标签:位置 一点 特定 tde 排序 printf gui nsf else
给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若该树的带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。
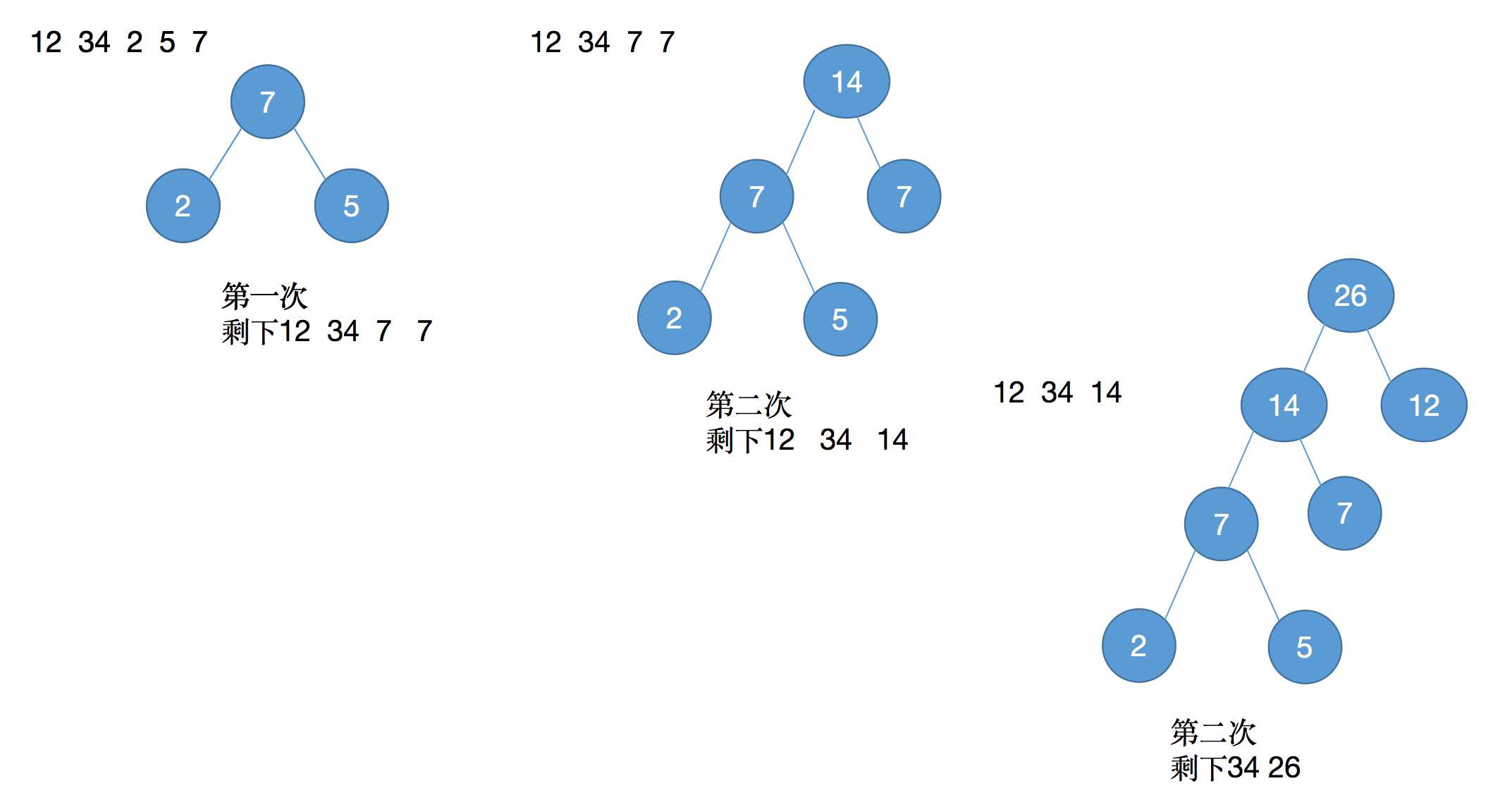
假设一组权值,一个权值是一个结点,12 34 2 5 7 ,在这其中找出两个最小的权值,然后组成一个新的权值,再次找出最小的权值结点。如图:
一个二叉树的结构体,一个数组的结构体。可以看出数组的结构体内部是包含一个二叉树结点的结构体的。
/**
* Created by 刘志通 on 2018/11/22.
