标签:style blog http color io ar 使用 java for
Java语言基本语法
一、标识符和关键字
| abstract | assert | boolean | break | byte | case | catch | char |
| class | const | continue | default | do | double | else | enum |
| extends | final | finally | float | for | goto | if | implements |
| import | instanceof | int | interface | long | native | new | package |
| private | protected | public | return | short | static | strictfp | super |
| switch | synchronized | this | throw | throws | transient | try | void |
| volatile | while |
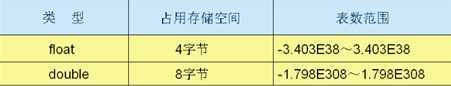
二、基本数据类型
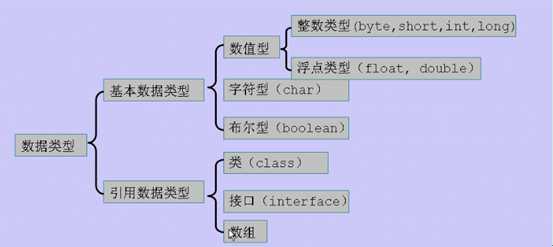
1. 整数类型(int为默认类型)
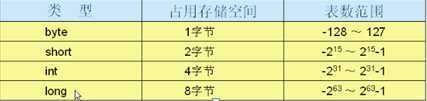
2. 浮点类型(double为默认类型)
3. 字符类型(2字节)
4. 布尔类型(1字节)
5. 默认值
6. 不同数据类型之间的转换
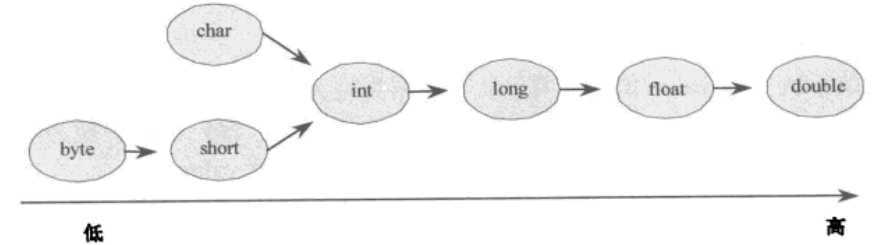
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { byte b = 100; int i = 22; float f = 78.98f; int res = b + i + (int)f; //此处对f使用了强制类型转换(int)f,转换后的值为78 System.out.println("res: "+res); //res: 200 } }
三、运算符与表达式
1. 算术运算符
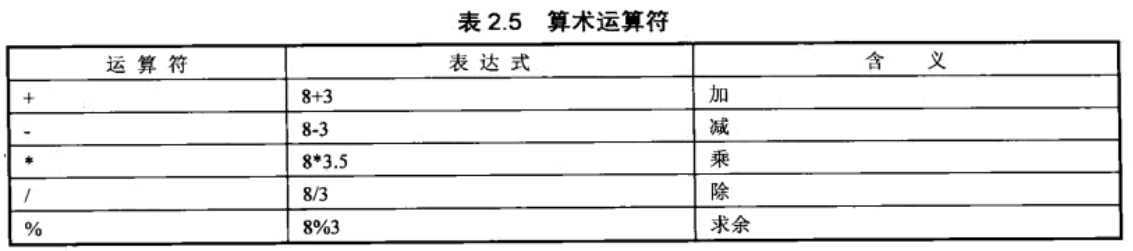
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 5; System.out.println(0/i); //0 System.out.println(0%i); //0 System.out.println(i/0); //除数不能为零,报异常java.lang.ArithmeticException System.out.println(i%0); //除数不能为零,报异常java.lang.ArithmeticException } }
2. 赋值运算符
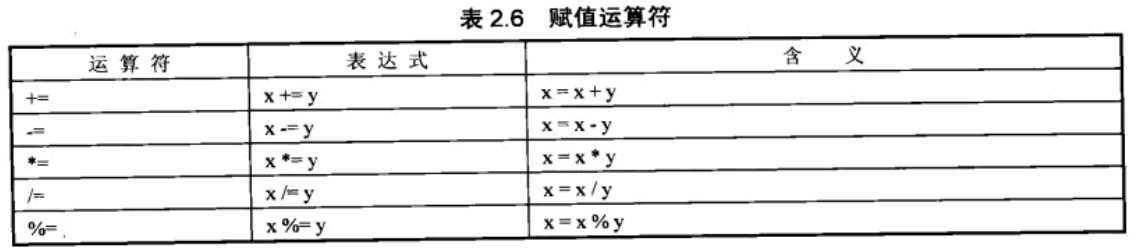
3. 自增自减运算符(++,--)
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 5; System.out.println(i++); //5 System.out.println(++i); //7 System.out.println(i); //7 System.out.println(--i); //6 System.out.println(i--); //6 System.out.println(i); //5 } }
4. 关系运算符
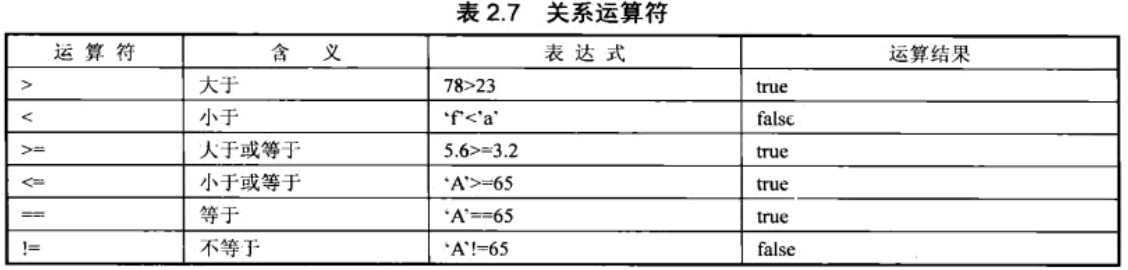
5. 逻辑运算符
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean t = true; boolean f = false; System.out.println(t && f); //false,短路与运算符,若运算符左侧为false则不计算右侧的表达式 System.out.println(t || f); //true,短路或运算符,若运算符左侧为true则不计算右侧的表达式 System.out.println(t & f); //false,与运算符,不管左侧是否为false都要计算右侧的表达式 System.out.println(t | f); //true,或运算符,不管左侧是否为true都要计算右侧的表达式 System.out.println(t ^ f); //true,异或运算符,只要左右两侧不相同则为true,反之为false System.out.println(!f); //true,取反运算符 } }
