标签:列表 字符串 art token date drop cto 端口修改 stdin
1、 详述iptables五链Iptables的主要功能是实现网络数据包进出设备及转发的控制,当数据包需要进入设备、从设备中流出或者经该设备转发、路由时,都可以使用iptables进行控制。
Netfilter/iptables IP 信息包过滤系统是一种功能强大的工具,可用于添加、编辑和除去规则,这些规则是在做信息包过滤决定时,防火墙所遵循和组成的规则。这些规则存储在专用的信息包过滤表中,而这些表集成在Linux内核中。在信息包过滤表中,规则被分组放在我们所谓的链(chain)中。
Netfilter/iptables IP 信息包过滤系统都被称为单个实体,但它实际上由两个组件netfilter和iptables组成。
Netfilter组件也称为内核空间(kernelspace),是内核的一部分,由一些信息表过滤表组成,这些表包含内核用来控制信息包过滤处理的规则集。
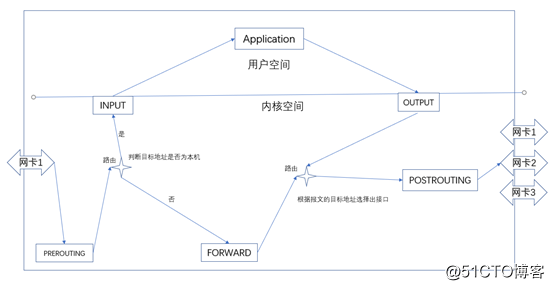
如上图所示,iptables五种链接分别是prerouting、input、output、forward、postrouting
流入本机: prerouting --> input ==> 用户空间进程;
流出本机: 用户空间进程==> output --> postrouting;
转发: prerouting --> forward --> postrouting;[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 237 packets, 17727 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 151 packets, 17334 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -I INPUT 1 -d 192.168.10.10 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 21,22,80,8080,443 -j ACCEPT
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 3 packets, 176 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
8 576 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 8 packets, 1388 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.10.10 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 21,22,80 -m state --state INVALID -j REJECT
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
343 22920 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80 state INVALID reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 30 packets, 3048 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -s 192.168.10.10 -d 192.168.10.0/24 -p tcp --sport 80 -m string --algo bm --string "sex" -j REJECT
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 2 packets, 100 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
755 53000 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80 state INVALID reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 44 packets, 4388 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 192.168.10.10 192.168.10.0/24 tcp spt:80 STRING match "sex" ALGO name bm TO 65535 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.10.0/24 -d 192.168.10.10 -p tcp --dport 80 -m time --timestart 00:30 --timestop 12:30 --weekdays Mon,Sun -j DROP
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 200 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1133 78104 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80 state INVALID reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.10.0/24 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:80 TIME from 00:30:00 to 12:30:00 on Mon,Sun UTC
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 41 packets, 3852 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 192.168.10.10 192.168.10.0/24 tcp spt:80 STRING match "sex" ALGO name bm TO 65535 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.10.10 -p tcp --dport 21 -m connlimit --connlimit-above 2 -j REJECT
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1403 96028 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80 state INVALID reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.10.0/24 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:80 TIME from 00:30:00 to 12:30:00 on Mon,Sun UTC
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:21 #conn src/32 > 2 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 16 packets, 1584 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 192.168.10.10 192.168.10.0/24 tcp spt:80 STRING match "sex" ALGO name bm TO 65535 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -I INPUT -d 192.168.10.10 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m limit --limit 5/minute --limit-burst 3 -j ACCEPT
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 icmptype 8 limit: avg 5/min burst 3
1665 113K ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80 state INVALID reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.10.0/24 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:80 TIME from 00:30:00 to 12:30:00 on Mon,Sun UTC
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:21 #conn src/32 > 2 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 20 packets, 1944 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 192.168.10.10 192.168.10.0/24 tcp spt:80 STRING match "sex" ALGO name bm TO 65535 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 --tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST,URG,PSH SYN -j REJECT
[root@xiaochen ~]# iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22 flags:0x3F/0x02 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 icmptype 8 limit: avg 5/min burst 3
1910 130K ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80,8080,443
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 multiport dports 21,22,80 state INVALID reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.10.0/24 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:80 TIME from 00:30:00 to 12:30:00 on Mon,Sun UTC
