标签:flight rev div for 超时 时间 通过 内核 use
linux 4.9内核,bbr的带宽估计问题。
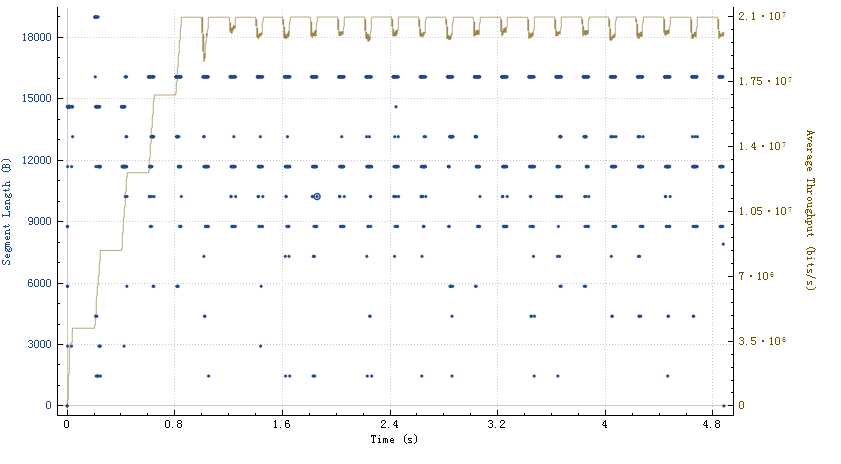
一个正常的bbr流量图:
一个异常的bbr流量图:
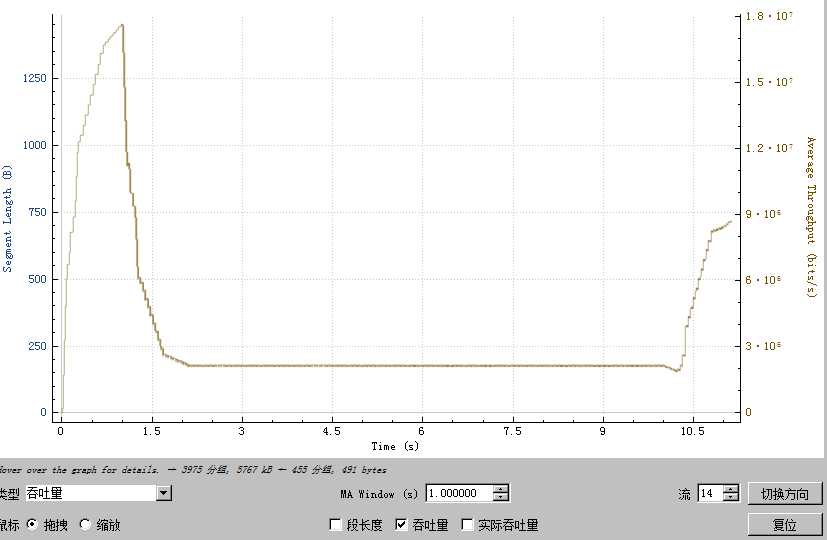
可以看出,异常的bbr流量图,出现了一个很低的带宽,且稳定在这个带宽10s左右,而正常情况下,这个文件下载不应该超过10s,由于流量消耗大于流量的下载,导致了用户播放卡顿。
通过分析,我们确认了bbr在应对delay_ack时,出现带宽估计偏低的情况,比如正常的min_rtt是1.3ms,但是delay_ack的时候,是40ms左右,而由于probe_rtt需要10秒之后进行,那么对应的
bw乘以最小的rtt则处于偏低的状态,在稳定10s之后,bbr会主动探测rtt,
bbr探测rtt的时候,行为是什么样的呢?对于4.9内核版本来说,是最多发送4个mss包:
cwnd = max(cwnd_gain * bottleneck_bandwidth * min_rtt, 4)
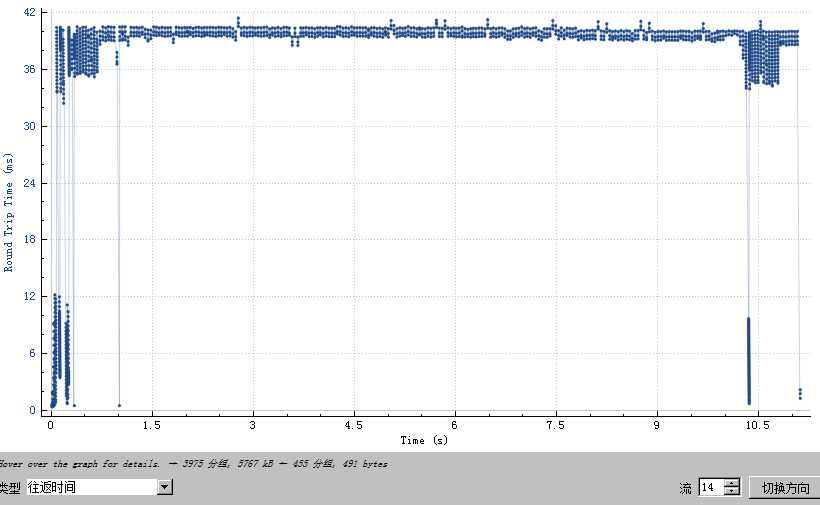
从10.3s左右的时间的流量图来看,可以看到一个很明显的向下缺口,就是探测最小rtt的行为,每个rtt之后4个包,流量再次下降。
这个持续的时间为0.2s,也就是代码里面如下的描述:
/* The goal of PROBE_RTT mode is to have BBR flows cooperatively and * periodically drain the bottleneck queue, to converge to measure the true * min_rtt (unloaded propagation delay). This allows the flows to keep queues * small (reducing queuing delay and packet loss) and achieve fairness among * BBR flows. * * The min_rtt filter window is 10 seconds. When the min_rtt estimate expires, * we enter PROBE_RTT mode and cap the cwnd at bbr_cwnd_min_target=4 packets. * After at least bbr_probe_rtt_mode_ms=200ms and at least one packet-timed * round trip elapsed with that flight size <= 4, we leave PROBE_RTT mode and * re-enter the previous mode. BBR uses 200ms to approximately bound the * performance penalty of PROBE_RTT‘s cwnd capping to roughly 2% (200ms/10s). * * Note that flows need only pay 2% if they are busy sending over the last 10 * seconds. Interactive applications (e.g., Web, RPCs, video chunks) often have * natural silences or low-rate periods within 10 seconds where the rate is low * enough for long enough to drain its queue in the bottleneck. We pick up * these min RTT measurements opportunistically with our min_rtt filter. :-) */ static void bbr_update_min_rtt(struct sock *sk, const struct rate_sample *rs)
虽然经过10s,根据探测rtt之后的min_rtt应该修正为40ms左右,会导致流量上升,但由于我们的分片文件已经播放卡顿超时,客户端会断链。
结论:如果下载的流媒体文件过小,不建议开启bbr。特别是客户端进入delay_ack非常早的情况。
参考资料:
https://queue.acm.org/detail.cfm?id=3022184
标签:flight rev div for 超时 时间 通过 内核 use
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/10087622blog/p/10334643.html