --取整函数(大):ceil() select ceil(-2.001) value from dual; --(-2) --取整函数(小):floor() select floor(-2.001) value from dual; --(-3) --取整函数(截取):trunc() select trunc(-2.001) value from dual; -- (-2) --四舍五入:round() select round(1.234564,4) value from dual; --(1.2346) --取平方:Power(m,n) select power(4,2) value from dual; --(16) --取平方根:SQRT() select sqrt(16) value from dual; --(4) --取随机数:dbms_random(minvalue,maxvalue) select dbms_random.value() from dual; (默认是0到1之间) select dbms_random.value(2,4) value from dual; (2-4之间随机数) --取符号:Sign() select sign(-3) value from dual; --(-1) select sign(3) value from dual; --(1) --取集合的最大值:greatest(value) select greatest(-1,3,5,7,9) value from dual; --(9) --取集合的最小值:least(value) select least(-1,3,5,7,9) value from dual; --(-1) --处理Null值:nvl(空值,代替值) select nvl(null,10) value from dual; --(10) select nvl(score,10) score from student;
rownum相关
--rownum小于某个数时可以直接作为查询条件(注意oracle不支持select top) select * from student where rownum <3; --查询rownum大于某个数值,需要使用子查询,并且rownum需要有别名 select * from(select rownum rn ,id,name from student) where rn>2; select * from (select rownum rn, student.* from student) where rn >3; --区间查询 select * from (select rownum rn, student.* from student) where rn >3 and rn<6; --排序+前n条 select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRUVER d order by drivernumber)t )p where p.rn<10; --排序+区间查询1 select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t )p where p.rn<9 and p.rn>6; --排序+区间查询2 select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t where rownum<9 )p where p.rn>6;--效率远高于方式一
分页查询
(假设每页显示10条)
不包含排序:
--效率低 select * from (select rownum rn, d.* from DJDRIVER d )p where p.rn<=20 and p.rn>=10;
select * from (select rownum rn, d.* from DJDRIVER d )p where p.rn between 10 and 20; --效率高 select * from (select rownum rn, d.* from DJDRIVER d where rownum<=20 )p where p.rn>=10;
包含排序:
--排序+区间查询1(效率低)
select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t )p where p.rn<=20 and p.rn>=10;
select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t )p where p.rn between 10 and 20; --排序+区间查询2(效率高)
select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t where rownum<=20 )p where p.rn>=10;
时间处理
1. to_char和to_date基本使用
--日期 --年 yyyy yyy yy year --月 month mm mon month --日+星期 dd ddd(一年中第几天) dy day --小时 hh hh24 --分 mi --秒 ss
eg1:
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘)currenttime,
to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy‘) year,
to_char(sysdate,‘mm‘) month,
to_char(sysdate,‘dd‘) day,
to_char(sysdate,‘day‘) week,
to_char(sysdate,‘hh24‘)hour,
to_char(sysdate,‘mi‘) minute,
to_char(sysdate,‘ss‘) second
from dual;

eg2:
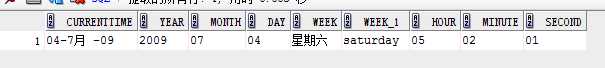
select to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘)currenttime,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘yyyy‘)year,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘mm‘)month,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘dd‘) day,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘day‘) week,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘day‘,‘NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE=American‘) week, --设置语言
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘hh24‘)hour,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘mi‘) minute,
to_char(to_date(‘2009-07-04 05:02:01‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘),‘ss‘) second
from dual;
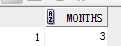