6. 位运算符
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { //在位运算符中1相当于true,0相当于false int b1 = 6; //二进制为00000000 00000000 00000000 00000110 int b2 = 11; //二进制为00000000 00000000 00000000 00001011 System.out.println(b1 & b2); //按位与运算符,二进制为00000000 00000000 00000000 00000010,结果为2 System.out.println(b1 | b2); //按位或运算符,二进制为00000000 00000000 00000000 00001111,结果为15 System.out.println(b1 ^ b2); //按位异或运算符,二进制为00000000 00000000 00000000 00001101,结果为13 System.out.println(~b1); //按位取反运算符,二进制为11111111 11111111 11111111 11111001,结果为-7 System.out.println(b1 << 2); //左移位运算符,二进制为00000000 00000000 00000000 00011000,结果为24 int b3 = -14; //二进制为11111111 11111111 11111111 11110010 System.out.println(b3 >> 2); //带符号右移位运算符,二进制为11111111 11111111 11111111 11111100,结果为-4 System.out.println(b3 >>> 2); //无符号右移位运算符,二进制为00111111 11111111 11111111 11111100,结果为1073741820 } }
7. 三元运算符
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1; int b = 2; int c = 4; int res = c==a+b?++a:c>a+b?++b:++c; //三元运算符 (表达式)?(值1):(值2),若表达式为true则取值1,反之取值2 System.out.println(res); //++b,结果为3 } }
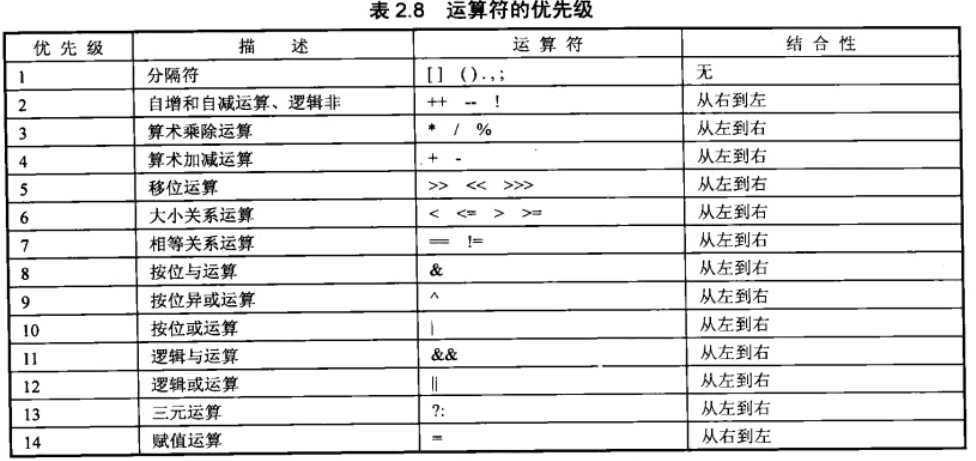
8. 运算符优先级
四、数组
1. 一维数组
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] i; //声明一个整型的一维数组变量 int ii[]; //声明一个整型的一维数组变量 i = new int[5]; //创建一个长度为5的一维数组对象,并将变量i指向该对象 float[] f = new float[5]; //直接创建一个长度为5的单精度浮点型一维数组对象,并将变量f指向该对象 double[] d = {1, 2, 3.4, 4.5}; //直接初始化一个一维数组元素 System.out.println(d[3]); //通过数组下标来获取数组内的元素,数组下标从0开始,结果为4.5 System.out.println(f[0]); //当创建出一个数组对象时,该对象内的数组元素为该数据类型的默认值,所以此处结果为0.0 //System.out.println(i[5]); //当通过数组下标来获取数组内元素时,[]内的值>=数组长度则报异常java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(数组下标越界) //System.out.println(ii[0]); //若一个数组变量只声明而未指向某一个具体的数组对象时,编译出错 System.out.println(d.length); //得到该数组的长度,结果为4 } }
2. 二维数组
