标签:cell 时间 process clu 常用函数 serve my.ini rac 流程
引言:现在的社会处于一个数字化时代,很多事物都可以转化为数字形式储存起来,所以数据无处不在,手机联系人,微信消息,银行卡账号,人口信息,图书信息,消费记录等等.所以我们要用到数据库去管理这些信息.1、人工管理阶段
特点:
数据不能长期保存
数据不能共享
数据不具有独立性
程序本身管理数据2、文件系统阶段
特点:
数据可长期保存
数据由文件系统管理
数据冗余大、共享性差
数据独立性差3、数据库系统阶段
特点:
数据实现结构化
数据实现了共享性
数据独立性强
数据粒度变小1、数据库系统涉及的几个概念
DB:Database(数据库)
DBMS:Database Management System数据库管理系统
DBS:数据库系统
计算机硬件、软件
DB
DBMS
DBA(数据库管理员)2、常见的数据库管理系统
* Oracle 甲骨文
* MySQL 甲骨文
* Sql Server 微软 (主要用在windows环境)
* DB2 IBM公司
* SQLlite 用在移动端开发一般使用MySQL
3、MySQL
为什么选择MYSQL?
(1)开源
(2)免费
(3)跨平台
(4)性能较好
(5)用户多,在很多软件公司中使用4、MySQL数据的安装
(1)获取MYSQL安装程序
http://www.mysql.com/downloads/
MySQL Community Edition
(2)两种安装包
Msi包(安装版)
解压缩版(3)解压缩版安装与卸载(初学者最好使用解压缩版)
解压后 bin/mysql.exe 客户端程序 bin/mysqld.exe 服务器端程序 bin/mysqldump.exe 数据备份程序
初始化(只需要执行一次) bin/mysqld --initialize --console 初始化结束会生成data的文件夹,其中保存系统和用户的数据
注意记录临时密码 w8ef!u*y5nZg
启动数据库服务 bin/mysqld --console 端口用的是3306 可以使用Ctrl+C 停止服务程序,或者直接关闭窗口(4)使用客户端连接(首先开启服务端)
使用客户端连接 bin/mysql -u 用户名 -p
初始化时mysql有一个 root (数据库管理员用户)
bin\mysql -uroot -p
正确登录后会出现 mysql> 提示符,要退出用quit命令
修改密码(只需要执行一次)
alter user ‘root‘@‘localhost‘ identified by ‘root‘;
(5)配置mysql的bin目录至环境变量(只需要执行一次),在path中配置
(6)将mysql安装为系统服务(只需要执行一次) bin\mysqld install 服务名
如果服务名没有提供,默认为MySQL
如果要卸载服务:sc delete 服务名
如果安装服务或删除时出现权限不足,用管理员身份运行cmd(黑窗口)
5、MYSQL的目录结构
Bin:mysql应用程序目录
Data:一般为数据目录
Docs:文档
Include:头文件
Lib:库文件
Mysql-test:测试目录
Share:存放字符集及不同语言信息
Sql-bench:压力测试工具
Mydefault.ini :mysql配置文件6、数据库基本概念
数据库:一个数据库管理系统(DBMS)可以管理多个数据库
数据表:一个数据库中有多个数据表
数据行:一个数据表中有多个数据行
数据列(字段):一行数据有多个列
视图:虚拟表
索引:用于加快对表数据的访问
主键:主键字段不允许为空并且唯一标识表中的一行
外键:用于指定两个表之间的关系
事务:更新数据的一个程序单元7、建库
设置默认的字符编码
一种是在建库语句上带上字符编码
另一种是在启动服务时添加配置文件
(1)建库SQL语句(在mysql提示符下运行)
create database 数据库名 character set utf8mb4;
mysql中的utf8字符不够完整,utf8mb4是完整版本的
删除数据库
drop database 数据库名;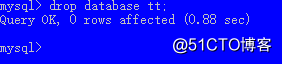
查看建库信息
show create database 数据库名;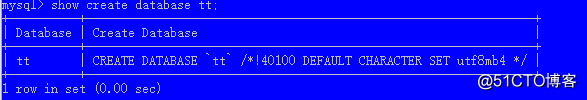
(2)要修改全局的设置,在mysql解压目录添加 my.ini 配置文件,在其中输入(推荐)
[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8mb4
停止旧服务,删除旧服务,安装新服务,启动新服务
net stop mysql
sc delete mysql
mysqld install
net start mysql一个库中有多张表,每张表里有多条数据
表分成行(row 横向)与列(column 纵向)
学号 姓名 性别
1 张三 男
2 李四 女
...

