标签:世界 元素 占用 技术 参数 统一 传统 算数运算 bit
电脑的传输,还有储存的实际上都是高低电平,对应01001001
# ASCII:美国标准信息交换代码, 只规定了英文字母数字和一些特殊字符
用8位二进制表示(一个字节)一个字符
最初只用了后7位,将拉丁文编码后占用了最高位
# Unicode:万国码 ,为解决传统的字符编码方案的局限而产生的,为每种语言的每个设定了统一并且唯一的二进制编码
最开始16位 之后32位 中文32位,4个字节
# utf-8:可变长 unicode transformation format 对unicode编码的压缩和优化
ascii 1个字节
欧洲 2个字节
亚洲 3个字节
# GBK:国内使用
英文 1个字节
中文 2个字节
1、各个编码之间的二进制,是不能互相识别的,会产生乱码
2、文件的储存、传输,不能是unicode(只能是utf-8 utf-16 gbk gb2312 ascii等)
# 内存中统一采用unicode,浪费空间来换取可以转换成任意编码(不乱码),硬盘可以采用各种编码,如utf-8,保证存放于硬盘或者基于网络传输的数据量很小,提高传输效率与稳定性。
unicode占用空间:
python2在编译安装时,可以通过参数 --enable-unicode=ucs2 或 --enable-unicode=ucs4,分别用于指定使用2个字节、4个字节表示一个unicode字符;python3无法进行选择,默认使用ucs4。
# 查看当前python中表示unicode字符串时占用的空间:
import sys
print(sys.maxunicode)
# 如果值是 65535, 则表示使用ucs2标准,即:2个字节表示
# 如果值是 1114111, 则表示使用ucs4标准,即:4个字节表示
# python3:
str 在内存中是用unicode编码
bytes类型 编码方式:utf-8 gbk gb2312 ascii等
python3环境下:
str 在内存中是用unicode编码 不能直接储存、传输
要经过bytes类型转换,才能进行储存、传输
bytes类型:
对于英文:
str :表现形式:s = ‘tianhe‘
编码方式:01011100 unicode
bytes :表现形式:s = b‘tianhe‘
编码方式:01010000 utf-8 gbk 。。。
对于中文:
str :表现形式:s = ‘天河‘
编码方式:01110100 unicode
bytes :表现形式:s = b‘\xe5\xa4\xa9\xe6\xb2\xb3‘
编码方式:01010110 utf-8 gbk 。。。

1 s = ‘tianhe‘
2 s1 = b‘tianhe‘
3 print(s,type(s)) # tianhe <class ‘str‘>
4 print(s1,type(s1)) # b‘tianhe‘ <class ‘bytes‘>
5 s = ‘天河‘
6 # s1 = b‘天河‘ #SyntaxError: bytes can only contain ASCII literal characters.
7 print(s,type(s))
8 # print(s1,type(s1))
9
10 s1 = ‘tianhe‘
11 ‘‘‘ encode 编码 如何将str-->bytes‘‘‘
12 s11 = s1.encode(‘utf-8‘)
13 # s12 = s1.encode(‘gbk‘)
14 print(s11) # b‘tianhe‘
15 # print(s12) # SyntaxError: Non-UTF-8 code starting with ‘\xa1‘ in file D:/python/Program/d12_21.py on line 2, but no encoding declared; see http://python.org/dev/peps/pep-0263/ for details
16
17 s2 = ‘天河‘
18 s21 = s2.encode(‘utf-8‘)
19 print(s21) # b‘\xe5\xa4\xa9\xe6\xb2\xb3‘
20 s22 = s2.encode(‘gbk‘)
21 print(s22) # b‘\xcc\xec\xba\xd3‘
# python2默认ascii python3默认utf-8 python2无法识别中文
1 #! /usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf8 -*- 3 4 print(‘你好,世界‘)
# python2 和 python3

1 print ‘abc‘
2 range() xrange() 生成器
3 raw_input()