* @describe 哈夫曼树的简介
* 编程思想:
* 1:方式简介:
* 利用数组(二叉树结构体类型),来存放初始权值(首次认为权值就是一个树跟,左右孩子分别是NULL),在数组初始化的之后排序,然后拿出index=0,1,更新
* 权值根,
* 2:所用知识:
* 数组,链表存储,二叉树结构体。
*/
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdio.h"
/**
* @describe 二叉树结构体
* 结构形式:Lchild data Rchild
* */
typedef struct twoTree {
int data;
struct twoTree *Lchild, *Rchild;
} twoTree, *twoTreeL;
typedef struct {
twoTreeL data[100];
int length;
} arrayMy;
arrayMy InitList(arrayMy &L) {
// 初始化表,一个空表。
L.length = 0;
return L;
}
/**
* 冒泡排序
* */
void swap(int *weigth,int n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j+1<n-i; j++){
if (weigth[j] > weigth[j+1]){
int temp;
temp = weigth[j];
weigth[j] = weigth[j+1];
weigth[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
对于初始化数组可以看出是把每一个元素写成了二叉树结构的一个结点添加到了一维数组中,初始状态左右孩子都是NULL,data是权值,还有两个方法是插入和删除,之所以有这两个方法是因为,要对数组进行操作的时候需要对数组元素更新,找出前两个最小元素后,要立马删除这两个元素,然后把这两个元素相加得到的结果添加到数组中,添加时要有序添加,否则还要排序。这里面有注释,不懂也可以留言。
int ListDelete(arrayMy &L, int pos) {
if (pos > L.length) {
printf("删除角标不合法");
return -1;
}
printf("\n删除%d\n",L.data[pos]->data);
int i;
//在插入的同时,i要保证在pos以及pos后方,入1,2,3,4,5当在第3个插入时,须把原有的第三个数据以及以后数据后移一位,空出第三个位置。
for (i = pos; i <= L.length; i++) {
L.data[i - 1] = L.data[i];
}
L.length--;
return 0;//返回0表示成功;
}
int ListInsert(arrayMy &L, twoTreeL data) {
printf("插入%d\n",data->data);
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++) {
if (data->data >= L.data[i]->data) {
pos = i;
printf("pos---%d\n",pos);
break;
}
}
int i;
//在插入的同时,i要保证在pos以及pos后方,入1,2,3,4,5当在第3个插入时,须把原有的第三个数据以及以后数据后移一位,空出第三个位置。
for (i = L.length; i > pos; i--) {
L.data[i] = L.data[i - 1];
}
L.data[pos] = data;
L.length++;
return 0;
}
/**
* 数组初始化
* */
void arrayInit(int *weigth, int n, arrayMy &arr) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
twoTreeL treeL = (twoTreeL) malloc(sizeof(twoTree));
treeL->Lchild = NULL;
treeL->Rchild = NULL;
treeL->data = weigth[i];
arr.data[i] = treeL;
arr.length++;
// arr->lenght++;
