标签:结果 namespace 初始化 csdn get 性能优化 构造 div people
我们创建某一个对象需要很大的消耗,而这个对象在运行过程中又不一定用到,为了避免每次运行都创建该对象,这时候延迟初始化(也叫延迟实例化)就出场了。
延迟初始化出现于.NET 4.0,主要用于提高性能,避免浪费计算,并减少程序内存要求。也可以称为,按需加载。
Lazy<T> xx = new Lazy<T>();//xx代表变量名
首先创建一个Student类,代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace LazyTest { class Student { public Student() { this.Name = "DefaultName"; Console.WriteLine("调用Student的构造函数"); } public string Name { get; set; } } }
创建一个控制台程序,代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace LazyTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Lazy<Student> student = new Lazy<Student>(); if (!student.IsValueCreated) { Console.WriteLine("Student未初始化"); } Console.WriteLine(student.Value.Name); if (student.IsValueCreated) { Console.WriteLine("Student已经初始化"); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
设置断点调试后发现,在new完之后,student的IsValueCreated的值是false,value的值是null
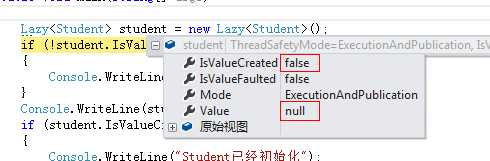
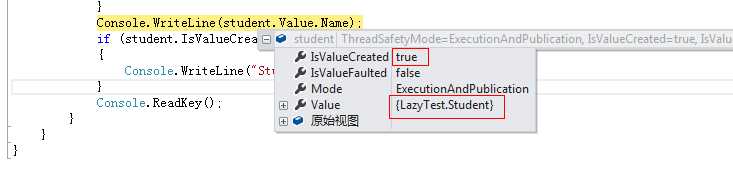
运行结果:
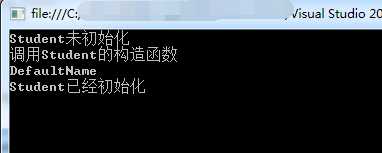
结果可以看出,Student是在输出Name属性才进行初始化的,也就是在第一次使用时才会去初始化,这样就可以达到减少消耗的目的。
这个例子很简单,也是Lazy<T>最基本的使用方式。我们还可以使用 Lazy<T> 的重载函数 Lazy<T> (Func<T>) 传入一个带返回值的委托来设置延迟初始化对象的属性值。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace LazyTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Lazy<Student> student = new Lazy<Student>(() => new Student { Name = "SetName" }); if (!student.IsValueCreated) { Console.WriteLine("Student未初始化"); } Console.WriteLine(student.Value.Name); if (student.IsValueCreated) { Console.WriteLine("Student已经初始化"); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
运行结果:
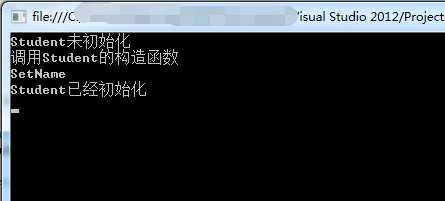
注:Lazy<T> 对象初始化默认是线程安全的,在多线程环境下,第一个访问 Lazy<T> 对象的 Value 属性的线程将初始化 Lazy<T> 对象,以后访问的线程都将使用第一次初始化的数据。
Lazy实现的原理应该是简单的,只是单独做了一个封装的类而已,下面是我们自我猜测的主要源码:
public class MyLazy<T> where T : new() { private static object _lock = new object(); private bool _isValueCreated = false; private T _value = default(T); public bool IsValueCreated { get { return _isValueCreated; } } public T Value { get { _isValueCreated = true; Monitor.Enter(_lock); if (_value==null) { _value = new T(); } Monitor.Exit(_lock); return _value; } } }
测试:
public class People { public People() { Console.WriteLine("被构造了"); } public string Name { get; set; } }
public static class Test { static void Main() { MyLazy<People> lazy = new MyLazy<People>(); Console.WriteLine(lazy.IsValueCreated); //False var p = lazy.Value.Name; //被构造了 Console.WriteLine(lazy.IsValueCreated); //True Console.ReadKey(); } }
当然了,这只是最简单的一种情况,然后我想到了源码中应该还会考虑到 类的单例,私有构造的各种情况。然后我用人家微软封装好的 Lazy做个测试吧。哎呀,官方的这咋还报错呢!
public static class Test { static void Main() { Lazy<People> lazy = new Lazy<People>(); var te = lazy.Value.Name; Console.ReadKey(); } } public class People { private People() { Console.WriteLine("被构造了"); } public string Name { get; set; } }
结果:
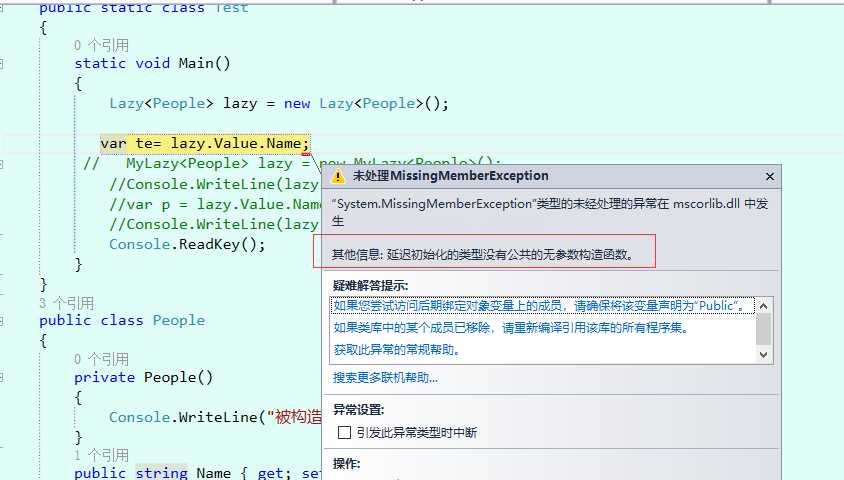
那我去看看Lazy的源码,找吐槽点了
有一个对象的创建开销很大,而程序可能不会使用它。例如,假定您的程序在启动时加载若干个对象实例,但只有一些对象实例需要立即执行。通过将不必要的对象的初始化延迟到已创建必要的对象之后,可以提高程序的启动性能。
参考文献:https://blog.csdn.net/yinghuolsx/article/details/73824220
标签:结果 namespace 初始化 csdn get 性能优化 构造 div people
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wwkk/p/10325490.html