1 print(‘abc‘)
2 range()
3 input()
1、算数运算
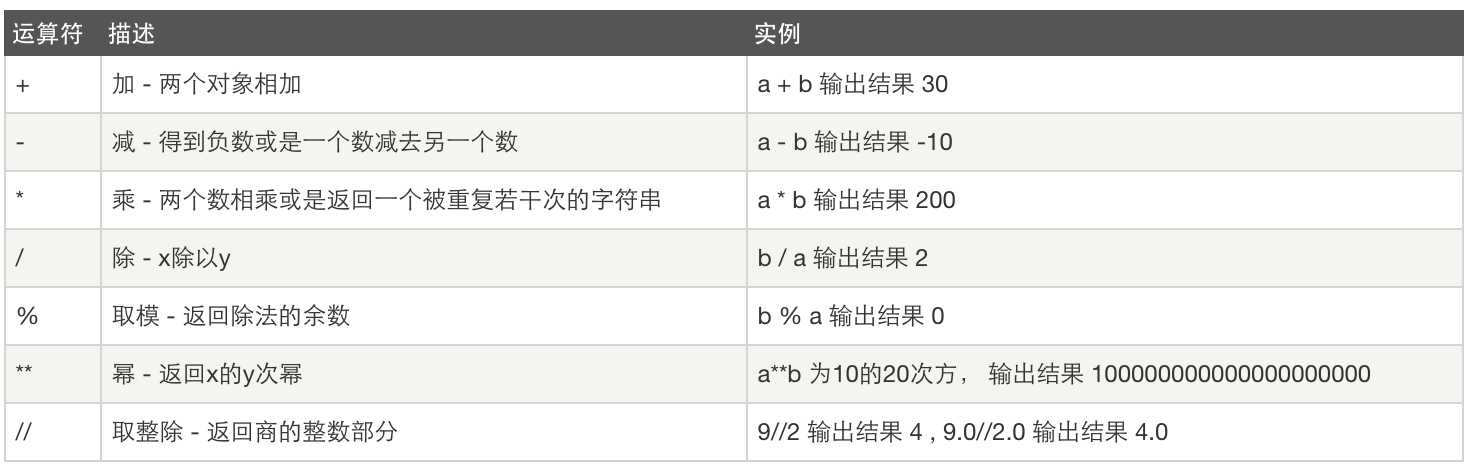
2、 比较运算
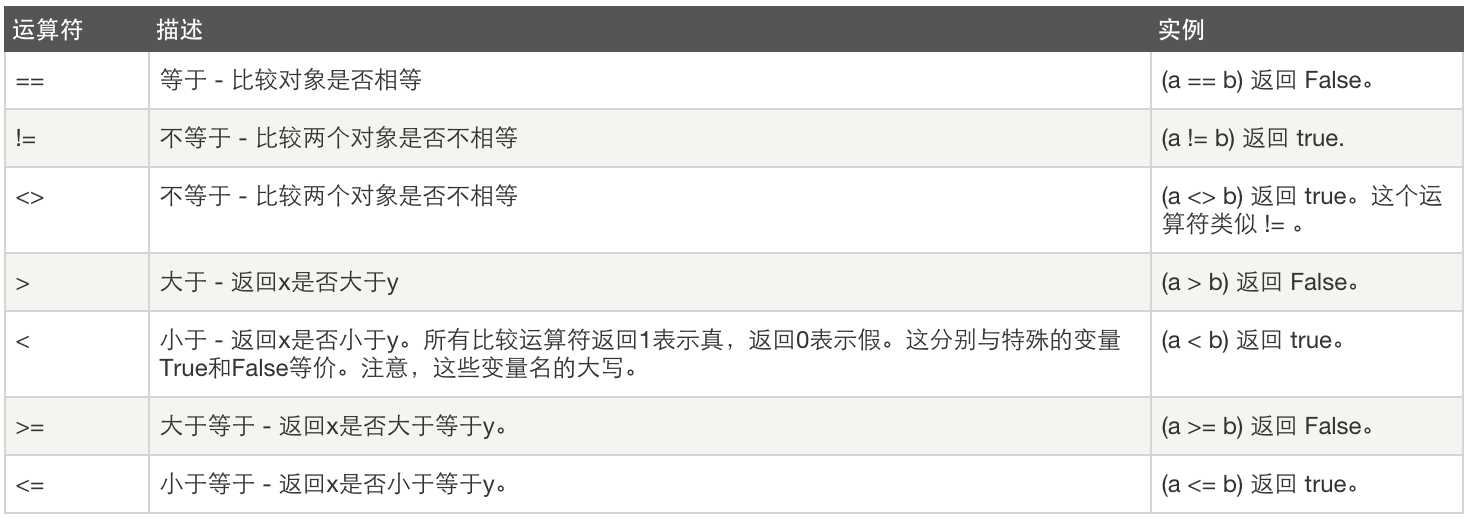
3、赋值运算
