标签:image body bsp 虚方法 16px private 处理 == method
先附上实例:

1 #pragma once 2 //dma.h -- inheritance and dynamic memory allocation 3 #ifndef DMA_H_ 4 #define DMA_H__ 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<cstring> 7 //Base Class Using DMA 8 class baseDMA 9 { 10 private: 11 char *label; 12 int rating; 13 void give_label(const char* b_label) //label的初始化 代码简化 14 {int len = std::strlen(b_label); label = new char[len + 1]; strcpy_s(label, len+1, b_label);} 15 public: 16 baseDMA(const char* b_label = "null", int b_rating = 0);//一般构造函数 17 baseDMA(const baseDMA& rs); //复制构造函数 18 void View() { std::cout << "baseDMA :" << label << std::endl; }//业务函数View 19 virtual void vView() { std::cout << "virtual baseDMA :" << label << std::endl; }//业务虚函数vView 20 virtual ~baseDMA(); 21 baseDMA& operator=(const baseDMA& rs); //赋值=运算符 22 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const baseDMA& rs); 23 }; 24 25 //derived class without DMA 26 //no destructor needed 27 //uses implicit copy constructor 28 //uses implicit assignment operator 29 class lacksDMA :public baseDMA 30 { 31 private: 32 enum { COLOR_LEN = 40 }; 33 char color[COLOR_LEN]; 34 public: 35 lacksDMA(const char* l_color = "blank", const char* l_label = "null", int l_rating = 0);//一般构造函数 36 lacksDMA(const char* l_color, const baseDMA& rs); //基类构造函数 37 void View(){ std::cout << "lacksDMA :" << color << std::endl; }//业务函数View 38 virtual void vView() { std::cout << "virtual lacksDMA :" << color << std::endl; }//业务虚函数vView 39 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const lacksDMA& rs); 40 }; 41 //derived class with DMA 42 class hasDMA :public baseDMA 43 { 44 private: 45 char* style; 46 void give_style(const char* h_style) //style的初始化 代码简化 47 {int len = std::strlen(h_style); style = new char[len + 1]; strcpy_s(style, len+1, h_style);} 48 public: 49 hasDMA(const char* h_style = "none", const char* h_lable = "null", int h_rating = 0);//一般构造函数 50 hasDMA(const char* s, const baseDMA& rs); //基类构造函数 51 hasDMA(const hasDMA& hs); //复制构造函数 52 void View() { std::cout << "hasDMA :" << this->style << std::endl; }//业务函数View 53 virtual void vView() { std::cout << "virtual hasDMA :" << style << std::endl; }//业务虚函数vView 54 ~hasDMA(); 55 hasDMA&operator=(const hasDMA& rs); //赋值=运算符 56 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &os, const hasDMA& rs); 57 }; 58 #endif // !DMA_H_

1 //dma.cpp -- dma class methods 2 #include "dma.h" 3 4 5 //baseDMA methods 6 baseDMA::baseDMA(const char* b_label, int b_rating) //一般构造函数 7 { 8 give_label(b_label); 9 /* int len = strlen(b_lable) + 1; 10 label = new char[len]; 11 strcpy_s(label,len, b_lable); */ 12 rating = b_rating; 13 } 14 baseDMA::baseDMA(const baseDMA& rs) //复制构造函数 15 { 16 give_label(rs.label); 17 /* int len = strlen(b_lable) + 1; 18 label = new char[len]; 19 strcpy_s(label,len, b_lable); */ 20 rating = rs.rating; 21 } 22 baseDMA::~baseDMA() { delete[] label; } 23 baseDMA& baseDMA::operator=(const baseDMA& rs) //赋值运算符 24 { 25 if (this == &rs) 26 return *this; 27 delete[]label; 28 give_label(rs.label); 29 /* int len = strlen(rs.label) + 1; 30 label = new char[len]; 31 strcpy_s(label, len, rs.label); */ 32 rating = rs.rating; 33 return *this; 34 } 35 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const