标签:nbsp statement dia finally 自学 cto 原来 flush 分代
1.团队课程设计博客链接
2.个人负责模块或任务说明
(1)到控制台实现GUI界面中浏览文件并选取文件的功能。
(2)业务逻辑代码中实现读取excel(.xls)
(3)数据库表利用POI导出成excel(固定行数)
(4)实现读取txt文件在GUI界面
(5)GUI界面中实现各个界面展示与各个界面的跳转
3.自己的代码提交记录截图

4.自己负责模块或任务详细说明
(1)实现浏览文件,选择文件功能:
主要需要JFileChooser文件选择器进行操作,将文件的路径封装成File实例进行使用。
界面展示:
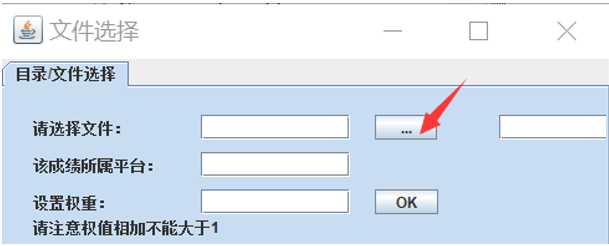
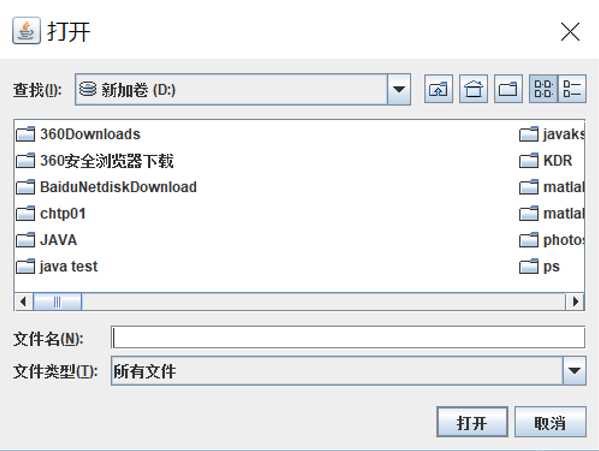
主要代码:
JFileChooser jfc = new JFileChooser();// 文件选择器 YFileChooser() { jfc.setCurrentDirectory(new File("d:\\"));// 文件选择器的初始目录定为d盘 ...} public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {// 事件处理 if (e.getSource().equals(button2)) { jfc.setFileSelectionMode(0);// 设定只能选择到文件 int state = jfc.showOpenDialog(null);// 此句是打开文件选择器界面的触发语句 if (state == 1) { return;// 撤销则返回 } else { File f = jfc.getSelectedFile();// f为选择到的文件 text2.setText(f.getAbsolutePath());//获得默认路径 } } ... }
(2)业务逻辑代码中实现读取excel(.xls)
实现读取excel文件内容,显示在控制台,主要利用POI的功能,利用其中的HSSFWorkbook(excel文档对象)等组件对excel表的内容与标题进行读取
主要代码:
/** * 获取单元格数据内容为字符串类型的数据 * * @param cell Excel单元格 * @return String 单元格数据内容 */ private String getStringCellValue(HSSFCell cell) { String strCell = ""; switch (cell.getCellType()) { case STRING: strCell = cell.getStringCellValue(); break; case NUMERIC: strCell = String.valueOf(cell.getNumericCellValue()); break; case BOOLEAN: strCell = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue()); break; case BLANK: strCell = ""; break; default: strCell = ""; break; } if (strCell.equals("") || strCell == null) { return ""; } if (cell == null) { return ""; } return strCell; } /** * 根据HSSFCell类型设置数据 * @param cell * @return */ private String getCellFormatValue(HSSFCell cell) { String cellvalue = ""; if (cell != null) { // 判断当前Cell的Type switch (cell.getCellType()) { // 如果当前Cell的Type为NUMERIC case NUMERIC: case FORMULA: { // 判断当前的cell是否为Date