create table 表名(
列1名 类型,
列2名 类型,
...
);create table student(
id int,
name varchar(10),
sex char(1)
);
整数类型: tinyint(1个字节), smallint(2个字节), int(4个字节), bigint(8个字节)
无符号数字 tinyint unsigned (0~255)
浮点类型: float, double
定点小数: decimal(总位数, 小数位数)
decimal(10, 2) 小数部分两位,整数部分最大8位
字符类型
char(长度) char(10) 表示最多存10个字符, 定长,效率高
varchar(长度) varchar(10) 表示最多存储10个字符,变长
"abc" "abc " 存储时,长度不足,用空格补齐
"abc" "abc" 存储时,根据实际长度存储,可以节省空间
日期类型
datetime
timestamp
insert into 表名(列1, 列2, ... 列n) values (值1, 值2, ... 值n);注意:值个数要与列个数一致
insert into student(id,name,sex) values(1, ‘张三‘, ‘男‘);
select 列1, 列2, ... from 表名;select id, name, sex from student;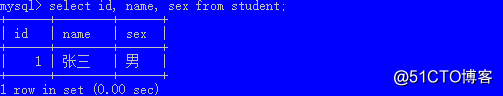
查看所有库
show databases;
show tables;
create table 表名(
列1名 类型 primary key,
列2名 类型,
...
);删表语法:drop table 表名;
create table student(
id int primary key,
name varchar(10),
sex char(1)
);insert into student(id,name,sex) values(null, ‘李四‘, ‘男‘);
自增列,用来解决主键冲突问题
在主键列后加入:auto_increment
1 2 3 4 ....
因为id列由数据库维护,所以有了自增列后就不需要给id列赋值了
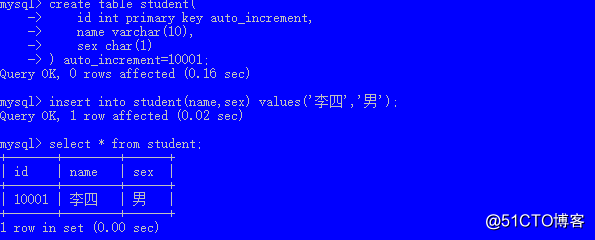
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(10),
sex char(1)
);
一次插入多条记录(mysql独有)
insert into student(name,sex) values(‘李四‘, ‘男‘),(‘王五‘, ‘男‘),(‘赵柳‘, ‘男‘);
查询所有列
select from student;
mysql会把翻译成:id,name,sex
delete from 表 where 条件;删除表(连表和数据一块删除)
drop table 表;只删除id=1004的记录
delete from student where id=6;
create table a ( birthday datetime );
insert into a (birthday) values (‘1988-5-4‘);
insert into a (birthday) values (‘1988-5-4 16:39:00‘);
设置自增列从1001开始的两种方法
1.创建表的时候
create table b (
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
) auto_increment=1001;2.修改表
create table b (
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
alter table b auto_increment=1001;SQL语句
create database 数据库名;
create table 表名(列定义); (重点)
drop database 数据库名;
drop table 表名;
alter table 表 ... (添加列, 修改列, 删除列, 重命名列8.0才有)
alter user 用户
