标签:public ... 流程图 取数 image div while循环 void 统计
7 循环流程控制语句
7.1 for循环的格式及基本使用
7.1.1 for循环语句格式:
for(初始化语句;判断条件语句;控制条件语句){
循环体语句;
}
7.1.2 循环的执行流程图:
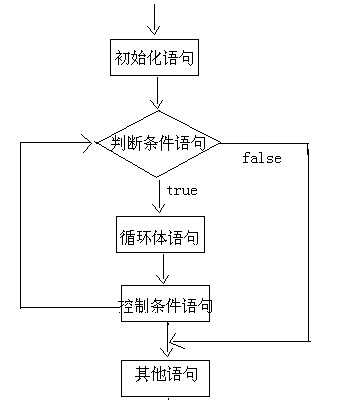
案例:
package com.lyc.test; public class ForDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //需求:在控制台输出10次"我好喜欢你" //原始写法: System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); System.out.println("-----------------------"); //用循环改进 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("我好喜欢你"); } } }
7.2 for循环练习
7.2.1 for循环实现获取指定范围数据
package com.lyc.test; public class ForDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //需求:获取数据1-5和5-1 //原始做法 System.out.println(1); System.out.println(2); System.out.println(3); System.out.println(4); System.out.println(5); System.out.println("------------------"); //用循环改进 for (int i = 1; i <=5; i++) { System.out.println(i); } System.out.println("------------------"); for (int i = 5; 1<=i; i--) { System.out.println(i); } } }
7.2.2 for循环实现1-5之间数据求和
package com.lyc.test; public class ForDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 需求:求1-5之间数字之和 // 定义求和变量,初始化值是0 int sum = 0; // 获取1-5之间的数据,用for循环实现 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { // 把每一次获取到的数据,累加起来 /** * sum = sum + i; * * 第一次: sum = 0 + 1 = 1 * 第二次: sum = 1 + 2 = 3 * 第三次: sum = 3 + 3 = 6 * 第四次: sum = 6 + 4 = 10 * 第五次: sum = 10 + 5 = 15 */ sum += i; } //输出结果 System.out.println("sum="+sum); } }
7.2.3 for循环实现1-100之间偶数和
package com.lyc.test; public class ForDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { //需求:求1-100之间的偶数和 //定义求和变量,初始值为0 int sum = 0; //获取1-100之间的数据,用for循环实现 for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){ if(i%2==0){//把获取到的数据进行判断,看是否是偶数 sum += i; } } //输出结果 System.out.println(sum); } }
7.2.4 for循环实控制台打印水仙花数和统计的个数
package com.lyc.test; public class ForDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 需求:在控制台输出所有的"水仙花数" /** * 什么是水仙花数? * 所谓的水仙花数就是指一个三位数,其个位数字的立方和等于概述本身 * 举例:153就是一个水仙花数 * 153 =1*1*1 + 5*5*5 + 3*3*3 * a:三位数其实就是告诉我们水仙花数的范围 * 100-999 * b:如何获取一个数据的每一个位上的数昵? * 如:153 * 个位:153%10=3; * 十位:153/10%10=5; * 百位:153/10/10%10=1; * 千位:... * 万位:... * c:让每个位上的立方和相加,并和该数数据进行比较,如果相等 * 则说明该数据是水仙花数,在控制台输出 */ //定义变量统计共有多少水仙花数,初始化值是0 int num = 0; //通过循环获取到每一个三位数 for (int i = 100; i <1000; i++) { int ge = i%10;//获取各位 int shi = i/10%10;//获取十位 int bai = i/10/10%10;//获取百位 //让每个位上的立方和相加,并和该数数据进行比较 if ((ge*ge*ge + shi*shi*shi + bai*bai*bai) == i) { System.out.println(i);//输出水仙花数 num++;//如果是水仙花数,则统计起来 } } System.out.println("共有"+num+"个水仙花数");//输出共有多少水仙花数 } }