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] i; //声明一个整型的二维数组变量 int ii[][]; //声明一个整型的二维数组变量 int[] iii[]; //声明一个整型的二维数组变量 i = new int[5][2]; //创建一个长度为5的二维数组对象,并将变量i指向该对象 float[][] f = new float[5][2]; //直接创建一个长度为5的单精度浮点型二维数组对象,并将变量f指向该对象 double[][] d = {{1}, {2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9,10}}; //直接初始化一个二维数组元素 System.out.println(d[3][1]); //通过数组下标来获取数组内的元素,数组下标从0开始,结果为8 System.out.println(f[0][0]); //当创建出二个数组对象时,该对象内的数组元素为该数据类型的默认值,所以此处结果为0.0 //System.out.println(i[5][0]); //当通过数组下标来获取数组内元素时,[]内的值>=数组长度则报异常java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(数组下标越界) //System.out.println(ii[0][0]); //若一个数组变量只声明而未指向某一个具体的数组对象时,编译出错 System.out.println(d.length); //得到该数组的长度,结果为4 System.out.println(d[2].length); //得到二位数组内的下标为2的那个一维数组的长度 } }
五、流程控制语句(if,switch,for,while,do...while)
1. 条件分支语句
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] score = new int[5]; score[0] = -7; score[1] = 65; score[2] = 80; score[3] = 90; score[4] = 59; for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) { if(score[i]>=0 && score[i]<60) { System.out.println("不及格"); }else if(score[i]>=60 && score[i]<80) { System.out.println("及格"); }else if(score[i]>=80 && score[i]<90) { System.out.println("良"); }else if(score[i]>=90 && score[i]<100) { System.out.println("优"); }else { System.out.println("成绩异常"); } } char ch = ‘a‘; switch(ch) { //switch括号内只支持 byte,short,int,char,enum五种数据类型,但是JDK1.7版本增加了String类型,所以相对于JDK1.7而言就是六种了 case ‘A‘: //case为switch语句的入口,break为出口,从入口开始执行,直到遇到出口或代码执行完毕才结束 case ‘a‘: System.out.println("优"); break; case ‘B‘: case ‘b‘: System.out.println("良"); break; case ‘C‘: case ‘c‘: System.out.println("及格"); break; default: //若上述条件均不匹配,则进default开始执行语句 System.out.println("不及格"); } } }
2. 循环语句
public class Test003 { public static void main(String[] args) { int res = 0; out: //out是一个标号,告诉java从哪里开始执行程序 for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { if(i==3) continue out; //continue终止本次循环,执行下次循环 if(i==5) break out; //break跳出循环 res = res + i; } System.out.println(res); //结果为1+2+4=7 int res2 = 0; int i = 1; in: do{ if(i==3) continue in; //continue终止本次循环,执行下次循环 if(i==5) break in; //break跳出循环 res2 = res2 + i; i++; }while(i<=10); System.out.println(res2); } }
标签:style blog http color io ar 使用 java for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/fendoudeya/p/j2se_java01.html