标签:详解 entity schema print utf-8 获取 etag 完成 XML
IOC(Inverse of Control)反转控制的概念,就是将原本在程序中手动创建对象的控制权,交由Spring框架管理。当某个Java对象(调用者)需要调用另一个Java对象(被调用者)时,在传统编程模式下,调用者通常会采用“new 被调用者”的代码方式来创建对象。这种方式会增加调用者与被调用者之间的耦合性,不利于后期代码的升级与维护。
当Spring框架出现后,对象的实例不再由调用者来创建,而是由Spring容器来创建。Spring容器会负责控制程序之间的关系,而不是由调用者的程序代码直接控制。这样,控制权由调用者转移到Spring容器,控制权发生了反转,这就是Spring的控制反转。
实现控制反转的是Spring IOC容器,Spring IOC容器的设计主要是基于Bean Factory和ApplicationContext两个接口。
BeanFactory由org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory接口定义,它提供了完整的IOC服务支持,是一个管理Bean的工厂,主要负责初始化各种Bean。
BeanFactory接口最常用的实现类是org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XMLBeanFactory,该类会根据XML配置文件中的定义来装配Bean。
BeanFactory实例创建代码如下:
@Test public void demo(){ FileSystemResource file = new FileSystemResource("C:\\demo\\applicationContext.xml"); BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(file); TestDao testDao = (TestDao) beanFactory.getBean("testDao"); testDao.sayHello(); }
由于使用BeanFactory实例加载Spring配置文件在实际开发中并不多见,所以对于该接口仅了解即可。
ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,也称为应用上下文,由org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口定义。ApplicationContext接口除了包含BeanFactory的所有功能以外,还添加了对国际化、资源访问、事件传播等内容的支持。
创建ApplicationContext接口实例通常有以下3中方法:
下面对这3种方法的代码做演示:
(1)ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext将从类路径目录(src根目录)中寻找指定的XML配置文件,代码示例:
@Test public void demo(){ //初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //通过容器获取testDao实例 TestDao testDao = (TestDao) application.getBean("testDao"); testDao.sayHello(); }
(2)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext将从指定文件的绝对路径中寻找XML配置文件,找到并装载完成ApplicationContext的实例化工作,代码示例:
@Test public void demo(){ ApplicationContext application = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:\\demo\\applicationContext.xml"); TestDao testDao = (TestDao) application.getBean("testDao"); testDao.sayHello(); }
(3)使用Web服务器实例化
通过Web服务器实例化ApplicationContext容器,一般使用org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener的实现方式,需要添加Spring-web依赖,pom.xml配置如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
在web.xml中配置代码如下:
<context-param> <!--加载src目录下的applicationContext.xml文件--> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!--指定以ContextLoaderListener方式启动Spring容器--> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
通过web.xml配置,web容器会自动加载context-param中的配置文件初始化ApplicationContext实例,然后就可以在web应用中通过WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext方法获取ApplicationContext的引用,Servlet中的代码如下:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws javax.servlet.ServletException, IOException { ApplicationContext application = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(request.getServletContext()); TestDao testDao = (TestDao) application.getBean("testDao"); testDao.sayHello(); }
DI (Dependency Injection)依赖注入的概念,在Spring中实现IOC容器的方法是依赖注入,依赖注入的作用是在使用Spring框架创建对象时动态地将其所依赖的对象(属性值)注入Bean组件中。
Spring框架的依赖注入通常有以下几种实现方式:
创建User类
package test; public class User { private String name; private int age; public User(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ‘}‘; } }
在applicationContext.xml文件中配置user实例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用构造方法注入--> <bean id="user" class="test.User"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="age" value="20"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
在测试方法中代码
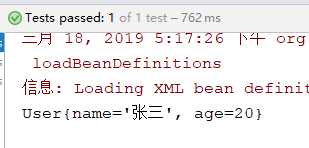
@Test public void demo(){ //初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //通过容器获取实例 User user = (User) application.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user); }
运行结果
创建Course课程类
package entity; public class Course { private String cname; public String getCname() { return cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course{" + "cname=‘" + cname + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } }
创建Student学生类