2)months_between
select months_between(to_date(‘03-31-2014‘,‘MM-DD-YYYY‘),to_date(‘12-31-2013‘,‘MM-DD-YYYY‘)) "MONTHS" FROM DUAL;
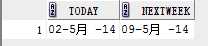
3)next_day
select sysdate today, next_day(sysdate,6) nextweek from dual;
4)时间区间
eg:
select cardid, borrowdate from borrow where to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) between to_date(‘2014-02-01 00:00:00‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) and to_date(‘2014-05-01 00:00:00‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘);
5)interval
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) currenttime,
to_char(sysdate - interval ‘7‘ year,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) intervalyear,
to_char(sysdate - interval ‘7‘ month,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) intervalMonth,
to_char(sysdate - interval ‘7‘ day,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) intervalday,
to_char(sysdate - interval ‘7‘ hour,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) intervalHour,
to_char(sysdate - interval ‘7‘ minute,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) intervalMinute,
to_char(sysdate - interval ‘7‘ second,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) intervalSecond
from dual;

6)add_months
select add_months(sysdate,12) newtime from dual;
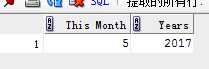
7)extract
select extract(month from sysdate) "This Month", extract(year from add_months(sysdate,36)) " Years" from dual;
字符函数
--字符函数
select substr(‘abcdefg‘,1,5)substr, --字符串截取
instr(‘abcdefg‘,‘bc‘) instr, --查找子串
‘Hello‘||‘World‘ concat, --连接
trim(‘ wish ‘) trim, --去前后空格
rtrim(‘wish ‘) rtrim, --去后面空格
ltrim(‘ wish‘) ltrim, --去前面空格
trim(leading ‘w‘ from ‘wish‘) deleteprefix, --去前缀
trim(trailing ‘h‘ from ‘wish‘) deletetrailing, --去后缀
trim(‘w‘ from ‘wish‘) trim1,
ascii(‘A‘) A1,
ascii(‘a‘) A2, --ascii(转换为对应的十进制数)
chr(65) C1,
chr(97) C2, --chr(十进制转对应字符)
length(‘abcdefg‘) len, --length
lower(‘WISH‘)lower,
upper(‘wish‘)upper,
initcap(‘wish‘)initcap, --大小写变换
replace(‘wish1‘,‘1‘,‘youhappy‘) replace, --替换
translate(‘wish1‘,‘1‘,‘y‘)translate, --转换,对应一位(前面的位数大于等于后面的位数)
translate(‘wish1‘,‘sh1‘,‘hy‘)translate1,
concat(‘11‘,‘22‘) concat --连接
from dual;

to_number
--to_number(expr)
--to_number(expr,format)
--to_number(expr,format,‘nls-param‘)
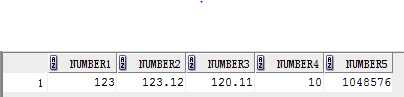
select to_number(‘0123‘)number1, --converts a string to number
trunc(to_number(‘0123.123‘),2) number2,
to_number(‘120.11‘,‘999.99‘) number3,
to_number(‘0a‘,‘xx‘) number4, --converts a hex number to decimal
to_number(100000,‘xxxxxx‘) number5
from dual;
聚合函数
student表如下:
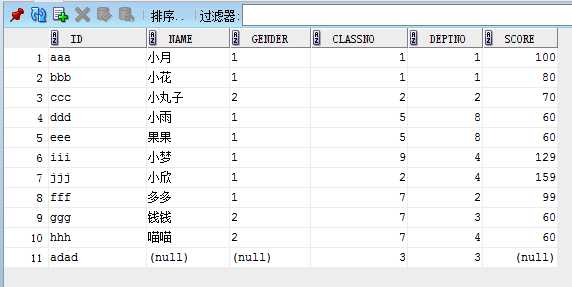
count:
--count (distinct|all) select count(1) as count from student;--效率最高 select count(*) as count from student; select count(distinct score) from student;
语句1结果:11
avg
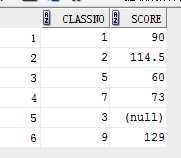
--avg (distinct|all) select avg(score) score from student; select avg(distinct score) from student; select classno,avg(score) score from student group by classno;
语句3输出结果:
max
--max (distinct|all) select max(score) from student; select classno, max(score) score from student group by classno;
min
--min (distinct|all) select min(score) from student; select classno, min(score) score from student group by classno;
stddev(standard deviation)标准差
--stddev select stddev(score) from student; select classno, stddev(score) score from student group by classno;