create -- 创建xx定义, drop -- 删除xx定义, alter -- 修改xx定义添加列
语法:alter table 表名 add 列名 数据类型;
例如:给student新增一个age列
alter table student add age tinyint unsigned;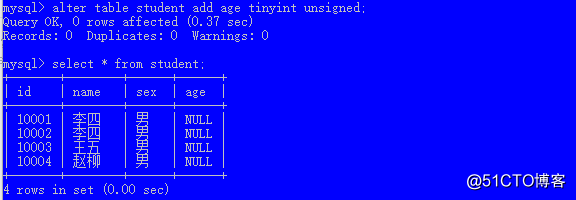
修改列
语法:alter table 表名 modify 列名 新类型;
例如要修改列的长度定义原来varchar(10)
alter table student modify name varchar(20);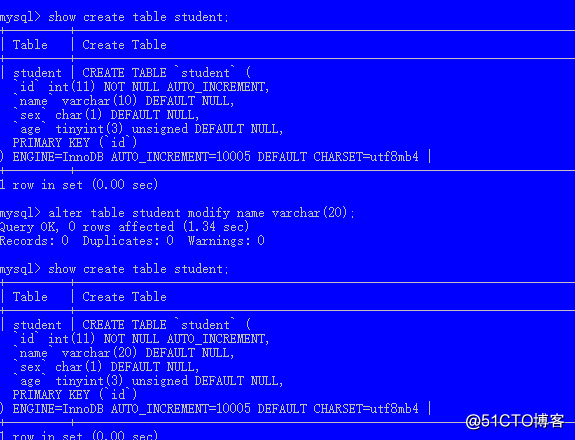
删除列
语法:alter table 表名 drop 列名;
重命名列
语法:alter table 表名 rename column 旧列名 to 新列名;(mysql8.0才有)
语法1:
insert into 表名(列...) values(值...); 插入一行语法2:
insert into 表名(列...) values(值...), (值...), (值...), (值...); 插入多行create table student2(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20),
sex char(1)
);语法3:从表1查询,把查询结果插入表2
insert into 表2 select * from 表1;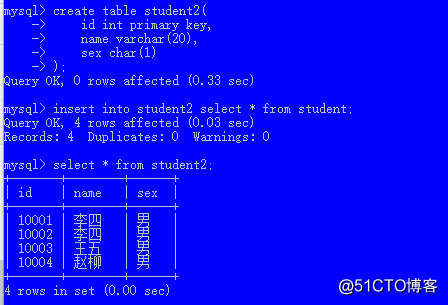
如果两张表结构不一样,可以在select后加具体的列名,以便和新表的列相匹配
例如:
create table student3(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20)
);
insert into student3 select id,name from student;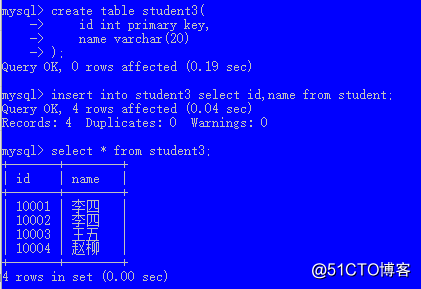
可以把外部文本文件的内容导入到数据库表中
语法:load data infile ‘文件路径\文件名字‘ into table 表名;
create table hero(
id int primary key,
name varchar(10),
loc varchar(10),
sex char(1),
birth int,
death int,
power int
);要让load data命令生效,必须修改设置:
[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8mb4
secure-file-priv=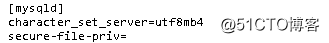
其中secure-file-priv默认是null值,表示不允许加载文件
可以改为具体目录名,表示只能从这个目录加载文件
如果改为"",表示可以从任意目录加载文件
例如:加载之前heroes.txt,把数据存入hero:
load data infile ‘e:\\heroes.txt‘ into table hero;
如果文件中的列分隔符是, 不是默认\t 键,需要用 fields TERMINATED BY来指定分隔符
load data infile ‘e:\\person.txt‘ into table person fields TERMINATED BY ‘,‘;source 文件路径/文件名
语法:
update 表名 set 列名=新值 where 条件;update person set sex=‘男‘; // 把所有记录性别都改为男
update person set sex=‘男‘ where id=1; // 只修改id=1的性别为男
语法:
delete from 表名; // 删除表中所有记录(危险操作)
delete from 表名 where 条件; // 删除满足条件的记录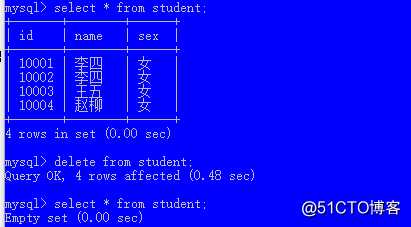
语法:
select 列名... from 表 where 条件 group by 分组条件 having 分组筛选条件 order by 排序条件 limit;= 等值匹配
