标签:scanf null union 有序 .com mem scan tree pst
func.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node * next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listHeadInsert(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listSortInsert(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listDeleteNode(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listPrint(pNode head);func.c
#include "func.h"
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listHeadInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *head) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
}
void listSortInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
pNode pCur, pPre;
pCur = pPre = *head;
if (NULL == *head) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else if (pCur->val > val) { //头插
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
else {
while (pCur) { //中间插入
if (val < pCur->val) {
pPre->next = newNode;
newNode->next = pCur;
break;
}
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
if (NULL == pCur) { //尾部插入
pPre->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
}
void listDeleteNode(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode pPre, pCur;
pPre = pCur = *head;
if (pCur == NULL) {
printf("list is empty!\n");
//printf("Delete failed , doesn't find the node!\n");
return;
}
else if (pCur->val == val) { //删除的是头部
*head = pCur->next;
}
else {
while (pCur) {
if (pCur->val == val) {
pPre->next = pCur->next;
break;
}
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
if (pCur == *tail) {
*tail = pPre;
}
if (NULL == pCur) {
printf("Don't find the node!\n");
}
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
main.c
#include "func.h"
int main() {
printf("please input the key of node:\n");
pNode head = NULL, tail = NULL;
int val;
while (scanf("%d", &val) != EOF) {
//listTailInsert(&head, &tail, val);
//listHeadInsert(&head, &tail, val);
listSortInsert(&head, &tail, val);
}
while (printf("please input delete num:\n"), scanf("%d", &val) != EOF){
listDeleteNode(&head, &tail, val);
listPrint(head);
}
listPrint(head);
return 0;
}"stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct tag{
int m_ival;
struct tag *next;
}Node,*pNode;
typedef struct{
pNode phead;//栈顶指针
int size;
}Stack,*pStack;
void initStack(pStack);
void pop(pStack);
void push(pStack,int);
int top(pStack);
int empty(pStack);
int size(pStack);"stack.c"
#include "stack.h"
void initStack(pStack p)
{
memset(p,0,sizeof(Stack));
}
void pop(pStack p)
{
if(!p->size)
{
printf("stack is empty\n");
return;
}
p->phead=p->phead->next;
p->size--;
}
void push(pStack p,int val)
{
pNode pNew=(pNode)calloc(1,sizeof(Node));
pNew->m_ival=val;
if(NULL==p->phead)
{
p->phead=pNew;
}else{
pNew->next=p->phead;//新结点的next指向原有头结点
p->phead=pNew;
}
p->size++;
}
int top(pStack p)
{
return p->phead->m_ival;
}
int empty(pStack p)
{
return !p->size;
}
int size(pStack p)
{
return p->size;
}"main.c"
#include "stack.h"
int main() {
Stack s;
initStack(&s);
push(&s, 5);
push(&s, 10);
printf("Stack size is %d\n", size(&s));
printf("Stack top val is %d\n", top(&s));
pop(&s);
printf("Stack top val is %d\n", top(&s));
pop(&s);
pop(&s);
return 0;
}#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1,sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
pNode head = NULL, tail = NULL;
void Union(pNode head1, pNode tail1, pNode head2, pNode tail2, int len1, int len2) {
int i = 0;
while (head1 && head2) {
if (head1->val >= head2->val) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head2->val);
head2 = head2->next;
}
else {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head1->val);
head1 = head1->next;
}
}
while (head1) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head1->val);
head1 = head1->next;
}
while (head2) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head2->val);
head2 = head2->next;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 1,2,7,9,13 };
int b[8] = { 3,4,6,8,9,11,15,19 };
pNode head1, head2, tail1, tail2;
head1 = head2 = tail1 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head1, &tail1, a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0;i < 8;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head2, &tail2, b[i]);
}
printf("两个有序链表:\n");
listPrint(head1);
listPrint(head2);
printf("合并后:\n");
Union(head1, tail1, head2, tail2, 5, 8);
listPrint(head);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
pNode* reverse(pNode *head) {
pNode a = *head, b = (*head)->next, c = b->next;
b->next = a;
a->next = NULL;
while (c) {
a = b;
b = c;
c = c->next;
b->next = a;
}
return b;
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 1,9,3,-2,7 };
pNode head, tail;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
pNode t = reverse(&head);
listPrint(t);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int a[10] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0 };
pNode head, tail, last;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
last = head;
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
head = head->next;
}
while (head) {
head = head->next;
last = last->next;
}
printf("倒数第四个节点的值为%d\n", last->val);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void findMidNode(pNode head) {
pNode t1, t2;
t1 = t2 = head;
while (t2) {
t2 = t2->next;
t2 = t2->next;
t1 = t1->next;
}
printf("中间节点为%d\n", t1->val);
}
int main() {
