标签:one run 需要 val 预测 ast import div als
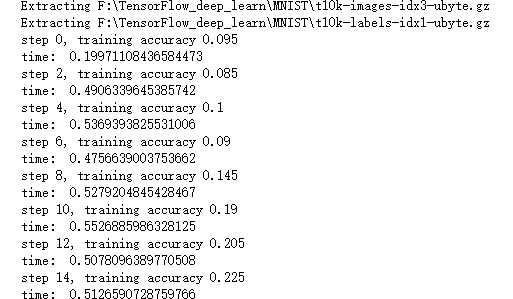
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import time # 声明输入图片数据,类别 x = tf.placeholder(‘float‘, [None, 784]) y_ = tf.placeholder(‘float‘, [None, 10]) # 输入图片数据转化 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) #第一层卷积层,初始化卷积核参数、偏置值,该卷积层5*5大小,一个通道,共有6个不同卷积核 filter1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 6])) bias1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([6])) conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(x_image, filter1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv1 + bias1) maxPool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) filter2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 6, 16])) bias2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([16])) conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(maxPool2, filter2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2 + bias2) maxPool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) filter3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 16, 120])) bias3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([120])) conv3 = tf.nn.conv2d(maxPool3, filter3, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv3 + bias3) # 全连接层 # 权值参数 W_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([7 * 7 * 120, 80])) # 偏置值 b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([80])) # 将卷积的产出展开 h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_conv3, [-1, 7 * 7 * 120]) # 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数 h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) # 输出层,使用softmax进行多分类 W_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([80, 10])) b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([10])) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) # 损失函数 cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv)) # 使用GDO优化算法来调整参数 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(cross_entropy) sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # 测试正确率 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) # 所有变量进行初始化 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据 mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets(‘F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\‘, one_hot=True) # 进行训练 start_time = time.time() for i in range(20000): # 获取训练数据 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代100个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率 if i % 2 == 0: train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy)) # 计算间隔时间 end_time = time.time() print(‘time: ‘, (end_time - start_time)) start_time = end_time # 训练数据 train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) # 关闭会话 sess.close()

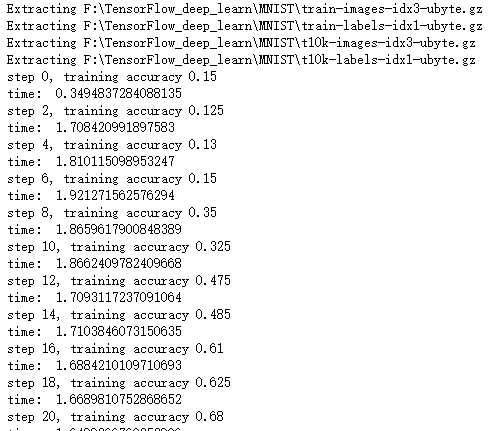
import time import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) #初始化单个卷积核上的偏置值 def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) #输入特征x,用卷积核W进行卷积运算,strides为卷积核移动步长, #padding表示是否需要补齐边缘像素使输出图像大小不变 def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) #对x进行最大池化操作,ksize进行池化的范围, def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # 声明输入图片数据,类别 x = tf.placeholder(‘float32‘, [None, 784]) y_ = tf.placeholder(‘float32‘, [None, 10]) # 输入图片数据转化 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 6]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([6]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 6, 16]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([16]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*16,120]) # 偏置值 b_fc1 = bias_variable([120]) # 将卷积的产出展开 h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 16]) # 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数 h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) W_fc2 = weight_variable([120,10]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) # 代价函数 cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv)) # 使用Adam优化算法来调整参数 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) # 测试正确率 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float32")) # 所有变量进行初始化 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据 mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets(‘F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\‘, one_hot=True) c = [] # 进行训练 start_time = time.time() for i in range(1000): # 获取训练数据 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代10个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率 if i % 2 == 0: train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) c.append(train_accuracy) print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy)) # 计算间隔时间 end_time = time.time() print(‘time: ‘, (end_time - start_time)) start_time = end_time # 训练数据 train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) sess.close() plt.plot(c) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(‘F:\\cnn-tf-cifar10-2.png‘, dpi=200) plt.show()
import time import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) #初始化单个卷积核上的偏置值 def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) #输入特征x,用卷积核W进行卷积运算,strides为卷积核移动步长, #padding表示是否需要补齐边缘像素使输出图像大小不变 def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) #对x进行最大池化操作,ksize进行池化的范围, def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # 声明输入图片数据,类别 x = tf.placeholder(‘float32‘, [None, 784]) y_ = tf.placeholder(‘float32‘, [None, 10]) # 输入图片数据转化 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024]) # 偏置值 b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) # 将卷积的产出展开 h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) # 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数 h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) # 代价函数 cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv)) # 使用Adam优化算法来调整参数 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) # 测试正确率 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float32")) # 所有变量进行初始化 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据 mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets(‘F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\‘, one_hot=True) c = [] # 进行训练 start_time = time.time() for i in range(1000): # 获取训练数据 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代10个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率 if i % 2 == 0: train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) c.append(train_accuracy) print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy)) # 计算间隔时间 end_time = time.time() print(‘time: ‘, (end_time - start_time)) start_time = end_time # 训练数据 train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) sess.close() plt.plot(c) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(‘F:\\cnn-tf-cifar10-1.png‘, dpi=200) plt.show()
import time import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) #初始化单个卷积核上的偏置值 def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) #输入特征x,用卷积核W进行卷积运算,strides为卷积核移动步长, #padding表示是否需要补齐边缘像素使输出图像大小不变 def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) #对x进行最大池化操作,ksize进行池化的范围, def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding=‘SAME‘) sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # 声明输入图片数据,类别 x = tf.placeholder(‘float32‘, [None, 784]) y_ = tf.placeholder(‘float32‘, [None, 10]) # 输入图片数据转化 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024]) # 偏置值 b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) # 将卷积的产出展开 h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) # 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数 h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,128]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([128]) h_fc2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) W_fc3 = weight_variable([128,10]) b_fc3 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc2, W_fc3) + b_fc3) # 代价函数 cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv)) # 使用Adam优化算法来调整参数 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-5).minimize(cross_entropy) # 测试正确率 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float32")) # 所有变量进行初始化 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据 mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets(‘F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\‘, one_hot=True) c = [] # 进行训练 start_time = time.time() for i in range(1000): # 获取训练数据 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代10个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率 if i % 2 == 0: train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) c.append(train_accuracy) print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy)) # 计算间隔时间 end_time = time.time() print(‘time: ‘, (end_time - start_time)) start_time = end_time # 训练数据 train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) sess.close() plt.plot(c) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(‘F:\\cnn-tf-cifar10-11.png‘, dpi=200) plt.show()
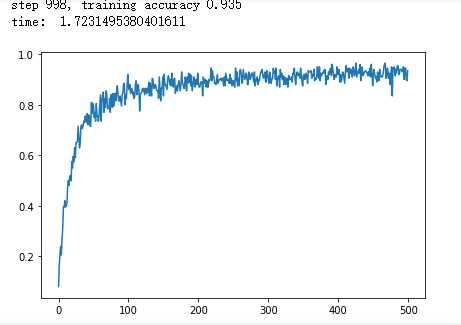
标签:one run 需要 val 预测 ast import div als
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tszr/p/10569822.html