!= 不等值匹配
> 大于
< 小于
>= 大于等于
<= 小于等于逻辑运算符组合多个条件
逻辑与(两个条件同时成立) and 例如:
select * from hero where sex=‘女‘ and loc=‘建业‘; 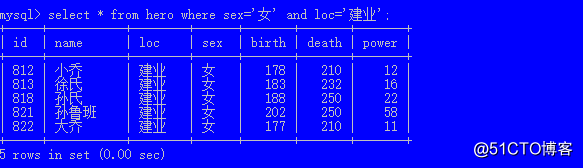
逻辑或(两个条件有一个成立,结果就是真) or
select * from hero where name=‘小乔‘ or id=200;
逻辑非 (条件取反) not 列 between 值1 and 值2 等价于 列 >= 值1 and 列 <= 值2, 注意小值要在前面,包含边界的值
列 in (值1,值2,... 值n) 等价于 列=值1 or 列=值2 ... or 列=值n 注意值列表的长度
like 模糊查询 其中匹配通配符 % 表示匹配0~多个任意字符
通配符 _ 表示匹配1个任意字符
例如:
select * from hero where power between 85 and 90;
select * from hero where power >= 85 and power <=90;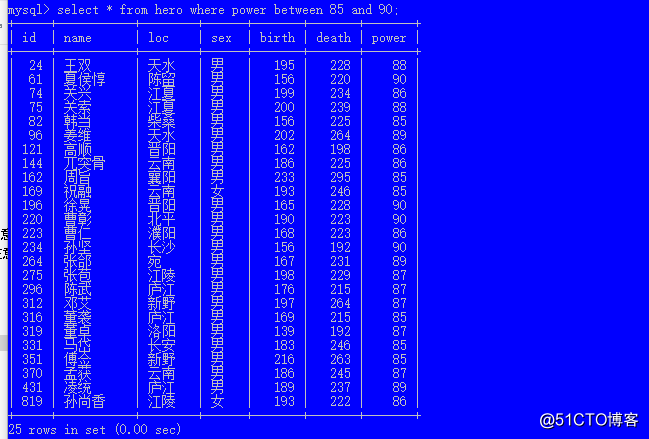
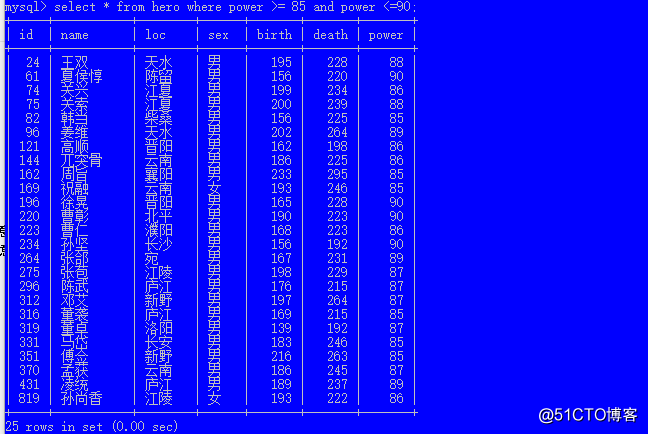
not in
not like
not between ... and排序条件:列名 升降序 如果升降序关键字省略,默认是asc
升序-> 由小到大 asc
降序-> 由大到小 desc
select * from hero order by power desc limit 10;多列排序: 排序条件1, 排序条件2 ...
先按照条件1排序,条件1中取值相同的,再按照条件2排序
limit m; // 最多返回m个结果
limit n,m; // 最多返回m个结果,n代表起始下标,下标从0开始经常用来实现分页应用,假设每页10条
第一页 limit 0,10;
第二页 limit 10,10;
第三页 limit 20,10;select count(*),max(sal),min(sal),sum(sal),avg(sal),deptno from emp group by deptno;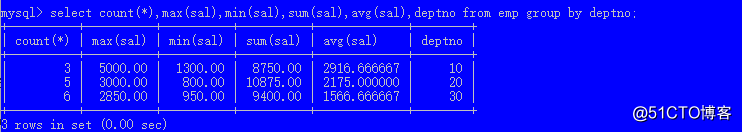
count(*) 表示求每组的个数
max(列) 求最大值
min(列) 求最小值
sum(列) 求和
avg(列) 求平均值分组之后,
where > group by > having > select > order by > limit // sql语句的执行顺序select count(*), deptno from emp where count(*) >=5 group by deptno; // 因为where先执行,这时候还没有分组,不知道个数,错误
select count(*), deptno from emp group by deptno having count(*)>=5;有时候筛选条件既可以写在where 上,也可以写在having (优先采用where)
select count(*), deptno from emp where deptno=10 or deptno=30 group by deptno;
select count(*), deptno from emp group by deptno having deptno=10 or deptno=30;多个列取值都相同的分为一组
group by 列1,列2 ...select count(*),deptno,job from emp group by job,deptno;多列分组时,列的顺序不影响结果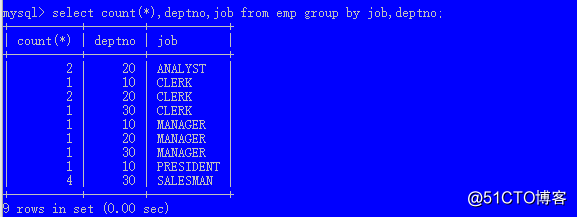
select ... from 表1 inner join 表2 on 连接条件
where group by having order by limit;select empno,ename,sal,emp.deptno,dept.deptno,dname,loc from emp inner join dept on emp.deptno = dept.deptno;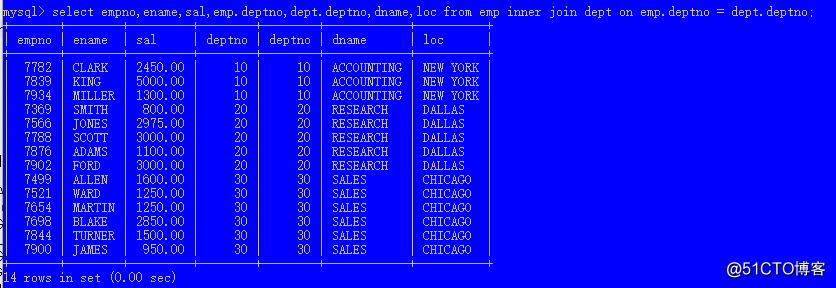