int a[11] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0,-8 };
pNode head, tail, last;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
findMidNode(head);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int judge(pNode head) {
pNode slow, fast;
slow = fast = head;
while (fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
fast = fast->next;
if (slow == fast) {
printf("有环!\n");
return 0;
}
}
printf("无环!\n");
return 1;
}
int main() {
int a[11] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0,-8 };
int b[11] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0,-8 };
pNode head, tail;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
if (judge(head)) { //无环,输出链表
listPrint(head);
}
printf("------------------\n");
pNode head2, tail2;
head2 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head2, &tail2, b[i]);
}
tail2->next = head2; //构造环
if (judge(head2)) { //有环不输出
listPrint(head2);
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void findcommon(pNode head1, pNode head2, int len1, int len2) {
if (len1 > len2) {
while (len1 - len2) {
head1 = head1->next;
--len1;
}
}
else {
while (len2 - len1) {
head2 = head2->next;
--len2;
; }
}
while (head1&&head2) {
if (head1 == head2) {
printf("公共节点是%d\n", head1->val);
return;
}
head1 = head1->next;
head2 = head2->next;
}
printf("无公共节点!\n");
return;
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 1,2,7,9,13 };
int b[10] = { 3,4,6,8,9,11,15,19,9,2 };
int c[5] = { 20,21,22,23,24 };
pNode head1, head2, tail1, tail2;
head1 = head2 = tail1 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head1, &tail1, a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0;i < 10;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head2, &tail2, b[i]);
}
findcommon(head1, head2, 5, 10);
pNode head3, tail3;
head3 = tail3 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head3, &tail3, c[i]);
}
tail1->next = head3;
tail2->next = head3;
findcommon(head1, head2, 10, 15);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void DeleteCommon(pNode *head) {
pNode pCur, pPre, pFree;
pPre = *head;
pCur = (*head)->next;
while (pCur) {
if (pCur->val == pPre->val) {
pFree = pCur;
pPre->next = pCur->next;
pCur = pCur->next;
free(pFree);
}
else {
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
}
}
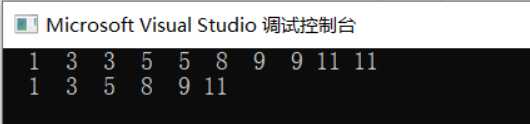
int main() {
int a[10] = { 1,3,3,5,5,8,9,9,11,11 };
pNode head, tail;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
DeleteCommon(&head);
listPrint(head);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node
{
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void InsertTail(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val) {
pNode newNode = (char*)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void partition(pNode head, pNode *head1, pNode *tail1, pNode *head2, pNode *tail2) {
while (head) {
int t = head->val;
if (t % 2 == 1) {
InsertTail(head1, tail1, t);
}
else {
InsertTail(head2, tail2, t);
}
head = head->next;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head) {
while (head) {
printf("%-3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int a[9] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
pNode head, tail, head1, tail1, head2, tail2;
head = tail = head1 = tail1 = head2 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 9;++i) {
InsertTail(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
partition(head, &head1, &tail1, &head2, &tail2);
listPrint(head1);
listPrint(head2);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 10
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType c;
struct node *pleft;
struct node *pright;
}Node, *pNode;
void preOrder(pNode p)
{
if (p)
{
putchar(p->c);
preOrder(p->pleft);
preOrder(p->pright);
}
}
int main() {
ElemType c[N + 1] = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
int i, j;
pNode p[N]; //结构体指针数组
pNode root;
for (i = 0;i < N;++i) {
p[i] = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
p[i]->c = c[i];
}
root = p[0];
j = 0;
for (i = 1;i < N;++i) {
if (NULL == p[j]->pleft) {
p[j]->pleft = p[i];
}
else if (NULL == p[j]->pright) {
p[j]->pright = p[i];
j++;
}
}
preOrder(root);
return 0;
}#include<stdio.h>
#define N 10
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType c;
struct node *pleft;
struct node *pright;
}Node, *pNode;
typedef struct queue {
pNode p; //指向树中某个节点
struct queue *next;
}Queue, *pQueue;
void preOrder(pNode p)
{
if (p)
{
putchar(p->c);
preOrder(p->pleft);
preOrder(p->pright);
}
}
int main() {
ElemType c;
pQueue queueHead = NULL, queueTail = NULL, newQueueNode, QueueFree;
pNode root = NULL, newTreeNode;
while (scanf("%c", &c) != EOF) {
if (c == '\n') break;
newTreeNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newTreeNode->c = c;
newQueueNode = (pQueue)calloc(1, sizeof(Queue));
newQueueNode->p = newTreeNode;
if (!root) {
root = newTreeNode;
queueHead = queueTail = newQueueNode;
}
else {
if (NULL == queueHead->p->pleft) {
queueHead->p->pleft = newTreeNode;
}
else if (NULL == queueHead->p->pright) {
queueHead->p->pright = newTreeNode;
QueueFree = queueHead;
queueHead = queueHead->next;
free(QueueFree);
}
//尾插法
queueTail->next = newQueueNode; //指向新节点
queueTail = newQueueNode; //更新队列尾
}
}
preOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
标签:scanf null union 有序 .com mem scan tree pst
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10665177.html