标签:user view des 单例 private nfa 修改 singleton 相同
Inversion of Control:控制反转,就是将对象的创建权反转交给spring
IoC的好处
传统方式的程序编写,底层的实现切换了,需要修改源代码
使用spring之后,实现类都交给IoC容器中的BeanFactory来管理,通过工厂+反射+配置文件来实现程序的解耦合
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User"> class BeanFactory{ public static Object getBean(String id) {//id:bean标签的id Class clazz = Class.forName(className);//className:bean标签的class return clazz.newInstance(); } }
IoC和DI
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User"> <property name="id" value="1"/> <property name="name" value="qf"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean>IoC:控制反转,就是将对象的创建权反转给spring
DI:依赖注入,前提必须有IoC的环境,然后Spring管理这个类的时候把这个类依赖的属性注入进来
描述:Class A中用到了Class B的对象b,一般情况下,需要在A的代码中显式的new一个B的对象。采用依赖注入技术之后,A的代码只需要定义一个私有的B对象,不需要直接new来获得这个对象,而是通过相关的容器控制程序来将B对象在外部new出来并注入到A类里的引用中。而具体获取的方法、对象被获取时的状态由配置文件(如XML)来指定
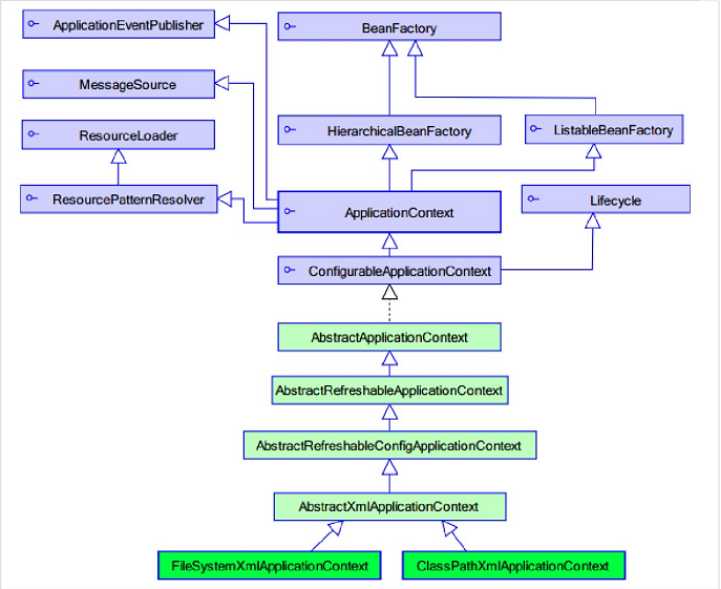
- ApplicationContext是新版本spring的工厂类、BeanFactory是老版本spring的工厂类
- ApplicationContext继承了BeanFactory接口
- BeanFactory在调用getBean方法时才会生成类的实例;ApplicationContext在加载配置文件时就会生成类的实例
- ApplicationContext接口有两个实现类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径下的配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext :加载文件系统下的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="qf"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
</beans>
bean标签

1 package com.qf.demo; 2 3 public class User { 4 5 private Long id; 6 private String name; 7 private Integer age; 8 9 public void setId(Long id) { 10 this.id = id; 11 } 12 public void setName(String name) { 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 public void setAge(Integer age) { 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public String toString() { 21 return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 22 } 23 24 public User(Long id, String name, Integer age) { 25 super(); 26 this.id = id; 27 this.name = name; 28 this.age = age; 29 } 30 public User() { 31 super(); 32 } 33 34 public void init() { 35 System.out.println("初始化----------"); 36 } 37 public void destroy() { 38 System.out.println("销毁----------"); 39 } 40 }
applicationContext.xml中配置spring管理User对象时配置init属性和destroy属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="qf"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类
public class TestDemo {
@Test
public void test() {
// ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// ApplicationContext类里没有close方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user1);
// User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user");
// System.out.println(user2);
context.close();
}
}
console输出结果
初始化---------- User [id=1, name=qf, age=18] 销毁----------
注:如果bean中配置scope="prototype",测试会发现destroy不执行,即工厂无法close
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User" scope="prototype">
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user");
User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user2 == user1);
}
false
true
xml方式
注解方式
public class TestBean {
public TestBean() {
System.out.println("无参构造方式实例化完成");
}
}
<bean id="test" class="com.qf.demo.TestBean"></bean>
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
TestBean test = (TestBean) context.getBean("test");
System.out.println(test);
}
无参构造方式实例化完成 com.qf.demo.TestBean@635c714a
package com.qf.demo;
public class TestBeanFactory {
public static Bean getBean() {
System.out.println("静态工厂实例化完成");
return new Bean();
}
}
class Bean{
}
<bean id="test" class="com.qf.demo.TestBeanFactory" factory-method="getBean"></bean>
package com.qf.demo;
public class BeanInstance {
public Bean getInstance() {
System.out.println("实例工厂方式实例化bean完成");
return new Bean();
}
}
<bean id="instance" class="com.qf.demo.BeanInstance"/> <bean id="test" factory-bean="instance" factory-method="getInstance"/>
标签:user view des 单例 private nfa 修改 singleton 相同
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/qf123/p/10240216.html