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.10.10 tcp dpt:21 #conn src/32 > 2 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 17 packets, 1724 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT tcp -- * * 192.168.10.10 192.168.10.0/24 tcp spt:80 STRING match "sex" ALGO name bm TO 65535 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable一台网关主机用上nat的主要目的是要隐藏网关内网中的主机。如果一个网关设备不开启nat功能,仅仅只能将报文实现网络转发,而不会修改报文的任何源ip和目标ip。此时内网中的客户端和互联网外的主机通信时,一个怀有恶意的外网主机会得到内网客户端的地址,然后用扫描工具扫描客户端主机的各种端口服务,找到有薄弱项的服务发起远程***,此时很容易攻克这台主机,并用这台主机当作跳板,继续从内网去***内部其他的重要的主机。当网关主机上开启了nat功能后,网关在转发报文到互联网或者从互联网转发报文到内网服务器的时候,把报文中的内网主机地址统统改成网关的外网地址,外部的主机只能看到网关的地址,这样就做到安全保护内网中主机的操作。
网关开启nat后,请求报文和相应报文是通过内存中的连接追踪表来进行地址转换的。内网中的客户端通过网关的地址转换访问外网的服务器主机叫做SNAT(source network address translation),外网主机访问经过网关地址转换的内网中提供各种服务的主机叫做DNAT(destination network address translation),httpd只开放8080端口,把8080端口映射到80,能正常以80访问叫做PNAT
[root@localhost ~]# sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
[root@localhost ~]# route add default gw 192.168.10.11
[root@localhost ~]# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
default 192.168.10.11 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eno16777736
default 192.168.10.2 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eno16777736
default 192.168.50.1 0.0.0.0 UG 101 0 0 eno33554960
192.168.10.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eno16777736
192.168.50.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eno33554960
[root@localhost ~]# route add -net 192.168.0.0/24 gw 192.168.50.10
[root@localhost ~]# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
default 192.168.10.11 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eno16777736
default 192.168.10.2 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eno16777736
default 192.168.50.1 0.0.0.0 UG 101 0 0 eno33554960
192.168.0.0 192.168.50.10 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eno33554960
192.168.10.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eno16777736
192.168.50.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eno33554960[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 192.168.50.10
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
SNAT all -- 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere to:192.168.50.10[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.0.0/24 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.10.10
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DNAT all -- anywhere 192.168.0.0/24 to:192.168.10.10
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
SNAT all -- 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere to:192.168.50.10[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.0.0/24 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DNAT all -- anywhere 192.168.0.0/24 to:192.168.10.10
REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere 192.168.0.0/24 tcp dpt:http redir ports 8080
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
SNAT all -- 192.168.0.0/24 anywhere to:192.168.50.10sudo : 当我们去执行某个命令时,是切换用户以另外一个用户的身份运行。这个是在sudo文件中设定的另外一个发起人,这个发起人一般是管理员,并在文件中定义好发起人能够运行的命令列表,之后就能够临时切换发起人来执行这些命令,这种授权机制就是sudo,其中sudo的配置文件位置在/etc/sudoers,可以使用专用命令visudo来编辑这个文件完成授权。
sudo:
su:switch user
用户切换
(1) su -l user
(2) su -l user -c ‘COMMAND‘sudo:
能够让获得授权的用户以另外一个用户的身份运行指定的命令;
授权机制:授权文件 /etc/sudoers
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
编译此文件的专用命令:visudo
授权项:
who where=(whom) commands
users hosts=(runas) commands
users:
username
#uid
%groupname
%#gid
user_alias
支持将多个用户定义为一组用户,称之为用户别名,即user_alias;
hosts:
ip
hostname
NetAddr
host_alias
runas:
...
runas_alias
commands:
command
directory
sudoedit:特殊权限,可用于向其它用户授予sudo权限;
cmnd_alias
定义别名的方法:
ALIAS_TYPE NAME=item1, item2, item3, ...
NAME:别名名称,必须使用全大写字符;
ALIAS_TYPE:
User_Alias
Host_Alias
Runas_Alias
Cmnd_Alias示例:
[root@localhost ~]# useradd fedora
[root@localhost ~]# echo fedora | passwd --stdin fedora
Changing password for user fedora.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@localhost ~]# su – fedora
[fedora@localhost ~]$ useradd user1
-bash: /usr/sbin/useradd: Permission denied
[fedora@localhost ~]$ exit
logout
[root@localhost ~]# visudo
fedora ALL=(ALL) /usr/sbin/useradd,/usr/sbin/userdel ##添加一行内容
[root@localhost ~]# su – fedora
fedora@localhost ~]$ sudo useradd user1
We trust you have received the usual lecture from the local System
Administrator. It usually boils down to these three things:
#1) Respect the privacy of others.
#2) Think before you type.
#3) With great power comes great responsibility.
[sudo] password for fedora:
[fedora@localhost ~]$ tail -1 /etc/passwd
user1:x:1001:1001::/home/user1:/bin/bash
[fedora@localhost ~]$ sudo userdel user1
[fedora@localhost ~]$ id user1
id: user1: no such user[root@localhost ~]# usermod -a -G wheel fedora
[root@localhost ~]# newgrp wheel
[root@localhost ~]# id fedora
uid=1000(fedora) gid=1000(fedora) groups=1000(fedora),10(wheel)
[root@localhost ~]# visudo
%wheel ALL=(ALL) /usr/sbin/useradd,/usr/sbin/userdel
[root@localhost ~]# su - fedora
Last login: Wed Feb 13 23:19:34 CST 2019 on pts/0
[fedora@localhost ~]$ sudo -k
[fedora@localhost ~]$ sudo useradd user3
[sudo] password for fedora:
[fedora@localhost ~]$ id user3
uid=1001(user3) gid=1001(user3) groups=1001(user3)
[fedora@localhost ~]$ sudo userdel user3
[fedora@localhost ~]$ id user3
id: user3: no such user标签:列表 字符串 art token date drop cto 端口修改 stdin
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/13929964/2349801