表1 表1别名
select empno,ename,sal,e.deptno,d.deptno,dname,loc
from emp e inner join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;+-------+--------+---------+--------+ +--------+------------+----------+
| empno | ename | sal | deptno | | deptno | dname | loc |
+-------+--------+---------+--------+ +--------+------------+----------+
| 7369 | SMITH | 800.00 | 20 | | 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 7499 | ALLEN | 1600.00 | 30 | | 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 7521 | WARD | 1250.00 | 30 | | 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 7566 | JONES | 2975.00 | 20 | | 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 7654 | MARTIN | 1250.00 | 30 | | 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 7698 | BLAKE | 2850.00 | 30 | | 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 7782 | CLARK | 2450.00 | 10 | | 10 | ACCOUNTING | NEW YORK |
| 7788 | SCOTT | 3000.00 | 20 | | 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 7839 | KING | 5000.00 | 10 | | 10 | ACCOUNTING | NEW YORK |
| 7844 | TURNER | 1500.00 | 30 | | 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 7876 | ADAMS | 1100.00 | 20 | | 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 7900 | JAMES | 950.00 | 30 | | 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 7902 | FORD | 3000.00 | 20 | | 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 7934 | MILLER | 1300.00 | 10 | | 10 | ACCOUNTING | NEW YORK |
+-------+--------+---------+--------+
+--------+------------+----------+
| deptno | dname | loc |
+--------+------------+----------+
| 10 | ACCOUNTING | NEW YORK |
| 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 40 | OPERATIONS | BOSTON |
+--------+------------+----------+
表1 inner join 表2 on 连接条件 (内连接:两张表的记录必须完全满足连接条件,才会出现在最后结果中)