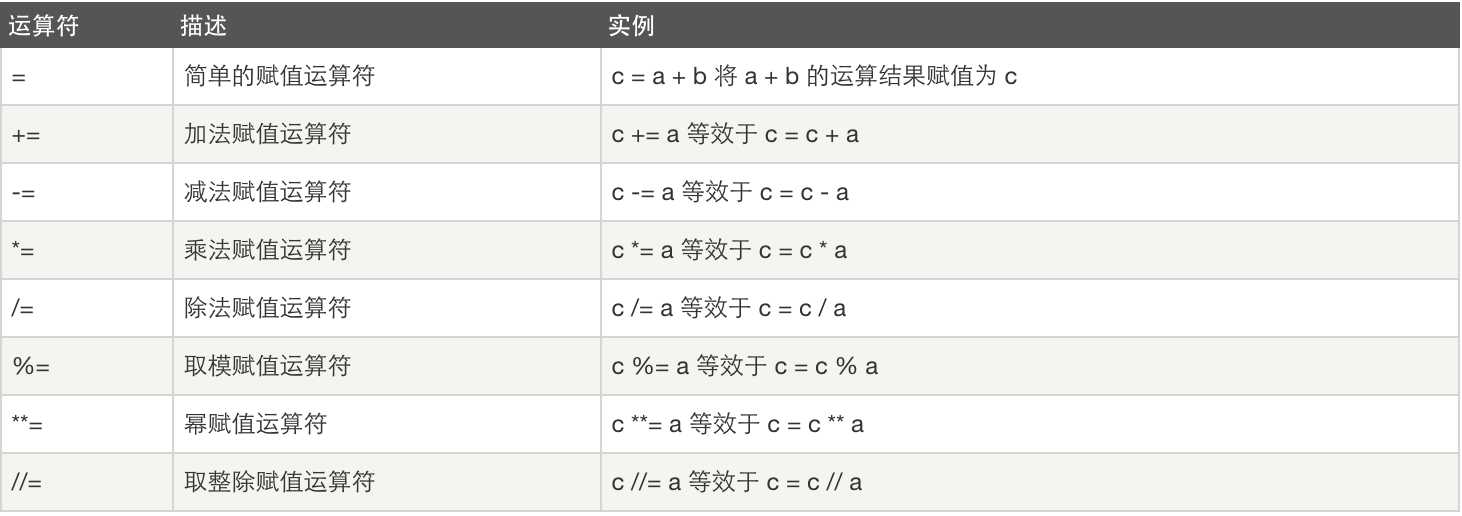
4、逻辑运算:and or not
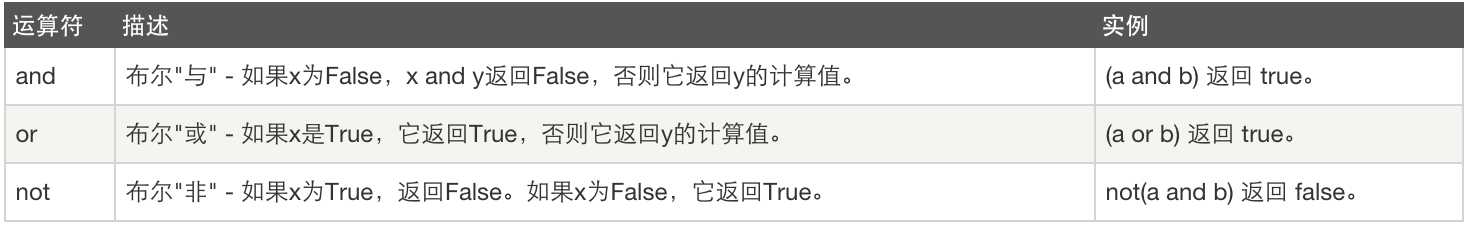
逻辑运算优先级:() > not > and > or
同一优先级从左往右计算