baseDMA& rs) 36 { 37 os << "Label:" << rs.label << std::endl; 38 os << "Rating: " << rs.rating << std::endl; 39 return os; 40 } 41 42 //lacksDMA methods //一般构造函数 43 lacksDMA::lacksDMA(const char* l_color, const char* l_label, int l_rating) :baseDMA(l_label, l_rating) 44 { 45 strncpy_s(color, l_color, 39); 46 color[39] = ‘\0‘; 47 } 48 lacksDMA::lacksDMA(const char* c, const baseDMA& rs) : baseDMA(rs) //基类构造函数 49 { 50 strncpy_s(color, c, COLOR_LEN - 1); 51 color[COLOR_LEN - 1] = ‘\0‘; 52 } 53 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os,const lacksDMA& ls) 54 { 55 os << (const baseDMA&)ls; 56 os << "Color: " << ls.color << std::endl; 57 return os; 58 } 59 //void lacksDMA::View() { const baseDMA& bs = *this; std::cout << "lacksDMA :" << bs.label; } 60 //hasDMA methods 61 hasDMA::hasDMA(const char* h_style, const char* h_label, int h_rating) :baseDMA(h_label, h_rating) 62 { //一般构造函数 63 give_style(h_style); 64 /* int len = strlen(h_style) + 1; 65 style = new char[len]; 66 strcpy_s(style, len, h_style ); */ 67 } 68 hasDMA::hasDMA(const char* h_style, const baseDMA& rs) : baseDMA(rs) //基类构造函数 69 { 70 give_style(h_style); 71 /* int len = strlen(h_style) + 1; 72 style = new char[len]; 73 strcpy_s(style, len, h_style ); */ 74 } 75 hasDMA::hasDMA(const hasDMA& hs):baseDMA(hs) //复制构造函数 76 { 77 give_style(hs.style); 78 /* int len = strlen(h_style) + 1; 79 style = new char[len]; 80 strcpy_s(style, len, h_style ); */ 81 } 82 hasDMA::~hasDMA() { delete[] style; } 83 hasDMA&hasDMA::operator=(const hasDMA& hs) //赋值运算符 84 { 85 if (this == &hs) 86 return *this; 87 baseDMA::operator=(hs); 88 delete[]style; 89 give_style(hs.style); 90 /* int len = strlen(h_style) + 1; 91 style = new char[len]; 92 strcpy_s(style, len, h_style ); */ 93 return *this; 94 } 95 std::ostream&operator<<(std::ostream &os, const hasDMA&hs) 96 { 97 os << (const baseDMA&)hs; 98 os << "Style: " << hs.style << std::endl; 99 return os; 100 }
 dma-mamin.cpp
dma-mamin.cpp
1 #pragma once 2 //studentc.h -- defining aStudent class using containment 3 #ifndef STUDENTC_H_ 4 #define STUDENTC_H_ 5 6 #include<iostream> 7 #include<string> 8 #include<valarray> 9 class Student 10 { 11 private: 12 typedef std::valarray<double>ArrayDb; 13 std::string name; 14 ArrayDb scores; 15 //prevate method for scores output 16 std::ostream& arr_out(std::ostream& os)const; 17 public: 18 Student():name("Null Student"),scores(){} 19 explicit Student(const std::string &s):name(s),scores(){} 20 explicit Student(int n):name("Nully"),scores(n){} 21 Student(const std::string&s,int n):name(s),scores(n){} 22 Student(const std::string&s,const ArrayDb& a):name(s),scores(a){} 23 Student(const char*str, const double*pd, int n) :name(str), scores(pd, n){} 24 ~Student(){} 25 26 double Average()const; //get average scores 27 const std::string& Name()const; //get name 28 double&operator[](int i); //get scores[i] 29 double operator[](int i)const; 30 //friend input1 a word,2 a line; output 31 friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream &is, Student &stu); //cin>>name 32 friend std::istream& getline(std::istream&is, Student& stu); //cout<<name 33 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&os,const Student &stu); //cout<<name and arr_out()scores 34 }; 35 #endif // ! STUDENTC_H_ 36 /* valarray类简介 37 函数构造例子 38 valarray<double> v1;//an array of double,size 0 39 valarray<int> v2(8); //an array of 8 int elements 40 valarray<int> v2(8); //an array of 8 int elements, each set 10 41 double gps[5]={1,2,3,4,5}; 42 valarray<double> v2(gps,4); //an array of 4 elements,initalized to the first 4 elements of gps 43 valarray<int> v={6,7,8,9,10,11}; 44 方法: 45 operator[]() size() sum() max() min() 46 */