sum
--sum select sum(score) from student; select classno, sum(score) score from student group by classno;
median--中位数
--median select median(score) from student; select classno, median(score) score from student group by classno;
案例1--学生选课
1. 创建表 stu(学生表),course(课程表),选课表(s_c)
--创建表 create table STU ( id NUMBER not null, name VARCHAR2(255) ) ; create table COURSE ( id NUMBER not null, coursename VARCHAR2(255) ) ; create table S_C ( sid NUMBER, cid NUMBER, score NUMBER );
2.插入数据
--插入数据 Insert into STU (ID,NAME) values (1,‘wish‘); Insert into STU (ID,NAME) values (2,‘rain‘); Insert into STU (ID,NAME) values (3,‘july‘); Insert into STU (ID,NAME) values (4,‘joey‘); Insert into COURSE (ID,COURSENAME) values (1,‘math‘); Insert into COURSE (ID,COURSENAME) values (2,‘english‘); Insert into COURSE (ID,COURSENAME) values (3,‘Japanese‘); Insert into COURSE (ID,COURSENAME) values (4,‘chinese‘); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (1,1,80); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (1,2,90); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (2,4,100); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (4,4,90); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (4,1,100); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (4,3,80); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (4,2,80); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (2,1,90); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (2,4,100); Insert into S_C (SID,CID,SCORE) values (3,1,60);
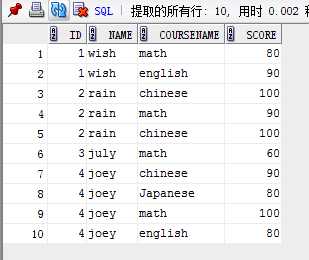
3.查询学生选课情况
with vt as (select s.id,s.name,c.coursename,sc.score from stu s, course c, s_c sc where s.id=sc.sid and c.id=sc.cid) select * from vt order by id;
结果:
案例2--图书馆借阅
1.创建表: 图书(book),读者(reader),借阅(borrow)
--创建表 book
create table book(
bookId varchar2(30), --图书总编号
sortid varchar2(30), --分类号
bookname varchar2(100), --书名
author varchar2(30), --作者
publisher varchar2(100),--出版单位
price number(6,2) --价格
);
--创建表 reader
create table reader (
cardId varchar2(30), --借书证号
org varchar2(100), --单位
name varchar2(100), --姓名
gender varchar2(2), --性别
title varchar2(30), --职称
address varchar2(100) --地址
);
--创建表 borrow
create table borrow(
cardId varchar2(30), --借书证号
bookId varchar2(30), --图书总编号
borrowDate varchar2(30) --借阅时间
);
2.插入数据
--插入数据-book insert into book (bookId,sortid,bookname,author,publisher,price) values (‘aaa‘,‘a1‘,‘gone with the wind‘,‘CA‘,‘renmin‘,‘103‘); insert into book (bookId,sortid,bookname,author,publisher,price) values (‘bbb‘,‘a2‘,‘the little prince‘,‘CB‘,‘jixie‘,‘30‘); insert into book (bookId,sortid,bookname,author,publisher,price) values (‘ccc‘,‘a3‘,‘the ordinary world‘,‘CC‘,‘renmin‘,‘130‘); insert into book (bookId,sortid,bookname,author,publisher,price) values (‘ddd‘,‘a4‘,‘the little women‘,‘CA‘,‘dianzi‘,‘110‘); --插入数据-reader insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘xxx‘,‘A‘,‘wish‘,‘1‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘uuu‘,‘A‘,‘luna‘,‘1‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘vvv‘,‘B‘,‘harry‘,‘1‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘www‘,‘C‘,‘chander‘,‘2‘,‘professor‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘yyy‘,‘A‘,‘joey‘,‘2‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘zzz‘,‘B‘,‘richard‘,‘2‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘OOO‘,‘A‘,‘micheal‘,‘2‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘ppp‘,‘A‘,‘richal‘,‘2‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘abp‘,‘A‘,‘michal‘,‘2‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); insert