表1 left outer join 表2 on 连接条件 (左外连接)
表1 right outer join 表2 on 连接条件 (右外连接)select empno, ename, e.deptno, d.deptno, d.dname, d.loc
from emp e left outer join dept d on d.deptno=e.deptno;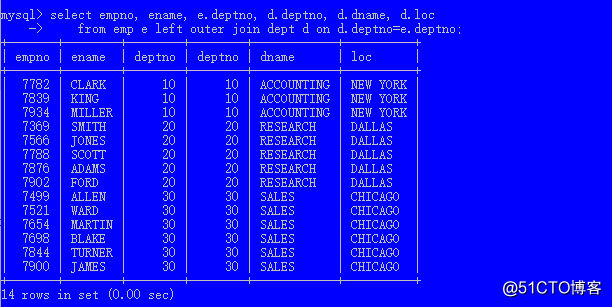
left outer join 位于连接左侧的表,不管是否连接到了记录,都会出现在结果中
符合连接条件的记录,和内连接效果一样
不符合连接条件的记录,对应另一张表的列都是null值
right outer join 位于连接右侧的表,不管是否连接到了记录,都会出现在结果中
outer可以省略
select ... from 表1,表2 where 连接条件;select e.empno,e.ename,e.deptno,d.deptno,d.dname from emp e, dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno;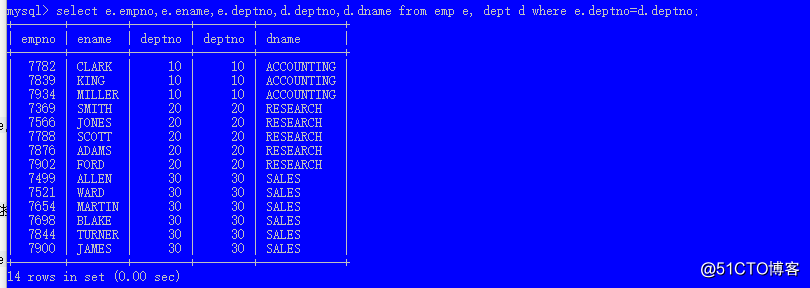
select ... from 表1 inner|left join 表2 using(deptno); // 两张表的连接列名要相同select e.empno,e.ename,e.deptno,d.deptno,d.dname from emp e inner join dept d using(deptno);select count(*) from emp; // 求整张表的行数
select max(sal) from emp; // 求整张表的工资最大值
Bit Functions 位运算函数
Comparison operators 比较运算符
Control flow functions 流程控制
Date and Time Functions 日期函数
year() 截取年份
month()
date()
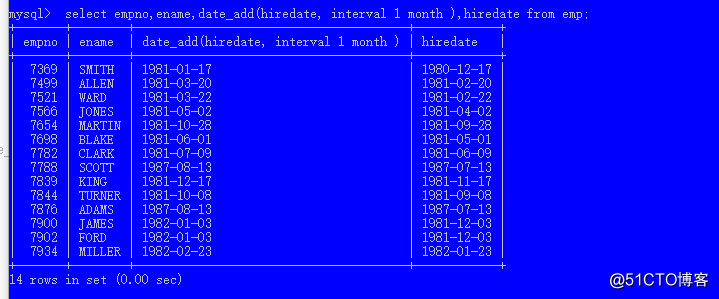
date_add(日期 时间间隔); 其中时间间隔的语法:interval n 单位
select empno,ename,date_add(hiredate, interval 1 month ),hiredate from emp; 加一个月
select empno,ename,date_add(hiredate, interval 3 day ),hiredate from emp; 加3天
SELECT EXTRACT(DAY_MINUTE FROM ‘2009-07-02 13:02:03‘); 提取日期中的从天到分钟的部分
select now() 获取当前时间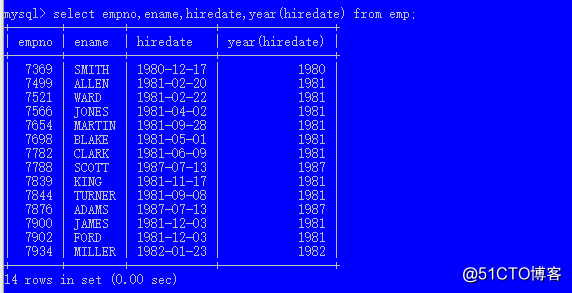
Encryption Functions 加密
Information Functions
Logical operators 逻辑运算符
Miscellaneous Functions 剩余的函数
Numeric Functions 数学函数
rand() 生成一个从[0.0 ~ 1.0) 之间的随机小数, 小于1.0
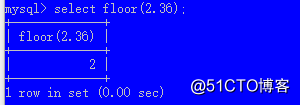
floor() 舍去小数
round() 四舍五入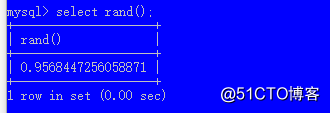
String Functions 字符串函数
left(字符串, n) n代表从左边要截取的字符
lower()
upper()
substr(字符串,下标, 长度) 下标从1开始
求字符串长度的例子:select * from hero where char_length(name)=4;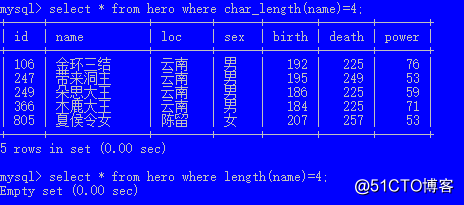
标签:cell 时间 process clu 常用函数 serve my.ini rac 流程
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/13670525/2329006