标签:bin data har 针对 可见 编码 unsigned tin nal
Java的基本输出流类是java.io.OutputStream;
public abstract calss OutputStream
此类常用的写入数据的基本方法如下:
public abstrat void write(int b) throws IOException public void write(byte[] data) throws IOException public void write(byte[] data, int offset, int length) throws IOException public void flush() throws IOException public void close() throws IOException
常见子类(针对流介质):
Java的基本输出流类是java.io.InputStream;
public abstract calss InputStream
此类常用的写入数据的基本方法如下:
public abstract int read() throws IOException public int read(byte[] input) throws IOException public int read(byte[] input, int offset, int length) throws IOException public long skip(long n) throws IOException public int available() throws IOException public void close() throws IOException public void mark(int readAheadLimit) public void reset() throws IOException public boolean markSupported()
常见子类(针对流介质):
过滤器流主要将原始数据做为字节处理,如通过压缩数据或解释为二进制数字,或做缓冲处理等,过滤器以链的形式进行组织使用,如图:
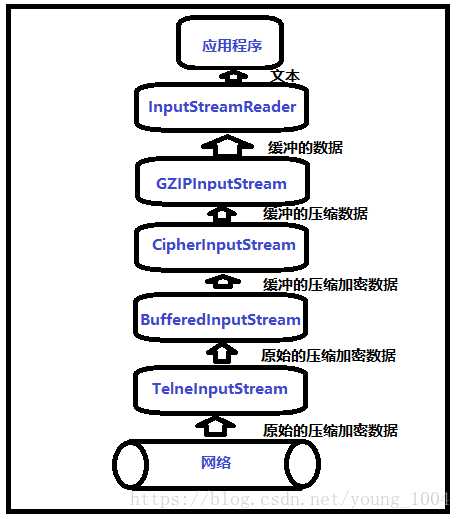
过滤器流串连在一起,示例如下:
// 方式一:一般写法,出现多个指向同一个源的流
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
BufferedInputStream bin = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
// 方式二:建议:大多数情况下,应当只使用链中最后一个过滤器流进行实际的读/写,尽量不要有多个中间流出现
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
in = new FileInputStream(in);
// 方式三:如果必须使用超类中没有声明的过滤器流的其它方法,可以直接在一个流中构建另一个流
DataOutPutStream dout = new DataOutPutStream (
new BufferedOutPutStream(
new FileInputStream("data.txt")
)
)
// 有一个作为缓冲区的保护字节数组buf,当调用某个流的read()方法时,从先缓冲区获取数据,没有时,流才从底层的源中读取数据,它会从源中读取尽可能多的数据存入缓冲区,
// 而不管是否马上需要所有这些数据,不会立即用到的数据可以在以后调用read()时读取
BufferedInputStream
// 将写入的数据存储在缓冲区中buf,直到缓冲区或刷新输出流,然后它将数据一次性全部写入底层输出流 BufferedOutputStream
PrintStream类是大多数程序员都会遇到的第一个过滤器输出流,因为System.out就是一个PrintStream。还可以使用下面两个构造函数将其他输出流串链到打印流:
public PrintStream(OutputStream out) public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush)
如果autoFlush参数为true,那么每次写入1字节数组或换行,或者调用println()方法时,都会刷新输出流。除了平常的write()、flush()和close()方法,PrintStream还有9个重载的print()方法和10个重载的println方法:
public void print(boolean b)
public void print(char c)
public void print(int i)
public void print(long l)
public void print(float f)
public void print(double d)
public void print(char s[])
public void print(String s)
public void print(Object obj)
public void println()
public void println(boolean x)
public void println(char x)
public void println(int x)
public void println(long x)
public void println(float x)
public void println(double x)
public void println(char x[])
public void println(String x)
public void println(Object x)
每个print()方法都将其参数以可见的方式转换为一个字符串,再用默认的编码方式把字符串写入底层输出流。println()方法也完成相同操作,但会在所写的行末尾追加一个与平台有关的行分隔符。
在网络编程中应尽量避免使用PrintStream。原因如下:
数据流可以用二进制格式读/写Java的基本数据类型和字符串。所用的二进制格式主要用于在两个不同java程序之间交换数据(如:网络连接、数据文件、管道或其他中间介质)
DataInputStream DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream提供了常见的11种方法,可以写入特定的Java数据类型