into reader(cardid, org, name,gender, title, address) values (‘ccp‘,‘A‘,‘mike‘,‘2‘,‘student‘,‘bupt‘); --插入数据-borrow insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘xxx‘,‘aaa‘,‘2014-4-29‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘xxx‘,‘bbb‘,‘2014-4-29‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘xxx‘,‘ccc‘,‘2014-4-28‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘yyy‘,‘ccc‘,‘2014-4-28‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘yyy‘,‘ddd‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘yyy‘,‘aaa‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘zzz‘,‘bbb‘,‘2014-4-28‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘zzz‘,‘ddd‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘zzz‘,‘aaa‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘uuu‘,‘bbb‘,‘2014-4-28‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘uuu‘,‘ddd‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘uuu‘,‘aaa‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘uuu‘,‘ccc‘,‘2014-4-26‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘vvv‘,‘bbb‘,‘2014-4-28‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘vvv‘,‘ddd‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘www‘,‘aaa‘,‘2014-4-27‘); insert into borrow(cardid,bookid,borrowdate) values(‘www‘,‘ccc‘,‘2014-4-26‘);
表信息如下:
book------> reader-------> borrow
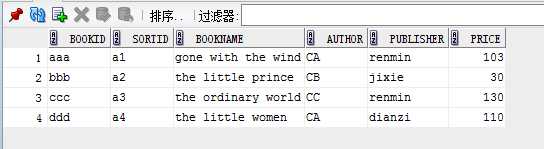
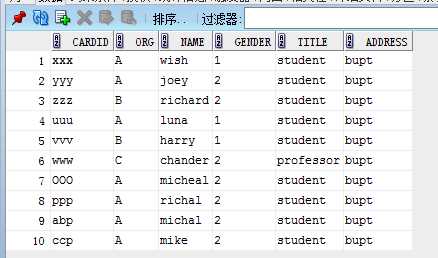
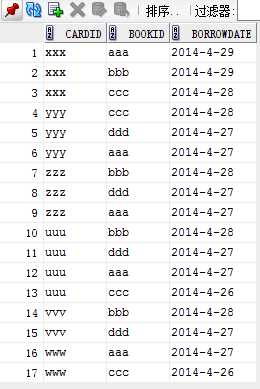
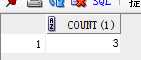
3. 查询A单位借阅图书的读者人数和人员详细信息
人数:
with vt1 as (select cardid from reader where reader.org=‘A‘) select count(1) from vt1 where exists (select cardid from borrow where borrow.cardid=vt1.cardid);
详细信息:
with vt1 as (select cardid,name,org from reader where reader.org=‘A‘) select cardid,name,org from vt1 where exists (select cardid from borrow where borrow.cardid=vt1.cardid);
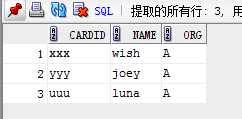
4.查询借书证号尾字符为‘p‘的读者
select cardid, name, org from reader where cardid like ‘%p‘;
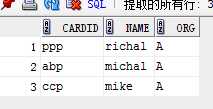
5. 查询名字以m开头的女性读者,‘1’显示为女,‘2’显示为男
select cardid, name, org, case when gender=‘1‘ then ‘女‘ when gender=‘2‘ then ‘男‘ else ‘其他‘ end gender from reader where name like ‘m%‘;
6. 2014年2-4月借过书的读者
1)查询满足条件的读者(仅包含cardid)--未去重
方式一:
select cardid, borrowdate from borrow where to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy‘)=‘2014‘ and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘mm‘)>=‘02‘ and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘mm‘)<=‘04‘;
方式二:
select cardid, borrowdate from borrow where to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy‘)=‘2014‘ --查询 and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy-mm‘)>=‘2014-02‘ and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy-mm‘)<=‘2014-04‘;
方式三:
select cardid, borrowdate from borrow where to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) between to_date(‘2014-02-01 00:00:00‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) and to_date(‘2014-05-01 00:00:00‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘);
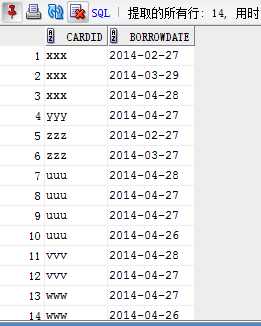
2) 查询+去重
