标签:sort nbsp arraylist else for 编号 header exti png
Farmer John变得非常懒,他不想再继续维护供奶牛之间供通行的道路。道路被用来连接N个牧场,牧场被连续地编号为1到N。每一个牧场都是一个奶牛的家。FJ计划除去P条道路中尽可能多的道路,但是还要保持牧场之间 的连通性。你首先要决定那些道路是需要保留的N-1条道路。第j条双向道路连接了牧场Sj和Ej(1 <= Sj <= N; 1 <= Ej <= N; Sj != Ej),而且走完它需要Lj的时间。没有两个牧场是被一条以上的道路所连接。奶牛们非常伤心,因为她们的交通系统被削减了。你需要到每一个奶牛的住处去安慰她们。每次你到达第i个牧场的时候(即使你已经到过),你必须花去Ci的时间和奶牛交谈。你每个晚上都会在同一个牧场(这是供你选择的)过夜,直到奶牛们都从悲伤中缓过神来。在早上 起来和晚上回去睡觉的时候,你都需要和在你睡觉的牧场的奶牛交谈一次。这样你才能完成你的 交谈任务。假设Farmer John采纳了你的建议,请计算出使所有奶牛都被安慰的最少时间。
第1行包含两个整数N和P。
接下来N行,每行包含一个整数Ci。
接下来P行,每行包含三个整数Sj, Ej和Lj。
5 <= N <= 10000,N-1 <= P <= 100000,0 <= Lj <= 1000,1 <= Ci <= 1,000。
思路: https://www.cnblogs.com/liuzhen1995/p/6522515.html
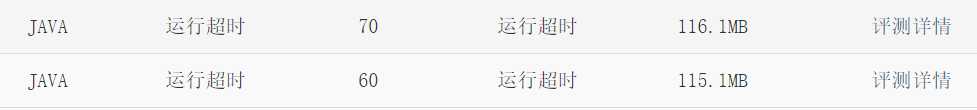
以下为两个代码,一个为60分,一个70分,因为在对象数组排序时,java里面没有现成的函数,对于 collections.sort()只能排 list 类型,
不愿意自己写排序,于是就将数组改为了list, 所以结果是60分,超时了,我们知道,在循环遍历取数时,链表比数组要慢很多的,数组
直接按下标取,而链表虽然有 list.get() 函数,但是去每个下标对应的值,都是从头遍历的很慢,故在第二个代码里面,我将list 转化为
数组了,得了 70 分。
List 提供了toArray的接口,所以可以直接调用转为object型数组
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); Object[] array=list.toArray();
上述方法存在强制转换时会抛异常,下面此种方式更推荐:可以指定类型
String[] array=list.toArray(new String[list.size()]);
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
public static List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<Edge>();
public static int f[] = new int[100003];
public static int w[] = new int[100003];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
n = cin.nextInt();
m = cin.nextInt();
int Min = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
w[i] = cin.nextInt();
if(Min > w[i]) {
Min = w[i];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
int v = cin.nextInt();
Edge edge = new Edge();
edge.x = a;
edge.y = b;
edge.w = v * 2 + w[a] + w[b];
edges.add(edge);
}
System.out.println(kruskal() + Min);
}
public static long kruskal() {
long ans = 0, ct = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i] = i;
}
//按 w 由小到大排序
Collections.sort(edges, new Comparator<Edge>() {
public int compare(Edge a, Edge b) {
return a.w - b.w;
}
});
for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
Edge edge = edges.get(i);
int x = edge.x;
int y = edge.y;
int w = edge.w;
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) {
ct++;
ans += w;
f[fx] = f[fy];
}
if(ct == n - 1) {
break;
}
}
if(ct < n - 1) {
System.out.println("不能找到最小生成树!");
}
return ans;
}
public static int find(int x) {
if(f[x] == x) {
return x;
}
else {
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
}
}
class Edge{
public int x;
public int y;
public int w;
public int getx() {
return this.x;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
public static List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<Edge>();
public static int f[] = new int[100003];
public static int w[] = new int[100003];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
n = cin.nextInt();
m = cin.nextInt();
int Min = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
w[i] = cin.nextInt();
if(Min > w[i]) {
Min = w[i];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
int v = cin.nextInt();
Edge edge = new Edge();
edge.x = a;
edge.y = b;
edge.w = v * 2 + w[a] + w[b];
edges.add(edge);
}
System.out.println(kruskal() + Min);
}
public static long kruskal() {
long ans = 0, ct = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i] = i;
}
//按 w 由小到大排序
Collections.sort(edges, new Comparator<Edge>() {
public int compare(Edge a, Edge b) {
return a.w - b.w;
}
});
// int len = edges.size();
// for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// System.out.println(edges.get(i).w);
// }
//转为数组
Edge[] temp = edges.toArray(new Edge[edges.size()]); //toArray(new String[list.size()]);
// System.out.println(temp[0].w + "---------");
for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
// Edge edge = edges.get(i);
// int x = edge.x;
// int y = edge.y;
// int w = edge.w;
int x = temp[i].x;
int y = temp[i].y;
int w = temp[i].w;
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) {
ct++;
ans += w;
f[fx] = f[fy];
}
if(ct == n - 1) {
break;
}
}
if(ct < n - 1) {
System.out.println("不能找到最小生成树!");
}
return ans;
}
public static int find(int x) {
if(f[x] == x) {
return x;
}
else {
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
}
}
class Edge{
public int x;
public int y;
public int w;
public int getx() {
return this.x;
}
}
标签:sort nbsp arraylist else for 编号 header exti png
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhumengdexiaobai/p/10434855.html