1 //studentc.cpp -- Student class using containment 2 #include "studentc.h" 3 using std::ostream; 4 using std::istream; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::string; 7 //public methods 8 double Student::Average()const 9 { 10 if (scores.size() > 0) 11 return scores.sum() / scores.size(); 12 else 13 return 0; 14 } 15 const string& Student::Name()const { return name; } 16 //use valarray<double>::operator[]() 17 double& Student::operator[](int i) { return scores[i]; } 18 double Student::operator[](int i)const { return scores[i]; } 19 //private method 20 ostream& Student::arr_out(ostream& os)const 21 { 22 int i; int lim = scores.size(); 23 if (lim > 0) 24 { 25 for ( i= 0; i < lim; i++) 26 { 27 os << scores[i] << " "; 28 if (i % 5 == 4) os << endl; 29 } 30 if (i % 5 != 0) os << endl; 31 } 32 else 33 os << " empty array "; 34 return os; 35 } 36 //friends 37 //use string version of operator>>() 38 istream& operator>>(istream& is, Student& stu) 39 { 40 is >> stu.name; 41 return is; 42 } 43 istream&getline(istream& is, Student &stu) 44 { 45 getline(is, stu.name); 46 return is; 47 } 48 ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const Student& stu) 49 { 50 os << "Scores for "<<stu.name<<":\n"; 51 stu.arr_out(os); 52 return os; 53 }

1 //use_stuc.cpp -- using acomposite class 2 //copile with studentc.cpp 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include "studentc.h" 5 using std::cin; 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 //void set(Student&sa, int n); 9 const int NStudent = 3; 10 const int NScoure = 5; 11 int main() 12 { 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 /* 17 Student ada[NStudent] = { Student(NScoure),Student(NScoure),Student(NScoure) }; 18 int i; 19 for (i = 0; i < NStudent; ++i) 20 set(ada[i], NScoure); 21 22 cout << "\nStudent List:\n"; 23 for (i = 0; i < NStudent; ++i) 24 cout << ada[i].Name() << endl; 25 26 cout << "\nResults:"; 27 for (i = 0; i < NStudent; ++i) 28 { 29 cout << endl << ada[i]; 30 cout << "average: " << ada[i].Average() << endl; 31 } 32 cout << "Done.\n"; 33 cin.get(); 34 35 void set(Student& sa, int n) 36 { 37 cout << "Please enter the student‘s name: "; 38 getline(cin, sa); 39 cout << "Please enter " << n << " quiz scores:\n"; 40 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 41 cin >> sa[i]; 42 while (cin.get() != ‘\n‘) 43 continue; 44 } */
类的继承格式: class lacksDMA :public baseDMA{… …}; baseDMA是基类,lacksDMA是派生类,public表示公有继承;如果有多个继承类需要用逗号隔开,
:public baseDMA,public std::string{};默认私有继承。
一、基类与派生类
数据关系:使用公有派生,基类的公有成员将成为派生类的公有成员,基类的私有部分将成为派生类的一部分,但只能通过基类的公有和保护方法访问。
隐式向上转换 意味着无需进行显示类型转换,就可以将基类指针或引用指向派生类对象。
| 特征 | 公有继承 | 保护继承 | 私有继承 |
| 公有成员变成 | 派生类公有成员 | 派生类的保护成员 | 派生类的私有成员 |
| 保护成员变成 | 派生类的保护成员 | 派生类的保护成员 | 派生类的私有成员 |
| 私有成员变成 | 只能通过基类接口访问 | 只能通过基类接口访问 | 只能通过基类接口访问 |
| 能否隐式向上转换 | 是 | 是(但只能在派生类中) | 否 |
