标签:des style blog http color io os ar 使用
与多点云处理有关的任务,点云的配准(Registration)是一个绕不开的问题。如何采用适当的算法,对特定的点云数据进行相对更优的配准,是点云配准过程中的关键任务。
配准结果通常被表达为一个代表缩放,旋转,平移的刚体变换的矩阵,该矩阵代表了两个点云的位置关系,即将其中一个点云(源点云,Source)施以这个刚体变换可以使它与另一个点云(目标点云,Target)配准。

图 1 目标点云(Target)
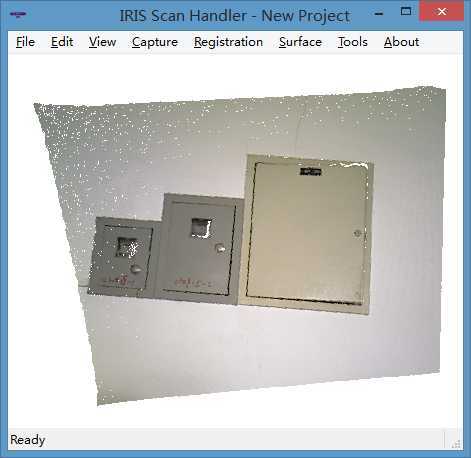
图 2 源点云(Source)
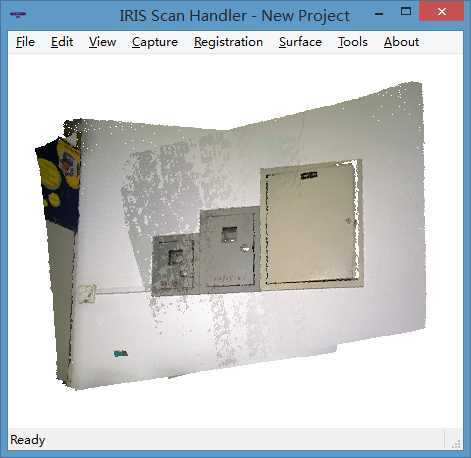
图 3 配准结果(该结果即通过本文所述的算法实现)
配准算法主要分为两类,一类采用迭代法,利用逐步逼近的方法使配准结果逐步趋于最优,常用于两个点云的位置相差不大的场合下的精确配准;一类通过确定两个点云的点的对应关系(分别在两个点云中映射的在实际空间中“相同的”点)并根据这些点对确定两幅点云的位置关系,常用于原始位置相差较大的粗略配准。本文所述的基于灰度特征的配准算法属于第二类。
部分针对点云进行配准的判据大多针对三维形状特征(例如图 2)。对于缺乏三维形状特征的点云来说,该类型的配准通常不会获得理想的效果。但是,基于 RGB-D 传感器可以获得二维彩色点阵图片的特点,通过二维特征确定点云位置关系,是解决这一问题的一个思路。这也是本文所述的基于灰度特征的关系对配准算法的主要原理。
为了描述上的方便,我们使用函数
void getGrayScaleRegMatrix(const Cloud &cloud_target, const Cloud &cloud_source, Matrix &matrix);
代表算法执行的入口,配准结果输出在 matrix 中。其中,Cloud / CloudPtr 是点云库 PCL 中的点云类和点云类的 boost 指针,Point 是 PCL 的点类,Matrix 是矩阵类型(常用 Eigen::Matrix4f)。
P.S. 该函数使用 void 作为函数返回的原因,是因为 Eigen 线性代数类库强烈建议不使用 pass-by-value 传递方法。不仅因为这一方法本身不在 C++ 的这种场合下被建议,同时,使用 pass-by-value 会因为编译器的数据类型对齐特性造成致命的运行时错误。此处,调用该函数的代码应保证存储结果的矩阵已经被事先分配内存。(参考:http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox-devel/TopicUnalignedArrayAssert.html)
//Surf_Threshold 是限定提取特征阈值的常量;ax_Remove_Threshold 是限定最大距离阈值的常量。详见下面的代码。 const double Max_Remove_Threshold = 750; const int Surf_Threshold = 750; //获取点云对应的二维点阵图信息。 IplImage* getIplImage(const CloudPtr &input_cloud) { //创建图像。 IplImage *image = cvCreateImage(cvSize((*input_cloud).width, (*input_cloud).height), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 3); //填充图像。 cv::Scalar pixel; for (int i = 0; i < (*image).height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < (*image).width; j++) { pixel.val[0] = (*input_cloud).points[i*(*image).width + j].b; pixel.val[1] = (*input_cloud).points[i*(*image).width + j].g; pixel.val[2] = (*input_cloud).points[i*(*image).width + j].r; cvSet2D(image, i, j, pixel); } } //返回创建的图像。 return image; } //配准主函数。 void getGrayScaleRegMatrix(const CloudPtr &cloud_target, const CloudPtr &cloud_source, Matrix &matrix) { //获取原始点云对应的二维点阵图信息。参考 getIplImage 函数。 IplImage *oriImageTarget = getIplImage(cloud_target); IplImage *oriImageSource = getIplImage(cloud_source); //将原始图像转换为灰度图像,备 SURF 特征点提取使用。 IplImage *grayImageTarget = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(oriImageTarget), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 1); cvCvtColor(oriImageTarget, grayImageTarget, CV_RGB2GRAY); IplImage *grayImageSource = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(oriImageSource), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 1); cvCvtColor(oriImageSource, grayImageSource, CV_RGB2GRAY); //提取 SURF 特征点,并存入 keypointsTarget 和 keypointsSource 向量。Surf_Threshold 是限定提取特征阈值的常量。 cv::SurfFeatureDetector detector(Surf_Threshold); std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypointsTarget; detector.detect(grayImageTarget, keypointsTarget); std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypointsSource; detector.detect(grayImageSource, keypointsSource); //计算 SURF 特征点的描述符。 