print(1>1 or 3<4 or 4>5 and 2>1 and 9>8 or 7<6)
print(not 2>1 and 3<4 or 4>5 and 2>1 and 9>8 or 7<6)
print(1>2 and 3<4 or 4>5 and 2>1 or 9<8 and 4>6 or 3<2)
print(8 or 3 and 4 or 2 and 0 or 9 and 7)
print(0 or 2 and 3 and 4 or 6 and 0 or 3)
print(0 and 9)
print(1 and 3)
print(not 0)
print(not 2)
print(0 or 8)
print(4 or 0)
print(6 or 2>1)
print(0 or 5<4)
print(3 or 2>1)
print(5<4 or 3)
print(2>1 or 6)
print(3 and 2>1)
print(0 and 3>2)
print(2>1 and 0)
print(1>2 and 4)
print(2>1 and 3)
print(3>1 and 2 or 2<3 and 3 and 4 or 3>2)
print(1>2 or 4<7 and 8 == 8)
# [‘True‘, ‘False‘, ‘False‘, ‘8‘, ‘4‘, ‘0‘, ‘3‘, ‘True‘, ‘False‘, ‘8‘, ‘4‘, ‘6‘, ‘False‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘True‘, ‘True‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘False‘, ‘3‘, ‘2‘, ‘True‘]
5、成员运算
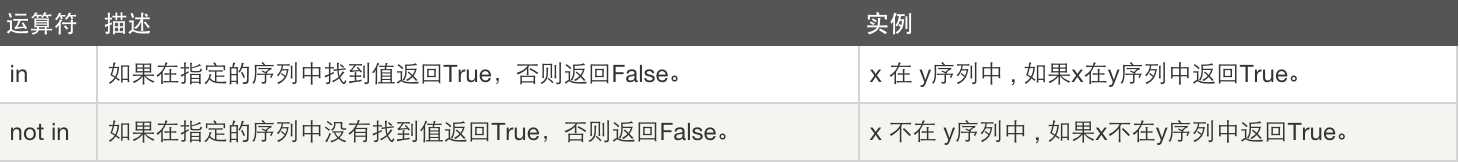
6、身份运算
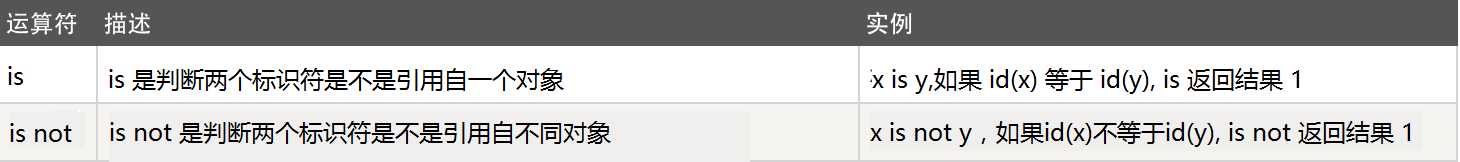
数字的范围:-5 -- 256
字符串: 1、不能有特殊字符
2、s*20 还是同一个地址,s*21以后都是两个地址
list dict tuple set 没有小数据池