if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { Date date = cell.getDateCellValue(); SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); cellvalue = sdf.format(date); } // 如果是纯数字 else { // 取得当前Cell的数值 DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0"); cellvalue= df.format(cell.getNumericCellValue()); } break; } // 如果当前Cell的Type为STRIN case STRING: // 取得当前的Cell字符串 cellvalue = cell.getRichStringCellValue().getString(); break; // 默认的Cell值 default: cellvalue = " "; } } else { cellvalue = ""; } return cellvalue; } public static void main(String[] args) { try { // 对读取Excel表格标题测试 InputStream is = new FileInputStream("d:\\mookmiddle-test.xls"); WriteExcelToDB excelReader = new WriteExcelToDB(); String[] title = excelReader.readExcelTitle(is); System.out.println("获得Excel表格的标题:"); for (String s : title) { System.out.print(s + " "); } // 对读取Excel表格内容测试 InputStream is2 = new FileInputStream("d:\\mookmiddle-test.xls"); Map<Integer, String> map = excelReader.readExcelContent(is2); System.out.println(" "); System.out.println("获得Excel表格的内容:"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("未找到指定路径的文件!"); e.printStackTrace(); } }
(3)实现将数据库表导出成excel:
利用POI技术,用HSSFWorkbook创建“Excel文件对象”,利用HSSFWorkbook对象创建Sheet对象,然后用Sheet对象返回行对象,最后用行对象得到Cell对象
4、对Cell对象读写
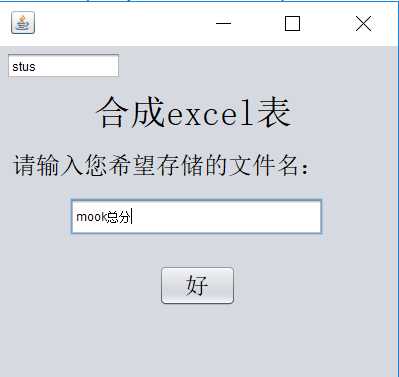
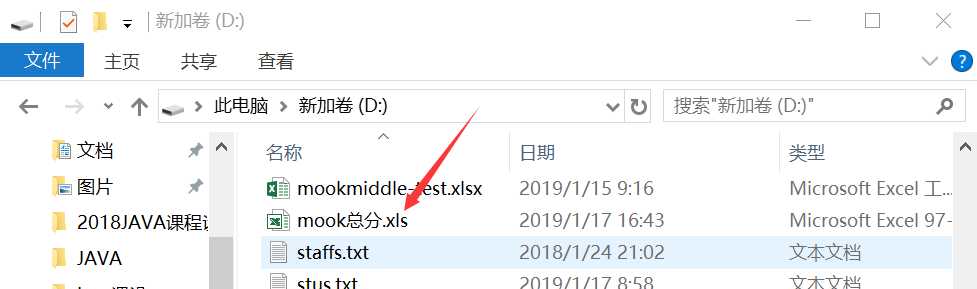
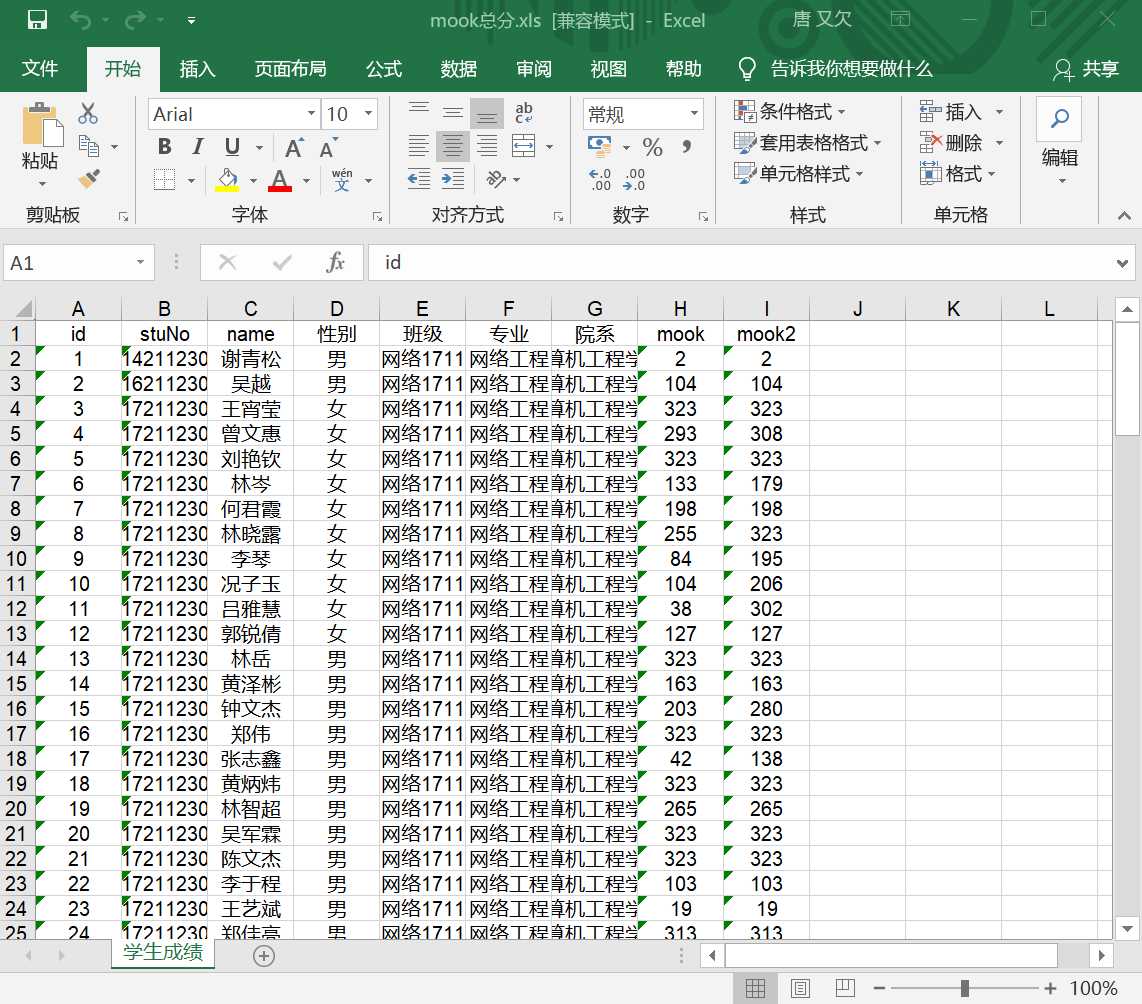
主要代码:
try { //连接数据库查询数据 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql="select * from st"; ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql); //获取结果集 rs = ps.executeQuery(); //用于获取字段的描述信息,比如字段名 ResultSetMetaData metaData = (ResultSetMetaData) rs.getMetaData(); //创建workBook对象 @SuppressWarnings("resource") HSSFWorkbook workBook=new HSSFWorkbook(); //在workBook对象中创建一张表格 HSSFSheet sheet= workBook.createSheet("学生成绩"); //设置每一列的宽度 int