标签:反序列化 注意 r.js utf-8 oat odi pickle image coder
序列化是将字典、列表等数据类型转化成一个字符串的过程
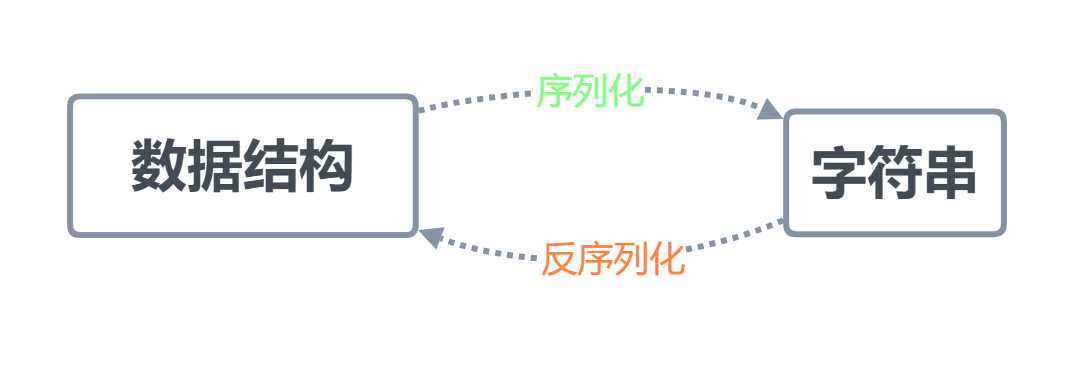
1. 以某种存储形式使自定义对象持久化(存储)
2. 将对象从一个地方传递到另一个我地方(传输)
3. 使程序更具维护性
json是很多语言通用的一种数据标准,json可以转化的数据类型包括:str int bool dict list(tuple) None
json模块有四种方法:dumps, loads, dump, load
dumps和loads
处理列表
import json lst = [1, 2, "a", "哈哈"] s = json.dumps(lst, ensure_ascii=False) # 包含非ascii字符时要加上ensure_ascii=False print(s[0]) # [ 可以像字符串一样取值 print(s[1]) # 1 print(s[1:8]) # 也可以切片 1, 2, " 注意列表元素之间有空格 print(s, type(s)) # [1, 2, "a", "哈哈"] <class ‘str‘> l1 = json.loads(s) print(l1, type(l1)) # [1, 2, ‘a‘, ‘哈哈‘] <class ‘list‘>
dumps也可以处理嵌套的数据类型,注意json会自动把字典的key变成字符串格式,元组转化之后会变成列表
1 import json 2 dic = {"1": {1: "青", 2: "梅", 3: "竹", 4: "马"}, "2": {1: "两", 2: "小", 3: "无", 4: "猜"}} 3 s = json.dumps(dic, ensure_ascii=False) 4 # print(s) 5 dic1 = json.loads(s) 6 print(dic1) # {‘1‘: {‘1‘: ‘青‘, ‘2‘: ‘梅‘, ‘3‘: ‘竹‘, ‘4‘: ‘马‘}, ‘2‘: {‘1‘: ‘两‘, ‘2‘: ‘小‘, ‘3‘: ‘无‘, ‘4‘: ‘猜‘}}
dump和load
dump和load用于将数据写入文件和读出
1 import json 2 dic = {1: "你", 2: "我"} 3 with open("序列化.json", encoding="utf-8", mode="w") as f1: 4 json.dump(dic, f1, ensure_ascii=False) 5 6 with open("序列化.json", encoding="utf-8", mode="r") as f2: 7 ret = json.load(f2) 8 9 print(ret) # {‘1‘: ‘你‘, ‘2‘: ‘我‘}
一次只能写入一个数据,超过一个读取就会出错
1 import json 2 dic1 = {1: "你", 2: "我"} 3 dic2 = {1: "我", 2: "你"} 4 a = None 5 with open("序列化.json", encoding="utf-8", mode="w") as f1: 6 json.dump(dic1, f1, ensure_ascii=False) 7 json.dump(dic2, f1, ensure_ascii=False) 8 9 with open("序列化.json", encoding="utf-8", mode="r") as f2: 10 ret1 = json.load(f2) # 报错json.decoder.JSONDecodeError: Extra data: line 1 column 21 (char 20) 11 ret2 = json.load(f2)
怎么同时写入多个数据呢,循环使用dumps,先用dumps把数据转化成json字符串,再用文件句柄写入
1 import json 2 dic1 = {1: "你", 2: "我"} 3 dic2 = {1: "我", 2: "你"} 4 a = None # 写进文件会变成null 5 b = 100 6 c = (1, 2, 3) 7 d = True 8 with open("序列化.json", encoding="utf-8", mode="w") as f1: 9 f1.write(json.dumps(dic1, ensure_ascii=False)) # {"1": "你", "2": "我"} 10 f1.write("\n") 11 f1.write(json.dumps(dic2, ensure_ascii=False)) # {"1": "我", "2": "你"} 12 f1.write("\n") 13 f1.write(json.dumps(a)) # null 14 f1.write("\n") 15 f1.write(json.dumps(b)) # 100 16 f1.write("\n") 17 f1.write(json.dumps(c)) # [1, 2, 3] # 元组反序列化之后是列表 18 f1.write("\n") 19 f1.write(json.dumps(d)) # true
json模块只能将常用的数据类型进行序列化,pickle模块是python独有的,可以将所有的python的数据类型(包括对象)序列化
