标签:ado asc t-sql 结果 dad 分组 逗号 set 搜索
插入数据语法格式:insert [into] <表名> [列名] values <值列表>;
insert into test (姓名,×××号,职务,出生日期,基本工资)values (‘张三‘,‘123465789‘,‘运维工程师‘,‘1995-10-01‘,12000) #向表中插入员工张三的信息
注意SQL语句中的符号都是在英文输入法中输入的,否则会报错。
更改表中数据update test set 基本工资=12000 where 姓名=‘李四‘ #把test表中的李四工资更改为12000元。
删除表中数据delete from test where 姓名=‘张三‘ #删除表中张三的行记录
delete from test #删除test表中所有行
truncate table test #删除test表中所有行
truncate 和delete 语句都用来删除记录,区别如下:
select查询语法结构
在SQL server中,select语句的语法如下:
select 要查询的列
[ into 生成新表的名 ]
from [表名]
[where 查询条件]
[group by 指定查询结果的分组条件] [ having ] 指定分组搜索条件,通常和group by 子句一起使用
[ order by 指定排序规则 desc&asc ] #desc为降序,asc为升序,默认不指定的话为升序条件表达式 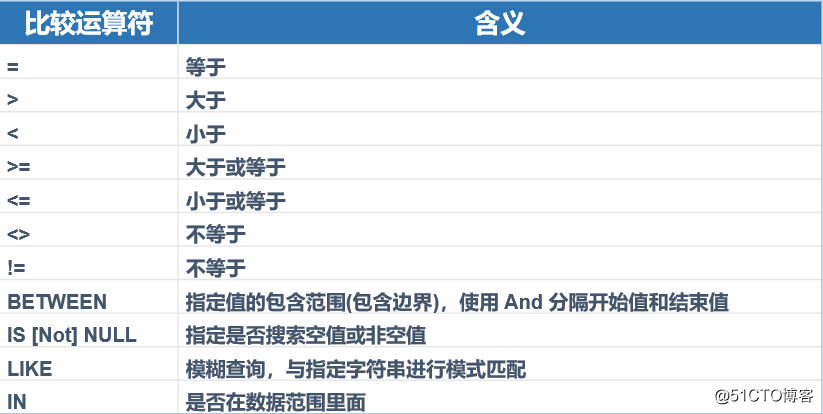
逻辑表达式
查询举例select * from test #把test表中的所有列信息都列举出来
select 姓名,职务,基本工资 from test #查询表中的姓名,职务,基本工资列内容
select 姓名 from test where 职务=‘运维人员‘ #查询表中所有运维人员的姓名
select * from test where 基本工资 between 8000 and 10000 #查询test表中基本工资8000到10000之间的员工所有信息
select * from test where 基本工资<10000 or 基本工资>20000 #查询表中基本工资低于10000或高于20000的员工所有信息
select * from test where 基本工资 in (8000,9000,10000) #查询表中工资为8000,9000,和10000的员工所有信息。
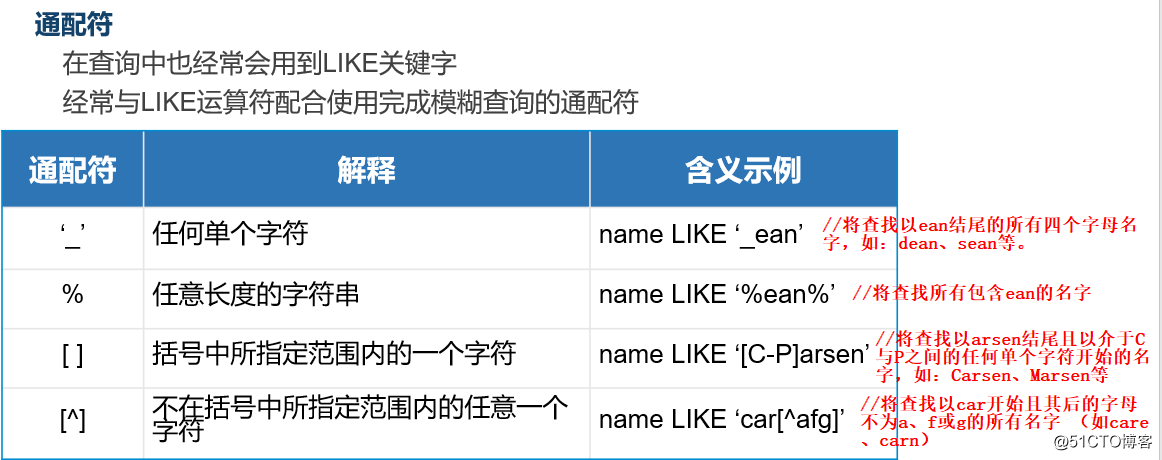
select * from test where ×××号 like ‘66%‘ #查询test表中×××号以66开头的员工所有信息。
select * from test where 姓名 like ‘杨%‘ and 职务=‘运维工程师‘ #查询表中姓杨的运维工程师的信息
select * from test where 备注 is not null #查询表中备注不为空的员工所有信息。
select top 5 * from test #查询表中前5行的数据。
select * from test order by 基本工资 desc #查询test表中所有的信息,并按照基本工资从高到低显示查询结果。
select distinct 职务 from test #查询test表中有哪些职务
使用SELECT生成新数据
1、select 使用into关键字:select 姓名,×××号,职务 into new01 from test #将test表中所有员工的姓名、×××号和职务生成一个新表new01。
2、insert 使用select关键字:
insert into Table_1 (姓名,职务,出生日期) select 姓名,职务,出生日期 from test where 基本工资>=15000 #将test表中所有基本工资大于等于15000的员工的姓名,职务,和出生日期保存到 Table_1表中(注意,这里的 Table_1表中需要提前建立)
3、使用union关键字:insert into table_1 (姓名,职务,出生日期) <br/>select ‘张三‘,‘运维‘,‘1995-01-01‘ union <br/>select ‘李四‘,‘运维‘,‘1996-01-01‘ union <br/>select 姓名,职务,出生日期 from test #将test表中所有员工的姓名、职务和出生日期,以及新输入的2名员工相关信息,一起保存到新表table_01
标签:ado asc t-sql 结果 dad 分组 逗号 set 搜索
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14154700/2373910