cv::SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor; cv::Mat descriptorsSource, descriptorsTarget; extractor.compute(grayImageTarget, keypointsTarget, descriptorsTarget); extractor.compute(grayImageSource, keypointsSource, descriptorsSource); //将两幅点云的描述符通过 Flann 算法进行特征点的关系对应。 cv::FlannBasedMatcher matcher; std::vector<cv::DMatch> matches; matcher.match(descriptorsSource, descriptorsTarget, matches); //获得对应关系列表。 std::vector<cv::Point2f> sourcePoints; std::vector<cv::Point2f> targetPoints; for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++) { sourcePoints.push_back(keypointsSource[matches[i].queryIdx].pt); targetPoints.push_back(keypointsTarget[matches[i].trainIdx].pt); } //使用 RANSAC 算法进行错误对应关系的去除。特征点对的保留与丢弃结果存储在 m_RANSACStatus 中。 std::vector<uchar> m_RANSACStatus; cv::findHomography(sourcePoints, targetPoints, CV_RANSAC, 3.0, m_RANSACStatus); //创建 PCL 适用的关系列表。 pcl::Correspondences correspondences; correspondences.empty(); int temp_x_target, temp_y_target, temp_index_target, temp_x_source, temp_y_source, temp_index_source; for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++) { if (m_RANSACStatus[i] == 1) //保留的对应点对。 { //四舍五入计算X、Y坐标,并计算其在点云中存储的位置。 temp_x_target = (int)(targetPoints[i].x + 0.5); temp_y_target = (int)(targetPoints[i].y + 0.5); temp_index_target = temp_y_target * (*grayImageTarget).width + temp_x_target; temp_x_source = (int)(sourcePoints[i].x + 0.5); temp_y_source = (int)(sourcePoints[i].y + 0.5); temp_index_source = temp_y_source * (*grayImageSource).width + temp_x_source; //若特征点对在三维点云中没有对应的空间点(没有深度信息)则不考虑该对应关系。 if ((*cloud_source).points[temp_index_source].z != (*cloud_source).points[temp_index_source].z) continue; if ((*cloud_target).points[temp_index_target].z != (*cloud_target).points[temp_index_target].z) continue; //存储对应关系。 pcl::Correspondence correspondence; correspondence.index_query = temp_index_source; correspondence.index_match = temp_index_target; correspondences.push_back(correspondence); } } //利用点云的空间特点,如果对应关系的相差距离过大,则去除该关系。Max_Remove_Threshold 是限定最大距离阈值的常量。 for (int i = 0;;) { if (i == correspondences.size()) break; if (Utils::getDistance((*cloud_target).points[correspondences[i].index_match], (*cloud_source).points[correspondences[i].index_query]) > Max_Remove_Threshold) { correspondences.erase(correspondences.begin() + i); } else i++; } //根据对应关系计算变换矩阵。 pcl::registration::TransformationEstimationLM<Point, Point> estimation; estimation.estimateRigidTransformation((*cloud_source), (*cloud_target), correspondences, matrix); }
代码中附带了算法实现过程的注释。对代码的具体的分析将在今后补上。
对于灰度 SURF 特征点及对应关系的确定,还可以对特征点的选取和关系的确定进行进一步的优化,避免严重错误的配准结果的出现。
从工程角度,上述代码对于特殊条件下可能出现的极端结果没有进行必要的处理。
OpenCV Feature Description http://docs.opencv.org/doc/tutorials/features2d/feature_description/feature_description.html
OpenCV学习笔记(九)——2维特征Feature2D http://blog.csdn.net/yang_xian521/article/details/6901762
Flaris帕 版权所有
转载请注明出处(●‘?‘●)
20141019 V1.0版
PrimeSense 三维重建开发小谈 (2) - 基于灰度特征的关系对配准算法
标签:des style blog http color io os ar 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Flaris/p/PrimeSense2.html