标签:翻页 源码 path reg python 开发 产品 情况 class
我们在浏览器访问一个网页是通过url地址去访问的,django管理url配置是在urls.py文件。当一个页面数据很多时候,通过会有翻页的情况,那么页数是不固定的,如:page=1.
也就是url路径里面带参数时候如何去处理呢?
由于django版本比较多,在查资料时候,也会看到不同的版本用不同写法,对于初学者来说是比较迷惑的,
总结了下,主要有三个:path、re_path、url,接下来具体分析下这三个有什么区别。
# helloworld/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.urls import re_path, path
from hello import views
urlpatterns = [
path("index/", views.index),
re_path(‘^$‘, views.index),
url(‘^demo/$‘, views.demo),
]
在浏览器上访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/, http://127.0.0.1:8000/, http://127.0.0.1:8000/demo/ 发现都能正确访问到对应内容。
打开path()和re_path()源码,就能看到path()的匹配规则是RoutePattern, re_pat()h匹配规则是RegexPattern
path = partial(_path, Pattern=RoutePattern) re_path = partial(_path, Pattern=RegexPattern)
再打开url()对应的源码,实际上就是return re_path(),后续统一用url()就可以了。
def url(regex, view, kwargs=None, name=None):
return re_path(regex, view, kwargs, name)
匹配路径统一在后面加个/,前面不用加/,如:index/、demo/、demo/page/
当访问的页面有分页的情况,对应的页数就不能写死,如访问:http://127.0.0.1:8000/demo/page=1 ,那就不能这样写死了
url(‘^demo/page=1$‘, views.demo)
如果想匹配任意的页数,前面的部分demo/page=不变,匹配任意数字,可以用正则\d+匹配
url(‘^demo/page=\d+$‘, views.demo)
这样在浏览器上输入任意page页数都能访问一个固定地址,依然不是我们想要的结果,我们希望不同的页数,访问不同的地址,于是可以写个带参数的视图函数
hello/views.py文件写个带参数的视图函数,当输入的page=后面不是数字就抛个异常404
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse, Http404
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello world ! django ~~")
def demo(request):
return render(request, ‘demo.html‘)
def page(request, num):
try:
num = int(num)
return render(request, ‘demo.html‘)
except:
raise Http404
urls.py配置
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.urls import re_path, path
from hello import views
urlpatterns = [
path("index/", views.index),
re_path(‘^$‘, views.index),
url(‘^demo/$‘, views.demo),
url(‘^demo/page=(\d+)$‘, views.page),
]
接下来可以浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:8000/demo/page=222 ,能返回demo.html页面。
视图函数里面返回的是一个静态的demo.html模板页面,后面会讲模板参数化配置
如果输入的page不是数字,如:http://127.0.0.1:8000/demo/page=aa , 会出现报错页面:Page not found (404)
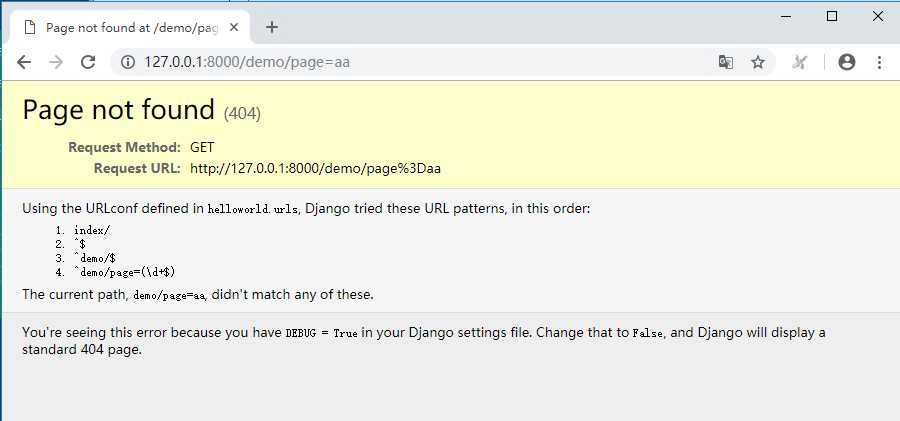
看到这种报错页面,因为Django设置文件setting.py里面有个参数 DEBUG = True,将其更改为False,Django将显示标准的404页面。
# SECURITY WARNING: don‘t run with debug turned on in production! DEBUG = True ALLOWED_HOSTS = []
由于处于开发阶段,DEBUG 默认为True,当开发完成正式发布产品上线时,需要将DEBUG = False
ALLOWED_HOSTS是域名访问权限,设置可以访问的域名,默认值为空[], 只允许localhost或127.0.0.1在浏览器上访问。
DEBUG 改成False之后,需要重新启动服务,同时需要加个ALLOWED_HOSTS 地址,如果想让所以的域名都能访问,可以设置为:ALLOWED_HOSTS = ["*"]
# SECURITY WARNING: don‘t run with debug turned on in production! DEBUG = False ALLOWED_HOSTS = ["*"]
执行:>python manage.py runserver 重新启动后,出现404就是下面这种标准的了
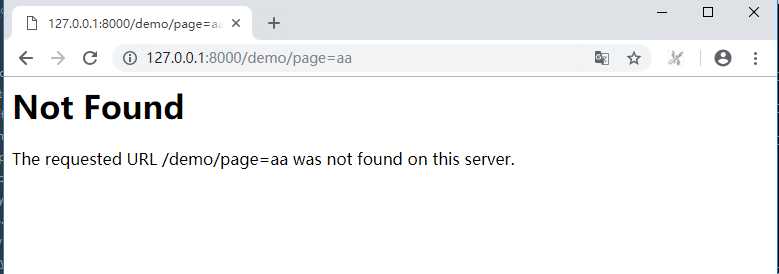
django更多关于urls学习可以参考【https://docs.djangoproject.com/zh-hans/2.0/topics/http/urls/】
标签:翻页 源码 path reg python 开发 产品 情况 class
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuxuchao/p/10404439.html