select distinct cardid from borrow where to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy‘)=‘2014‘ --查询+去重 and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy-mm‘)>=‘2014-02‘ and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy-mm‘)<=‘2014-04‘;
select distinct cardid from borrow where to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) between to_date(‘2014-02-01 00:00:00‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) and to_date(‘2014-05-01 00:00:00‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘);
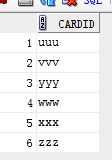
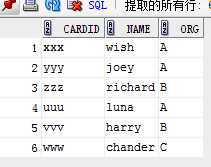
3)查询+去重+读者姓名等信息
with vt1 as (select distinct cardid from borrow where to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy‘)=‘2014‘ and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy-mm‘)>=‘2014-02‘ and to_char(to_date(borrowdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd‘),‘yyyy-mm‘)<=‘2014-04‘) select cardid, name,org from reader where exists (select cardid from vt1 where vt1.cardid=reader.cardid);
https://www.cnblogs.com/wishyouhappy/p/3700683.html
|
两个Date类型字段:START_DATE,END_DATE,计算这两个日期的时间差(分别以天,小时,分钟,秒,毫秒): 天: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE)) 小时: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24) 分钟: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24 * 60) 秒: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24 * 60 * 60) 毫秒: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)
|
Oracle计算时间差函数 2008-08-20 10:00 两个Date类型字段:START_DATE,END_DATE,计算这两个日期的时间差(分别以天,小时,分钟,秒,毫秒): 天: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE)) 小时: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24) 分钟: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24 * 60) 秒: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24 * 60 * 60) 毫秒: ROUND(TO_NUMBER(END_DATE - START_DATE) * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)
外加to_date与to_char函数:
ORACLE中:
select to_date(‘2007-06-28 19:51:20‘,‘yyyy-MM-dd HH24:mi:ss‘) from dual;
一般SQL中:
select to_date(‘2007-06-28 19:51:20‘,‘yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss‘) from dual;
区别:
1、HH修改为HH24。
2、分钟的mm修改为mi。
24 小时的形式显示出来要用 HH24
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-MM-dd HH24:mi:ss‘) from dual;
select to_date(‘2005-01-01 13:14:20‘,‘yyyy-MM-dd HH24:mi:ss‘) from dual;
to_date() function
1. 日期格式参数 含义说明
D 一周中的星期几
DAY 天的名字,使用空格填充到 9 个字符
DD 月中的第几天
DDD 年中的第几天
DY 天的简写名
IW ISO 标准的年中的第几周
IYYY ISO 标准的四位年份
YYYY 四位年份
YYY,YY,Y 年份的最后三位,两位,一位
HH 小时,按 12 小时计
HH24 小时,按 24 小时计
MI 分
SS 秒
MM 月
Mon 月份的简写
Month 月份的全名
W 该月的第几个星期
WW 年中的第几个星期 1. 日期时间间隔操作
当前时间减去 7 分钟的时间
select sysdate,sysdate - interval ‘7‘ MINUTE from dual
当前时间减去 7 小时的时间
select sysdate - interval ‘7‘ hour from dual
当前时间减去 7 天的时间
select sysdate - interval ‘7‘ day from dual
当前时间减去 7 月的时间
select sysdate,sysdate - interval ‘7‘ month from dual
当前时间减去 7 年的时间
select sysdate,sysdate - interval ‘7‘ year from dual
时间间隔乘以一个数字
select sysdate,sysdate - 8 *interval ‘2‘ hour from dual
2. 日期到字符操作
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) from dual
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss‘) from dual
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-ddd hh:mi:ss‘) from dual
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm iw-d hh:mi:ss‘) from dual
参考 oracle 的相关关文档 (ORACLE901DOC/SERVER.901/A90125/SQL_ELEMENTS4.HTM#48515)
3. 字符到日期操作
select to_date(‘2003-10-17 21:15:37‘,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss‘) from dual
具体用法和上面的 to_char 差不多。
4.TO_NUMBER