7.3 while循环的格式及基本使用
7.3.1 while循环语句格式
基本格式
while(判断条件语句){
循环语句体;
}
扩展格式
while(判断条件语句){
循环体语句;
控制条件语句;
}
7.3.2 执行流程图
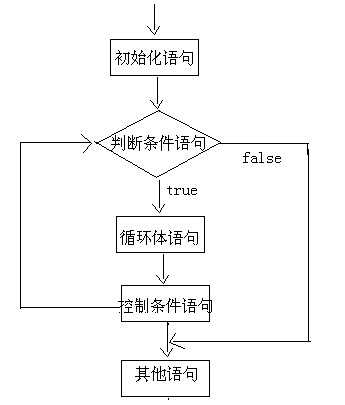
7.3.3 案例
package com.lyc.test; public class WhileDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // for循环输出 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("hello"); } System.out.println("----------------------"); //while循环实现 int x = 1; while(x<=10){ System.out.println("hello"); x++; } } }
7.3.4 while循环实现1-100之间数据求和
package com.lyc.test; public class WhileDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //求1-100之和 //for循环实现 /* int sum = 0;//定义变量 for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++){//获取1-100之间的数据 sum += i;//累加 } System.out.println("1-100之和是:"+sum); */ //while循环实现 int sum = 0; int i = 1; while(i<=100){ sum += i; i++; } System.out.println("1-100之和是:"+sum); } }
7.4 do...while循环的格式及基本使用
7.4.1 do...while循环语句格式
基本格式
do{
循环体语句;
}while(判断条件语句);
扩展格式
do{
循环体语句;
控制条件语句;
}while(判断条件语句);
执行流程图
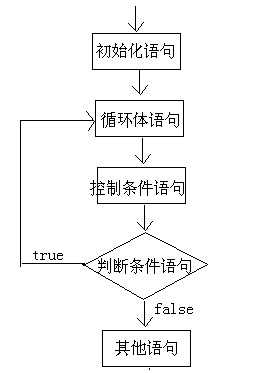
案例
package com.lyc.test; public class DoWhileDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 执行流程 * 1>执行初始化语句; * 2>执行循环体语句; * 3>执行控制条件语句; * 4>执行判断条件语句,看true还是false * 如果是true,继续 * 如果是false,结束 */ int x = 1; do { System.out.println("我好喜欢你┭┮﹏┭┮"); x++; } while (x<=10); } }
三种循环的区别
虽然可以完成同样的功能,但是还是有小区别:
do…while循环至少会执行一次循环体。
for循环和while循环只有在条件成立的时候才会去执行循环体
for循环语句和while循环语句的小区别:
控制条件语句所控制的那个变量,在for循环结束后,就不能再被访问到了,而while循环结束还可以继续使用,如果你想继续使用,就用while,否则推荐使用for。原因是for循环结束,该变量就从内存中消失,能够提高内存的使用效率。
7.5 控制循环语句
7.5.1 控制跳转语句break
Break的使用场景和作用
break的使用场景:
在选择结果switch语句中
在循环语句中
离开使用场景的存在是美哟意义的
break的作用:跳出单层循环
案例
package com.lyc.test; public class BreakDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * break:中断的意思 * 使用场景: * A.switch语句中 * B.循环中 * 作用: * 跳出循环,让循环提前结束 */ for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){ if (i==3) { break; } System.out.println(i); } } }
7.5.2 控制跳转语句continue
continue的作用:
单层循环对比break,然后总结两个的区别
break:退出当前循环
continue:退出本次循环,继续下次循环
案例
package com.lyc.test; public class ContinueDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * continue:继续的意思 * 使用场景:循环中 * 作用:结束本次循环,继续下次的循环 * 区别:break退出循环 * continue结束本次循环,继续下次的循环 */ for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) { if (i==3) {//如果等于3就不会输出,结束这次循环 continue; } System.out.println(i); } } }
标签:public ... 流程图 取数 image div while循环 void 统计
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/chao123/p/10235622.html