1 import pickle 2 dic1 = {1: "你", 2: "我"} 3 p1 = pickle.dumps(dic1) 4 print(p1) # b‘\x80\x03}q\x00(K\x01X\x03\x00\x00\x00\xe4\xbd\xa0q\x01K\x02X\x03\x00\x00\x00\xe6\x88\x91q\x02u.‘
pickle是将数据类型转化成bytes类型存入文件中,用load也可以读出来
with open("p1.pickle", mode="rb") as f2: # 注意这里是rb模式 re = pickle.load(f2) print(re) # {1: ‘你‘, 2: ‘我‘}
与json不同,pickle可以一次写入和读取多个数据
1 import pickle 2 dic1 = {1: "你", 2: "我"} 3 dic2 = {1: "我", 2: "你"} 4 a = None # 写进文件会变成null 5 b = 100 6 c = (1, 2, 3) 7 d = True 8 with open("p1.pickle", mode="wb") as f1: 9 pickle.dump(dic1, f1) 10 pickle.dump(dic2, f1) 11 pickle.dump(a, f1) 12 pickle.dump(b, f1) 13 pickle.dump(c, f1) 14 15 with open("p1.pickle", mode="rb") as f2: 16 ret1 = pickle.load(f2) 17 ret2 = pickle.load(f2) 18 ret3 = pickle.load(f2) 19 ret4 = pickle.load(f2) 20 ret5 = pickle.load(f2) # pickle反序列化出来还是元组 21 print(ret1) # {1: ‘你‘, 2: ‘我‘} 22 print(ret2) # {1: ‘我‘, 2: ‘你‘} 23 print(ret3) # None 24 print(ret4) # 100 25 print(ret5) # (1, 2, 3)
pickle也可以转化python对象
1 import pickle 2 def func(): 3 print(111) 4 5 6 with open("p2.pickle", mode="wb") as f1: # 模式必须是wb 7 pickle.dump(func, f1) 8 9 10 with open("p2.pickle", mode="rb") as f2: 11 re = pickle.load(f2) 12 print(re) # <function func at 0x000001D1FF081E18>
json与pickele比较
1. json是通用的,别的语言也可以识别,pickle只能python识别
2. json只能转化str int bool dict list(tuple) None,pickle可以转化所有Python数据类型
shelve也是python提供给我们的序列化工具,比pickle用起来更简单一些。shelve只提供给我们一个open方法,是用key来访问的,使用起来和字典类似
1 import shelve 2 f = shelve.open("shelve_file") # 写入了三个文件bak dat dir 3 f["key"] = {"int": 10, "float": 3.4} 4 f.close() 5 6 f = shelve.open("shelve_file") 7 print(f["key"]) # {‘int‘: 10, ‘float‘: 3.4} 8 f.close()
存储到shelve的文件一般不让修改,如果要修改可以加一个参数writeback=True
不加参数
1 f1 = shelve.open("shelve_file") 2 f1["key"]["int"] = 20 3 f1.close() 4 5 f2 = shelve.open("shelve_file") 6 print(f2["key"]) # {‘int‘: 10, ‘float‘: 3.4} 并没有修改
加上writeback=True
1 f3 = shelve.open("shelve_file", writeback=True) 2 f3["key"]["int"] = 20 3 f3.close() 4 5 f4 = shelve.open("shelve_file") 6 print(f4["key"]) # {‘int‘: 20, ‘float‘: 3.4} 7 f4.close()
1. 序列化就是把其他数据类型转化成字符串的过程
2. 常用的序列化模块是json,可以不同语言间通用,使用方法有dumps, loads 和dump, load
3. pickle是python独有的,可以转化所有Python数据类型
4. shelve像字典一样可以用key来访问,一般不让修改
标签:反序列化 注意 r.js utf-8 oat odi pickle image coder
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zzliu/p/10246407.html