使用TO_NUMBER函数将字符转换为数字
TO_NUMBER(char[, ‘格式‘])
数字格式格式
9 代表一个数字
0 强制显示0
$ 放置一个$符
L 放置一个浮动本地货币符
. 显示小数点
, 显示千位指示符
oracle中的to_date参数含义
1.日期格式参数含义说明
D 一周中的星期几
DAY 天的名字,使用空格填充到9个字符
DD 月中的第几天
DDD 年中的第几天
DY 天的简写名
IW ISO标准的年中的第几周
IYYY ISO标准的四位年份
YYYY 四位年份
YYY,YY,Y 年份的最后三位,两位,一位
HH 小时,按12小时计
HH24 小时,按24小时计
MI 分
SS 秒
MM 月
Mon 月份的简写
Month 月份的全名
W 该月的第几个星期
WW 年中的第几个星期 1.日期时间间隔操作
当前时间减去7分钟的时间
select sysdate,sysdate - interval ’7’ MINUTE from dual
当前时间减去7小时的时间
select sysdate - interval ’7’ hour from dual
当前时间减去7天的时间
select sysdate - interval ’7’ day from dual
当前时间减去7月的时间
select sysdate,sysdate - interval ’7’ month from dual
当前时间减去7年的时间
select sysdate,sysdate - interval ’7’ year from dual
时间间隔乘以一个数字
select sysdate,sysdate - 8 *interval ’2’ hour from dual
2.日期到字符操作
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,’yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) from dual
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,’yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss’) from dual
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,’yyyy-ddd hh:mi:ss’) from dual
select sysdate,to_char(sysdate,’yyyy-mm iw-d hh:mi:ss’) from dual
参考oracle的相关关文档(ORACLE901DOC/SERVER.901/A90125/SQL_ELEMENTS4.HTM#48515)
3. 字符到日期操作
select to_date(’2003-10-17 21:15:37’,’yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) from dual
具体用法和上面的to_char差不多。
4. trunk/ ROUND函数的使用
select trunc(sysdate ,’YEAR’) from dual
select trunc(sysdate ) from dual
select to_char(trunc(sysdate ,’YYYY’),’YYYY’) from dual
5.oracle有毫秒级的数据类型
--返回当前时间 年月日小时分秒毫秒
select to_char(current_timestamp(5),’DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF’) from dual;
--返回当前时间的秒毫秒,可以指定秒后面的精度(最大=9)
select to_char(current_timestamp(9),’MI:SSxFF’) from dual;
6.计算程序运行的时间(ms)
declare
type rc is ref cursor;
l_rc rc;
l_dummy all_objects.object_name%type;
l_start number default dbms_utility.get_time;
begin
for I in 1 .. 1000 loop
open l_rc for ‘select object_name from all_objects ‘|| ‘where object_id = ‘ || i;
fetch l_rc into l_dummy;
close l_rc;
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line ( round( (dbms_utility.get_time-l_start)/100, 2 ) ||‘ seconds ...‘ );
end;
https://www.cnblogs.com/hl3292/archive/2010/11/03/1868159.html
-------------在mac上安装oracle客户端-------------
1. 登入oracle的官网下载页面
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/intel-macsoft-096467.html
2. 选择适合的版本下载,我选的第一个 (Instant Client Package - Basic)
Instant Client Package - Basic: All files required to run OCI, OCCI, and JDBC-OCI applications
instantclient-basic-macos.x64-12.2.0.1.0-2.zip (68,160,048 bytes) (cksum - 2145539248)
3. 注册账号
会跳到登录界面,要是没有账号就需要注册一个,然后才能下载。
4. 下载完成之后,解压,将里边的全部文件放到~/lib 或者 /usr/local/lib 文件下
下载完后会有一个instantclient 的压缩包,后边会有版本号,如我下载的是instantclient_12_2,
解压,会有以下文件
将里边的文件,全部复制到~/lib 或者 /usr/local/lib 文件下
5. 设置环境变量
下面是我自己的目录存放位置,将/Users/lanc要改成你自己的目录。
在你的设置环境变量的文件夹中添加:
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/lanc/lib
步骤:
cd ~lib
pwd
cd ~
vi .bash_profile
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/lanc/lib
1
2
3
4
5
使设置的环境变量生效
source .bash_profile
进入oracle 的项目,在终端输入node , 进入node 的环境,然后输入var oracle = require(‘oracle’);
如果没有报错,就说明已经安装成功了
---------------------
作者:lanc336
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41767649/article/details/80627034
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
用 navicat连接oracle
http://wiki.navicat.com/wiki/index.php/Instant_client_required#Mac





