标签:++ std char s 初始 state nbsp char 时间片 class
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#define N 6
struct PCB
{
int pid; // 进程标识符
int rr; // 已运行时间
int time; // 进程要求运行时间
char state; // 进程的状态
struct PCB * next; // 链接指针
};
struct PCB pcb[N];
struct PCB *tail, *head, *rp;
void init()
{
int time;
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++ i)
{
pcb[i].pid = i;
pcb[i].rr = 0;
pcb[i].state = ‘w‘;
printf("请输入进程p%d需要运行的时间:", i);
scanf("%d", &pcb[i].time);
}
pcb[1].next = &pcb[2];
pcb[2].next = &pcb[3];
pcb[3].next = &pcb[4];
pcb[4].next = &pcb[5];
pcb[5].next = &pcb[1];
head = &pcb[1];
tail = &pcb[5];
}
// 显示表头
void print1()
{
printf("+---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------+\n");
printf("|\tpid\t|\trr\t|\ttime\t|\tSTATE\t|\n");
printf("|---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|\n");
}
// 显示各个进程的初始状态
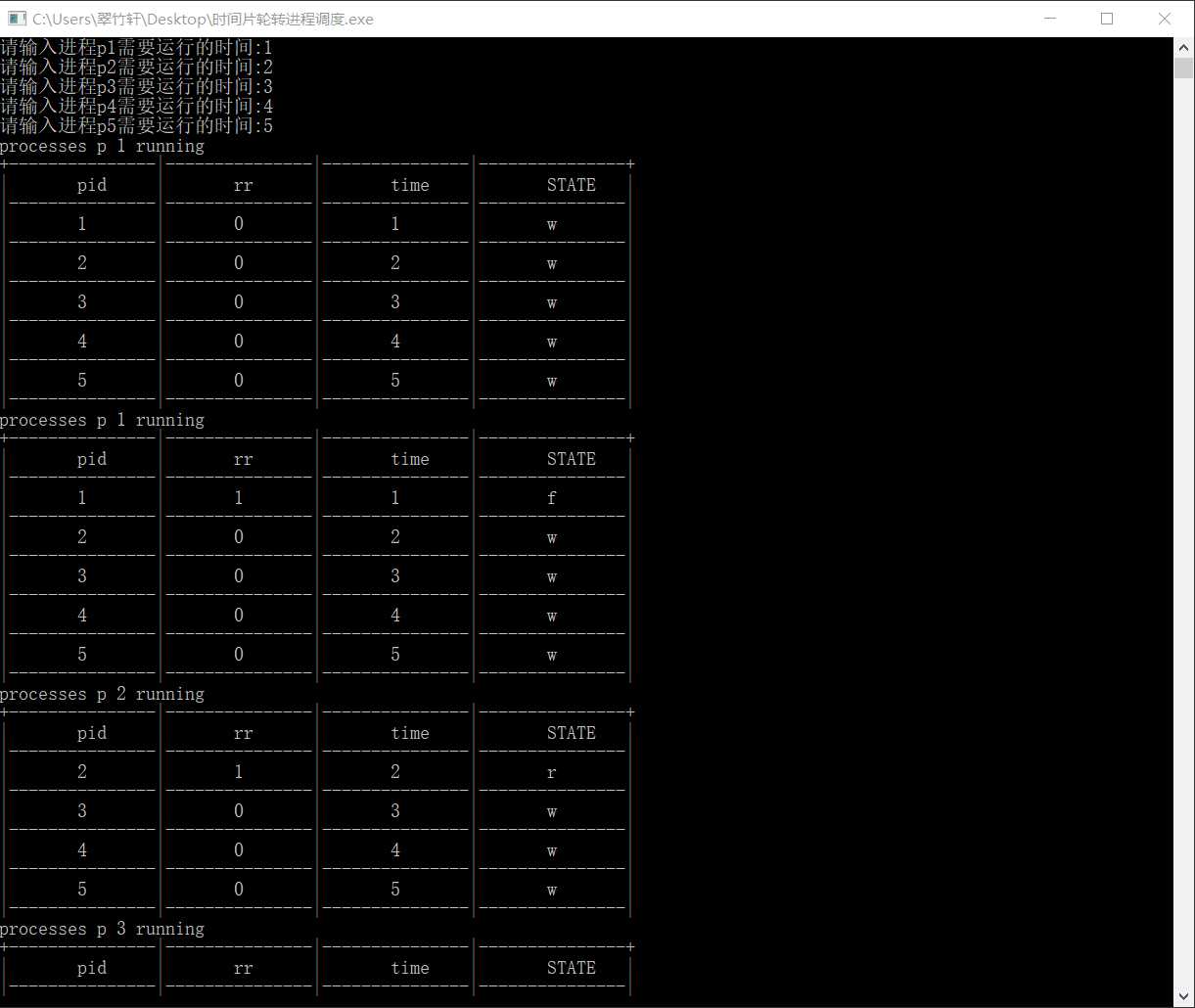
void print2()
{
printf("processes p %d running\n", head->pid);
print1();
printf("|\t%d\t|\t%d\t|\t%d\t|\t%c\t|\n", head->pid, head->rr, head->time, head->state);
printf("|---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|\n");
rp = head;
while(rp != tail)
{
rp = rp->next;
printf("|\t%d\t|\t%d\t|\t%d\t|\t%c\t|\n", rp->pid, rp->rr, rp->time, rp->state);
printf("|---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|\n");
}
}
// 运行
void operation()
{
int flag = 1;
while(flag <= 5)
{
head->rr ++;
if((head->rr == head->time) || (head->time == 0))
{
tail->state = ‘w‘; // 将进程状态设置为等待态
head->state = ‘f‘; // 将进程状态设置为终止态
print2();
head = head->next;
tail->next = head;
flag ++;
}
else
{
tail->state = ‘w‘; // 将进程状态设置为等待态
head->state = ‘r‘; // 将进程状态设置为运行态
print2();
tail = head;
head = head->next;
}
}
}
int main()
{
init();
print2();
operation();
return 0;
}
标签:++ std char s 初始 state nbsp char 时间片 class
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mjn1/p/10710326.html