标签:存在 control 字符串 写法 封装 singleton 反转 junit4 lob
Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
1.方便解耦,简化开发:
- Spring就是一个大工厂,专门负责生成Bean,可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护由Spring管理
2.AOP编程的支持:
- Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能
- 声明式事务的支持:只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程
3.方便程序的测试:
- Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring程序
4.方便集成各种优秀框架:
- Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的支持
5.降低JavaEE API的使用难度Spring:
- 对JavaEE开发中一些难用的API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调webservice用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低
Inverse of Control 反转控制的概念,就是将原本在程序中手动创建UserService对象的控制权,交由Spring框架管理,简单说,就是创建UserService对象控制权被反转到了Spring框架。
示例:
/src/beans.xml
<?xml version ="1.0"encoding ="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns= "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id="userService" class="com.chichung.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"> </bean> </beans>
如果表示层需要new一个service对象,则:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // UserService service = new UserServiceImpl(); // 原来创建service对象的方式 // service.add(); // Spring框架创建对象的方式 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); userService1.add(); } }
Dependency Injection 依赖注入,在Spring框架负责创建Bean对象时,动态的将依赖对象注入到Bean组件。
示例:
在UserService中提供一个get/set的name方法,在beans.xml中通过property去注入
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void add() { System.out.println("业务层"+name); } }
/src/beans.xml
<?xml version ="1.0"encoding ="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns= "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id="userService" class="com.chichung.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"> <property name="name" value="chichung"></property> </bean> </beans>
还有另一种方法是用命名空间p来注入,很少用
<?xml version ="1.0"encoding ="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns= "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id="userService" class="com.chichung.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" p:name="chichung"> </bean> </beans>
如果没有setter方法,也可以通过构造方法来注入。
例如有一个Student类
public class Student { private String name; private String password; private int age; public Student(String name, String password) { this.name = name; this.password = password; } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", password=‘" + password + ‘\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ‘}‘; } }
有两种方式:
1.示例:
<bean id="stu" class="com.chichung.Bean.Student"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="chichung"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="password" value="123"></constructor-arg> </bean>
2.示例:
<bean id="stu" class="com.chichung.Bean.Student"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="chichung" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="123" type="int"></constructor-arg> </bean>
1.类路径获取配置文件(常用)
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); userService1.add(); } }
2.文件系统路径获取配置文件
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("/home/chichung/桌面/JavaeePr/MavenTest2/target/classes/beans.xml"); UserService service = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); service.add(); } }
3.使用BeanFactory(少用)
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { BeanFactory BeanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("/home/chichung/桌面/JavaeePr/MavenTest2/target/classes/beans.xml")); UserService service = (UserService) BeanFactory.getBean("userService"); service.add(); } }
注意:
BeanFactory 采取延迟加载,第一次getBean时才会初始化Bean。而ApplicationContext是即时加载的。
Bean类:
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void add() { System.out.println("业务层"); } }
xml写法:
<bean id="userService" class="com.chichung.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"> </bean>
静态工厂:
public class UserServiceStaticFactory { public static UserService createUserService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); } }
xml写法:
<bean id="userService2" class="com.chichung.factory.UserServiceStaticFactory" factory-method="createUserService">
取得Spring容器的对象:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService service2 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService2"); service2.add(); } }
实例工厂:
public class UserServiceFactory { public UserService createUserService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); } }
xml写法:
<bean id="factory" class="com.chichung.factory.UserServiceFactory"></bean> <bean id="userService3" factory-bean="factory" factory-method="createUserService"></bean>
取得Spring容器的对象:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService service3 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService3"); service3.add(); } }
| 类别 | 说明 |
| singleton |
在Spring IoC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例,Bean以单例方式存在,默认值 |
| prototype |
每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,即每次调用getBean()时 ,相当于执行new XxxBean() |
| request |
每次HTTP请求都会创建一个新的Bean,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
| session |
同一个HTTP Session 共享一个Bean,不同Session使用不同Bean,仅适用于WebApplicationContext 环境 |
| globalSession |
一般用于Portlet应用环境,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext 环境 |
示例:

#{123}、#{‘jack‘} : 数字、字符串
#{beanId}:另一个bean引用
#{beanId.propName}:操作数据
#{beanId.toString()}:执行方法
#{T(类).字段|方法}:静态方法或字段
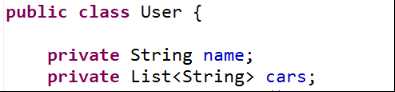
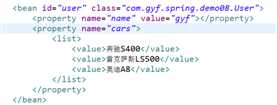
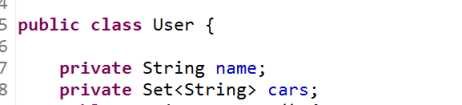
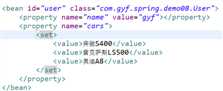
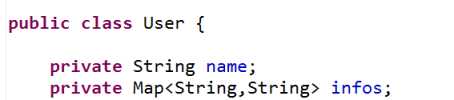

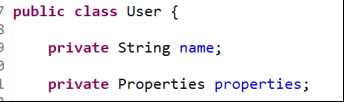


使用注解方式需要先开启注解。
beans.xml:
<?xml version ="1.0"encoding ="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns= "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--开启注解--> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config> <!--注解的位置--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.chichung.Bean"></context:component-scan> </beans>
1.@Component可以取代<bean class="">
示例:
bean.java
@Component public class Student { ... }
test.java
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Student student = context.getBean(Student.class); System.out.println(student); } }
2.@Component("[id]")可以取代<bean id="" class="">
bean.java
@Component("stu")
public class Student {
...
}
test.java
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Student student = (Student) context.getBean("stu"); System.out.println(student); } }
3.对于web开发的三层架构,提供了@Respository、@Service、@Controller快速使用。
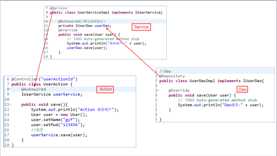
4.除了@Autowired,还可以用@Qualifier("")或者@Resource("")指定自动注入的名字


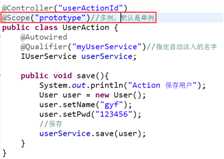
5.注解设置Bean的作用域@Scope
标签:存在 control 字符串 写法 封装 singleton 反转 junit4 lob
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/chichung/p/10388558.html