public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOException public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOException public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOException public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException public final void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException public final void writeChars(String s) throws IOException public final void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException
DataInputStream提供了常见的9种方法,可以读取二进制数据
public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException public final byte readByte() throws IOException public final char readChar() throws IOException public final short readShort() throws IOException public final int readInt() throws IOException public final long readLong() throws IOException public final float readFloat() throws IOException public final double readDouble() throws IOException public final String readUTF() throws IOException public final int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException public final int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException public final int read(byte[] input) throws IOException public final int read(byte[] input, int offset , int length) throws IOException public final int readFully(byte[] input) throws IOException public final int readFully(byte[] input, int offset , int length) throws IOException //不推荐使用 public final String readLine() throws IOException
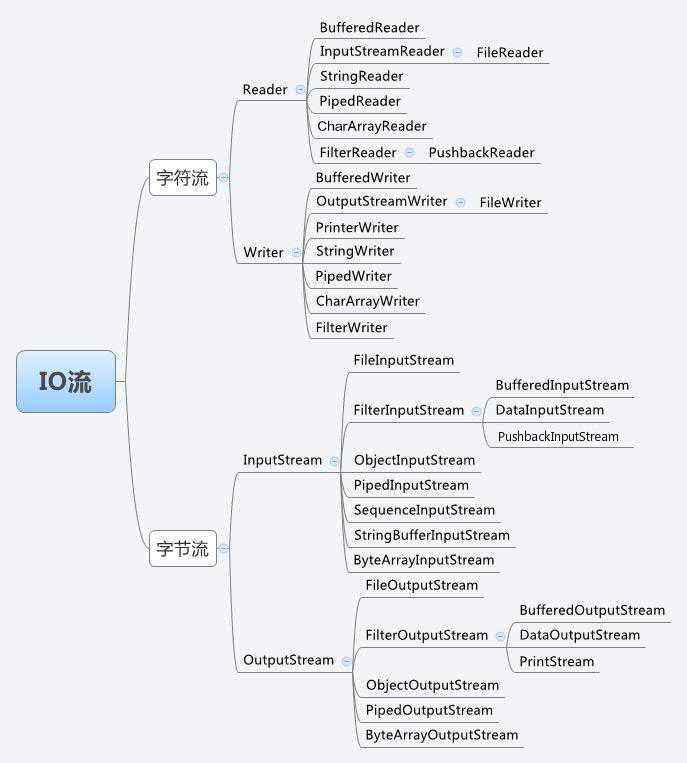
Java中提供了两个抽象超类定义读/写字符的基本API
Reader和Writer最重要的具体子类是:
java.io中的几个原始阅读器和书写器,它们可以读取字符而不需要一个底层的输入流,如下:
FileReader/FileWriter // 可以处理文件 StringReader/StringWriter CharArrayReader/CharArrayWriter
Reader是一个抽象类,从不直接使用,只通过子类来使用。有三个read()方法,另外还有skip()、close()、ready()、mark()、reset()和markSupported()方法:
protected Reader() protected Reader(Object lock) abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException public int read() throws IOException public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException public long skip(long n) throws IOException public boolean ready() throws IOException public boolean markSupported() public void mark(int readAheadLimit) throws IOException public void reset() throws IOException abstract public void close() throws IOException
nputStreamReader是Reader的最重要的具体子类。InputStreamReader从其底层输入流中读取字节。然后根据指定的编码发那个还是将字节转为字符,并返回这些字符。
构造函数如下:
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs)
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec)
Writer类是java.io.OutputStream类的映射。是一个抽象类常用的方法列表如下:
protected Writer() protected Writer(Object lock) public abstract void write(char[] text, int offset, int length) throws IOException public void write(int c) throws IOException public void write(char[] text) throws IOException public void write(String s) throws IOException public void write(String s, int offset, int length) throws IOException public abstract void flush() throws IOException public abstract void close() throws IOException
OutputStreamWriter 是Writer的最重要的具体子类, OutputStream会从Java程序接收字符,它会根据指定的编码方式将这些字符转换为字节,并写入底层输出流指定了要定入的输出流和使用的编码方式:
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String encoding) throws UnsupportedEncodingException
常用的过滤器如下:
标签:bin data har 针对 可见 编码 unsigned tin nal
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Terry-Wu/p/10108758.html