}
printf("初始化成功");
}
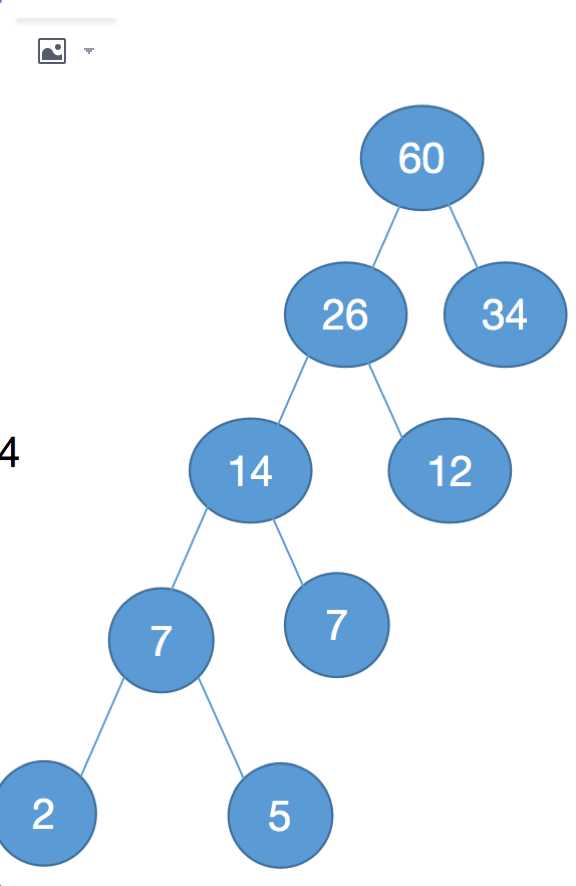
这是最重要的一点,首先拿到前两个权值结点,相加计算得到结果赋值给新建结点,然后删除数组中的前两个结点,插入新建结点,然后递归重复此操作。
/**
* @describe 哈夫曼算法
* */
arrayMy haFuManSF(arrayMy &arr) {
printf("\n个数%d", arr.length);
if (arr.length >= 2) {
twoTreeL tA = arr.data[0];//拿到第一个结点data数,(权值最小)。
twoTreeL tB = arr.data[1];//拿到第二个结点data数,(权值第二小)。
twoTreeL tc = (twoTreeL) malloc(sizeof(twoTree));//创建新的结点
tc->data = tA->data + tB->data;//相加结果加入到新建的data域。
tc->Lchild = tA;//让A称为左子树
tc->Rchild = tB;
ListDelete(arr, 0);//删掉数组的前两个结点元素。
ListDelete(arr, 0);
// printf(" geshu %d ",arr.length);
printf("还剩 ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
printf("%d ", arr.data[i]->data);
}
ListInsert(arr, tc);//插入新建结点元素。
printf("\n插入后 ");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
printf("%d ", arr.data[i]->data);
}
haFuManSF(arr);//然后递归,重复上面操作。
} else {
return arr;
}
// printf(" geshu %d ",arr.length);
return arr;
}
//先中后序遍历二叉树
void diGuiBianLi(twoTreeL tL, int xl) {
if (tL == NULL) {
return;
} else {
if (xl == 1) {
//先序遍历
printf("%d ", tL->data);
diGuiBianLi(tL->Lchild, xl);
diGuiBianLi(tL->Rchild, xl);
} else if (xl == 2) {
//中序遍历
diGuiBianLi(tL->Lchild, xl);
printf("%d ", tL->data);
diGuiBianLi(tL->Rchild, xl);
} else if (xl == 3) {
//后序遍历
diGuiBianLi(tL->Lchild, xl);
diGuiBianLi(tL->Rchild, xl);
printf("%d ", tL->data);
}
}
}
int main(void) {
//新建权值数组
int weigth[5] = {3,1 , 12, 4, 14};
//排序(升序)
swap(weigth,5);
//创建数组(存放权值和个数)
arrayMy arr;
arr = InitList(arr);
arrayInit(weigth, 5, arr);
//检测数组是否排序好
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr.data[i]->data);
}
//哈夫曼编程思想
arr = haFuManSF(arr);
twoTreeL treeL=arr.data[0];
printf("\n");
//先中后遍历
printf("\n先序遍历: ");
diGuiBianLi(treeL,1);
printf("\n中序遍历:");
diGuiBianLi(treeL,2);
printf("\n后序遍历:");
diGuiBianLi(treeL,3);
return 0;
}
完。
标签:位置 一点 特定 tde 排序 printf gui nsf else
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cmusketeer/p/10199706.html