标签:direct 失败 inux nbsp 管道 cas pipe ret 格式化输出
一、引言
FIFO常被称为有名管道,不同于管道(pipe)。pipe仅适用于“有血缘关系”的IPC。但FIFO还可以应用于不相关的进程的IPC。实际上,FIFO是Linux基础文件类型中的一种,是在读写内核通道。
函数原型:
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
成功返回 0, 失败返回 -1
命令:
mkfifo + 管道名 例:mkfifo fifo_one
操作步骤:
1) 通过命令行创建fifo;
2) 使用open、close、read、write等I/O函数操作fifo。
二、例程
1) 创建fifi:
#mkfifio fifo_one
2) fifo 写函数
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 9 void sys_err(char *str) 10 { 11 perror(str); 12 exit(-1); 13 } 14 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 15 { 16 int fd, i; 17 char buf[4096]; 18 19 if (argc < 2) { 20 printf("Please enter: ./a.out fifoname\n"); 21 return -1; 22 } 23 fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY);//打开fifo 24 if (fd < 0) 25 sys_err("open"); 26 27 i = 0; 28 while (1) {
printf("write fifo \n ");
29 sprintf(buf, "hello itcast %d\n", i++); //格式化输出到buf 31 write(fd, buf, strlen(buf)); //向fifo写入buf 32 sleep(1); 33 } 34 close(fd); 35 36 return 0; 37 }
3) fifo 读函数
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 9 void sys_err(char *str) 10 { 11 perror(str); 12 exit(1); 13 } 14 15 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 16 { 17 int fd, len; 18 char buf[4096]; 19 20 if (argc < 2) { 21 printf("Please enter: ./a.out fifoname\n"); 22 return -1; 23 } 24 fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);//打开fifo 25 if (fd < 0) 26 sys_err("open"); 27 while (1) { 28 len = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));//从fifo读取数据到buf 29 write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, len); //将buf写入标准输出 30 sleep(3); //多個读端时应增加睡眠秒数,放大效果. 31 } 32 close(fd); 33 return 0; 34 }
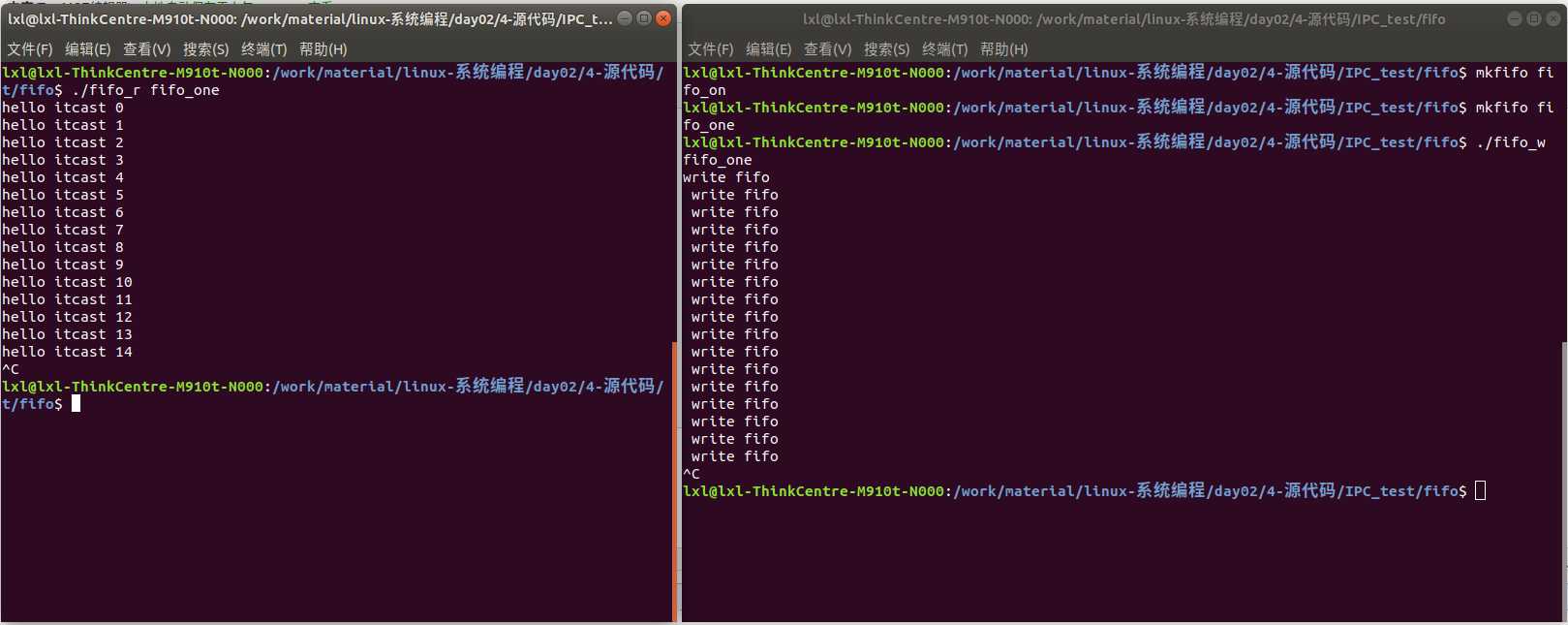
编译执行:
标签:direct 失败 inux nbsp 管道 cas pipe ret 格式化输出
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lxl-lennie/p/10242563.html