package entity; public class Student { private String name; private int age; private Course course; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ", course=" + course + ‘}‘; } //getter和setter方法 }
配置applicationContext.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用set方法注入--> <bean id="course" class="entity.Course"> <property name="cname" value="大学语文"></property> </bean> <bean id="student" class="entity.Student"> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> <property name="age" value="20"></property> <property name="course" ref="course"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试方法
@Test public void demo(){ //初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //通过容器获取实例 Student student = (Student) application.getBean("student"); System.out.println(student); }
运行结果

创建Course课程类
package entity; public class Course { private String cname; public String getCname() { return cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course{" + "cname=‘" + cname + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } }
创建Student学生类
package entity; public class Student { private String name; private int age; private Course course; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ", course=" + course + ‘}‘; } //getter和setter方法 }
配置applicationContext.xml文件,要在约束里面加入p名称空间的约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用p名称空间注入--> <bean id="course" class="entity.Course" p:cname="英语"></bean> <bean id="student" class="entity.Student" p:name="张三" p:age="20" p:course-ref="course"></bean> </beans>
测试方法
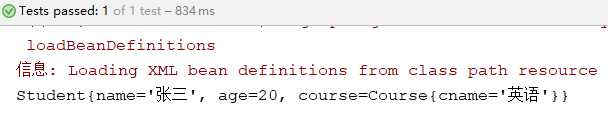
@Test public void demo(){ //初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //通过容器获取实例 Student student = (Student) application.getBean("student"); System.out.println(student); }
运行结果
我们可以使用SpEL(Spring expression language)Spring表达式语言,对依赖注入进行简化。
语法:#{表达式},例如 <bean id="" value="#{表达式}">
#{‘hello‘}:使用字符串
#{beanId}:使用另一个bean
#{beanId.content.toUpperCase()}:使用指定名属性,并使用方法
#{T(java.lang.Math).PI}:使用静态字段或方法
创建Course课程类
package entity; public class Course { private String cname; public String getCname() { return cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course{" + "cname=‘" + cname + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } }
创建Student学生类
package entity; public class Student { private String name; private int age; private Course course; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ", course=" + course + ‘}‘; } //getter和setter方法 }
配置applicationContext.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用SpEL方式注入--> <bean id="course" class="entity.Course"> <property name="cname" value="#{‘高数‘}"></property> </bean> <bean id="student" class="entity.Student"> <property name="name" value="#{‘小明‘}"></property> <property name="age" value="#{10}"></property> <property name="course" value="#{course}"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试方法
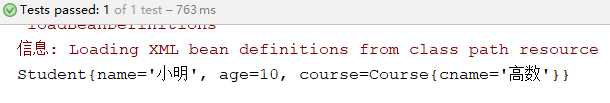
@Test public void demo(){ //初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext,加载配置文件 ApplicationContext application = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //通过容器获取实例 Student student = (Student) application.getBean("student"); System.out.println(student); }
运行结果
在使用SpEL时,配置中也可以调用方法,示例代码如下:
创建获取年龄的类
package entity; public class GetAge { public int createAge(){ return 20; } }
配置applicationContext.xml
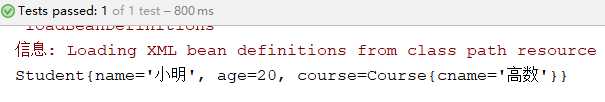
<!--使用SpEL方式注入--> <bean id="course" class="entity.Course"> <property name="cname" value="#{‘高数‘}"></property> </bean> <bean id="getAge" class="entity.GetAge"></bean> <bean id="student" class="entity.Student"> <property name="name" value="#{‘小明‘}"></property> <property name="age" value="#{getAge.createAge()}"></property> <property name="course" value="#{course}"></property> </bean>
执行测试方法,运行结果如下:
标签:详解 entity schema print utf-8 获取 etag 完成 XML
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jpwz/p/10559262.html