colnum=metaData.getColumnCount(); for(int i=0;i<colnum;i++){ sheet.setColumnWidth(i, 2000); } //单元格样式对象 HSSFCellStyle cellStyle = workBook.createCellStyle(); //设置文本居中 cellStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); //创建第0行,作为表格的表头 HSSFRow row=sheet.createRow(0); HSSFCell cell=null; for(int i=0;i<colnum;i++){ cell=row.createCell(i); //动态获取字段名 cell.setCellValue(metaData.getColumnLabel(i+1)); cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle); } int rowIndex=1; while(rs.next()){ //循环将查询出来的数据封装到表格的一行中 row=sheet.createRow(rowIndex); for(int i=0;i<colnum;i++){ cell=row.createCell(i); cell.setCellValue(rs.getString(i+1)); cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle); } rowIndex++; } FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(outPutFile); //输出流将文件写到硬盘 workBook.write(fos); fos.flush(); fos.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { rs.close(); ps.close(); conn.close(); }
(4)实现读取txt文件在GUI界面:
将选择txt文件的路径在文本字段上显示,获取文本字段上的路径,利用IO流将文件里的数据读取并将数据添加到要显示的文本框中。
界面展示:
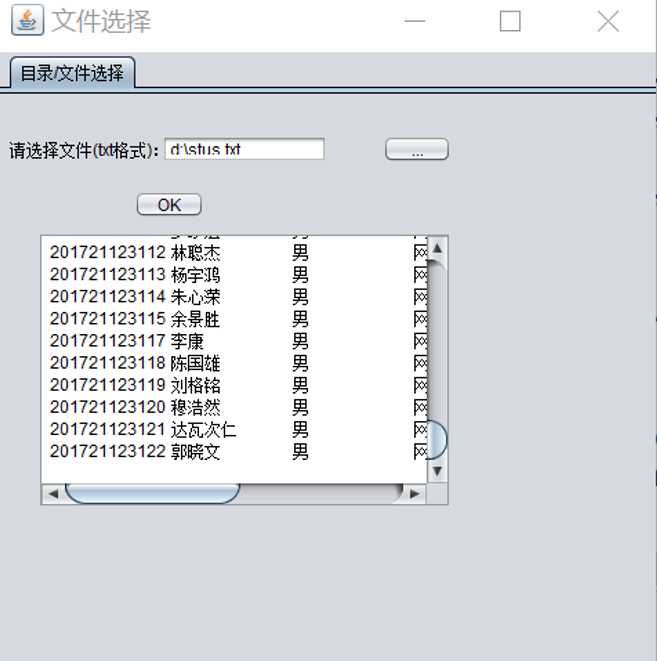
主要代码:
public void readFile() { String filename2 = text2.getText(); FileReader fr = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { fr = new FileReader(filename2); br = new BufferedReader(fr); String str; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { text4.append(str + "\n"); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { br.close(); fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5.课程设计感想
在这次课设的过程中,遇到很多困难,同时也学到很多东西,像数据库,POI,平时上课接触很少的地方需要自学与探讨。通过不断摸索,我解决了不少问题,但同时实现的代码bug重重,多亏队友的修改,让部分代码得以完善,像我写POI读取excel表时,做测试时用自己创的表没有问题,但测试老师提供的表时发现无法运行,最后发现是原来excel表的后缀有影响,应该要实现后缀为.xls与.xlsx都可读取。
通过这次课设,我意识到平时上课不能停留在课本,而忽视动手能力,否则课设的时候会及其痛苦。
标签:nbsp statement dia finally 自学 cto 原来 flush 分代
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tanghuan/p/10284765.html