标签:图片 self isl __name__ try yum exception 模块 tar
这个脚本用于扫描网络中的存活主机,通常在CMDB中自动获取主机的时候用到。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
执行这个脚本的主机要安装下面两个模块
pip3 install python-nmap 这个Python模块依赖操作系统的nmap
确保操作系统安装了nmap yum -y install nmap # for centos
主要功能:扫描网段获取存活主机以及主机是否为Linux。不是Linux的被标记为Unknown,这些主机会包括交换机、路由器、Windows等。
"""
import sys
from functools import partial
import nmap
import telnetlib
import asyncio
def timer(tagName):
import time
def wapper(func):
def aa(self, *args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
data = func(self, *args, **kwargs)
end = time.time()
consume = end - start
if consume > 60:
min, sec = divmod(consume, 60)
print("%s 执行耗时:%s 分 %s 秒。" % (tagName, str(min), str(sec)))
else:
print("%s 执行耗时:%s 秒。" % (tagName, str(consume)))
return data
return aa
return wapper
class ScanHost(object):
def __init__(self):
self._hostsinfor = []
@timer(tagName="扫描")
def scan(self, hosts=‘127.0.0.1‘, ports=None):
"""
扫描主机
:param hosts: 可以是IP也可以是网段,例如 192.168.100.10、192.168.100.0/24
:param ports: 可以写端口也可以写端口范围,例如22、22-33,默认是None也就是所有端口
:return: [{‘IP‘: ‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘Status‘: ‘up‘, ‘OSType‘: ‘Linux‘}, {}, {}]
"""
hostlist = self._scanner(hosts, ports)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
taskList = []
for hostdic in hostlist:
taskList.append(loop.create_task(self._isLinux(hostdic["IP"],)))
for task in taskList:
task.add_done_callback(partial(self._callback))
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(taskList))
return self._hostsinfor
def _callback(self, future):
res = future.result()
self._hostsinfor.append(res)
async def _isLinux(self, host, port=‘22‘):
"""
判断目标主机是否是Linux,这是通过telnet远程登录SSH端口号后根据输出内容来判断的
所以需要远程主机开启SSH服务
:param host:
:param port:
:return: True|False
"""
try:
tm = telnetlib.Telnet(host=host, port=port, timeout=5)
# 读取的内容通常是这样的 b‘SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_5.3\r\n‘ 字节,所以只需要判断是否含有OpenSSH就知道是否是Linux
# 因为默认Windows上面没有OpenSSH服务,虽然你可以单独安装通常来讲没必要。
b_content = tm.read_until(b‘\n‘, timeout=5)
str_content = str(b_content.decode(encoding=‘utf-8‘)).strip()
# 判断是否包含OpenSSH字符,这里统一用大写比较
if "OPENSSH" in str_content.upper():
return {"IP": host, ‘Status‘: ‘up‘, "OSType": "Linux"}
else:
return {"IP": host, ‘Status‘: ‘up‘, "OSType": "Unknown"}
except (ConnectionRefusedError, TimeoutError) as err:
return {"IP": host, ‘Status‘: ‘up‘, "OSType": "Unknown"}
except Exception as err:
print("Error occurd in class ScanHost function _isLinux")
print("Error message: ", err)
def _scanner(self, hosts, ports=None):
"""
探测某一主机是否存活或者探测给定网段内存活的主机
:param hosts: 可以是IP也可以是网段,例如 192.168.100.10、192.168.100.0/24
:param ports: 可以写端口也可以写端口范围,例如22、22-33
:return: [{‘IP‘: ‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘Status‘: ‘up‘}, {}, {}]
"""
data = []
try:
nm = nmap.PortScanner()
"""
-n 不显示主机名,不进行IP到主机名的反向解析
-sP 使用ICMP协议探测
-PE 显示哪些端口号开启
-sP -PE 使用IMCP和TCP来探测,结果不显示端口号
"""
nm.scan(hosts=hosts, ports=ports, arguments=‘-sP -PE ‘)
# 这里获取的只是返回的有效IP
hosts_list = nm.all_hosts()
for host in hosts_list:
# 通过nmap实例获取主机的信息
# print(nm[host])
data.append({"IP": host, "Status": nm[host]["status"]["state"]})
return data
except Exception as err:
print("Error occurd in class ScanHost function _scanner")
print("Error message: ", err)
def main():
sh = ScanHost()
print(sh.scan(hosts="172.16.48.0/24"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
main()
finally:
sys.exit()
判断是否是Linux主机的原理是这样的
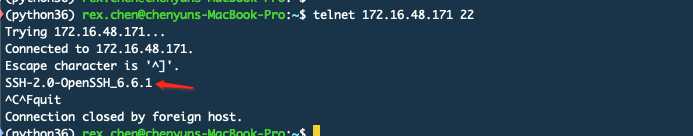
由于Linux主机通常默认都会开启ssh服务而且默认端口是22,所以telnet上去会出现红色箭头指向的内容。
扩展内容,当有了这些Linux主机后就可以远程执行dmidecode命令来获取更相信的服务器硬件方面的信息。这个功能在我的博客中也有。
标签:图片 self isl __name__ try yum exception 模块 tar
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yunxizhujing/p/10314914.html