C:\Windows\system32>python3
Python 3.5.3 (v3.5.3:1880cb95a742, Jan 16 2017, 16:02:32) [MSC v.1900 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> i1 = 6
>>> i2 = 6
>>> print(id(i1),id(i2))
1837769584 1837769584
>>> i1 = 300
>>> i2 = 300
>>> print(id(i1),id(i2))
82238656464 82247052592
>>> 字符串
>>> s1 = ‘tianhe‘
>>> s2 = ‘tianhe‘
>>> print(id(s1),id(s2))
82247736656 82247736656
>>> s1 = ‘tian*‘
>>> s2 = ‘tian*‘
>>> print(id(s1),id(s2))
82247736768 82247736712
>>> s1 = ‘tian‘*20
>>> s2 = ‘tian‘*20
>>> print(id(s1),id(s2))
82247745720 82247745992
>>> s1 = ‘t‘*20
>>> s2 = ‘t‘*20
>>> print(id(s1),id(s2))
82247730856 82247730856
>>> s1 = ‘t‘*21
>>> s2 = ‘t‘*21
>>> print(id(s1),id(s2))
82247730928 82247731000
>>>
# = 赋值 == 比较值是否相等 is 比较,比较的是内存地址

li1 = [1,2,3]
li2 = li1
print(li1 is li2)
print(id(li1),id(li2))
1、for循环
用户按照顺序循环可迭代对象中的内容
break、continue

li = [11,22,33,44]
for i in li:
print(i)
2、enumerate
为可迭代的对象添加序号

li = [‘tianhe‘,‘lingsha‘,‘勇气‘,‘shanzhu‘]
for i in enumerate(li):
print(i)
for index,name in enumerate(li,1):
print(index,name)
for index,name in enumerate(li,100): #起始位置默认是0,可更改
print(index,name)
3、range指定范围,生成指定数字
range(stop) range(start, stop[, step])

for i in range(5):
print(i)
for i in range(1,8):
print(i)
for i in range(1,8,3): #步长
print(i)
for i in range(8,1,-3): #反向步长
print(i)
for i in range(1,8,-3): #错误 什么都不报
print(i)
for i in range(8,-2): #错误 什么都不报
print(i)
for i in range(8,-2,-3):
print(i)
4、list dic 循环中删元素,会出问题

lis = [11,22,33,44,55]
for i in range(len(lis)):
print(i) #i = 0 i = 1 i = 2 i = 3
del lis[i]
print(lis) #[22, 33, 44, 55] [22, 44, 55] [22, 44] IndexError: list assignment index out of range

dic = {‘k1‘:‘v1‘,‘k2‘:‘v2‘,‘a3‘:‘v3‘}
# 删掉keys中含有k的键值对
# for i in dic:
# if ‘k‘ in i:
# del dic[i] # RuntimeError: dictionary changed size during iteration
# 法1
dic1 = {}
for i in dic:
if ‘k‘ not in i:
dic1.setdefault(i,dic[i])
dic = dic1
print(dic)
# 法2
l = []
for i in dic:
if ‘k‘ in i:
l.append(i)
# print(l)
for i in l:
# print(i)
del dic[i]
print(dic)

lis = [11,22,33,44,55,]
# 删掉索引为偶数的项
if len(lis) % 2 == 1:
for i in range(len(lis) - 1, -1, -2):
# print(i)
del lis[i]
# print(lis)
print(lis)
else:
for i in range(len(lis) - 2, -1, -2):
# print(i)
del lis[i]
# print(lis)
print(lis)
标签:世界 元素 占用 技术 参数 统一 传统 算数运算 bit
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wuyinglianjianjue/p/10052349.html