类型转换:只有派生类能转换为基类,但即使转换为基类也不能调用基类的私有成员,因为私有成员的作用域不在派生类中,基类公有成员则能。
类型关系:①is-a,即派生类is-a-kind-of基类,派生类只是基类数据与接口成员的扩充 如苹果(名称,颜色)-水果(热量,重量);
②ABC,如从矩形Ellipse和Circle类中,抽象出它们的共性,将这些特性放到一个ABC中,然后从ABC中派生出Circle和Ellipse类。(见dma代码)
③has-a,方式1私有继承,:private std::string,private std::valarray<int>{};方式2包含,{private:std::string str1;……};(见studentc代码)
has-a利用他人开发好的string 为动态内存分配省去了大量支持代码,方式1不能是公有继承,因为那样会使Student继承string的+接口,
而两个Student类型相加是无意义的。
建议使用③的包含方式,方式2比1强在string可以声明多个数据名称,而且可以直接对string数据操作。
二、重要函数
基类构造函数: 1. hasDMA::hasDMA(const char* h_style, const baseDMA& rs) : baseDMA(rs)
2. explicit Student(const std::string &s):name(s),scores(){}
eg1 :hasDMA是baseDMA的派生类,参数rs将转换为baseDMA变量去初始化 hasDMA对象的基类数据部分;参数s初始化数据name。
参数 初始化列表格式: ①基类名(能转换为基类的参数变量) ②类数据名称(参数变量) 如name(s)。多个参数参数用逗号隔开。
无参 其中score()调用valarray<double>()会默认构造函数,也可以有baseDMA();
注意,关键字explicit可防止 stu="hello world";这样的隐式转换。
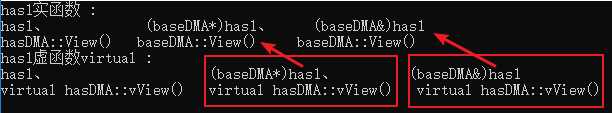
基类与派生类可以定义相同名称的函数。类对象(或该类引用、指针形式)将调用对应类的方法;(baseDMA)has1,(baseDMA&)has1,(baseDMA*)has1将调用基类方法。
虚函数格式:函数声明前加上关键字virtual。(虚函数可以不必实现)
对象(或该类引用、指针形式)将调用对应类的方法。(baseDMA)has1调用基类虚方法,(baseDMA&)has1,(baseDMA*)has1将调用派生类虚方法。eg:dmp-main.cpp

1 hasDMA has1("blue", "has_rank", 5); 2 baseDMA* has2 = &has1; baseDMA& has3 = has1; 3 cout << "has1实函数 :\nhas1、 (baseDMA*)has1、 (baseDMA&)has1\n"; 4 has1.View(); has2->View(); has3.View(); 5 cout << "\nhas1虚函数virtual :\nhas1、 (baseDMA*)has1、 (baseDMA&)has1\n"; 6 has1.vView(); has2->vView(); has3.vView(); 7 cout << "\n\n";
测试结果:
三、继承和动态内存分配
1.派生类不使用new 如dmp中lackDMA类不需要定义析构函数、复制构造函数和赋值运算符。基类构造函数还是要的。
2.派生类使用new 如dmp中hasDMA类需要使用这三个函数。
派生类的基类数据部分:一般构造函数和基类构造函数,复制构造函数和赋值运算符也需要重写。
所以基类(如果也使用了new)有3部分代码重复,派生类有4部分代码重复。
①class baseDMA{ private: char* label; int rating; void give_label(const char* b_label,int b_rating) //label的初始化 代码简化 { int len = std::strlen(b_label); label = new char[len + 1]; strcpy_s(label, len + 1, b_label); rating = b_rating; } 1、baseDMA::baseDMA(const char* b_label, int b_rating) //一般构造函数 { give_label(b_label,b_rating);} 2、baseDMA::baseDMA(const baseDMA& rs) //复制构造函数 { give_label(rs.label,rs.rating); } 3、baseDMA& baseDMA::operator=(const baseDMA& rs) //赋值运算符 { if (this == &rs) return *this; delete[]label; give_label(rs.label,rs.rating); return *this; } ②class hasDMA :public baseDMA{ private: char* style; void give_style(const char* h_style) //style的初始化 代码简化 {int len = std::strlen(h_style); style = new char[len + 1]; strcpy_s(style, len+1, h_style);} 1、hasDMA::hasDMA(const char* h_style, const char* h_label, int h_rating) :baseDMA(h_label, h_rating) //一般构造函数 参数列表-基类部分 { give_style(h_style); } 2、hasDMA::hasDMA(const char* h_style, const baseDMA& rs) : baseDMA(rs) //基类构造函数 参数列表-基类部分 { give_style(h_style);} 3、hasDMA::hasDMA(const hasDMA& hs):baseDMA(hs) //复制构造函数 参数列表-基类部分 { give_style(hs.style);} 4、hasDMA::~hasDMA() { delete[] style; } hasDMA& hasDMA::operator=(const hasDMA& hs) //赋值运算符 调用处理-基类部分eg,baseDMA::operator=(hs) { if (this == &hs) return *this; baseDMA::operator=(hs); //调用处理基类部分 delete[]style; give_style(hs.style); return *this; }
基类友元函数不是成员函数,派生类不能直接调用,但在可以强制转换为基类调用eg: os << (const baseDMA&)hs;
os<<hs操作须保证hs为const类型, 而(const hasDMA)类型只能调用const函数如 void View()const{};
标签:image body bsp 虚方法 16px private 处理 == method
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuchuan/p/10285487.html