标签:label lock eva xtend iss when result 入职 padding
输入验证是Spring处理的最重要Web开发任务之一。在Spring MVC中,有两种方式可以验证输入,即利用Spring自带的验证框架,或者利用JSR 303实现。本篇博客将介绍这两种输入验证方法。
本篇博客用两个不同的示例分别介绍这两种方式:spring-validator和jsr303-validator。
Converter和Formatter作用于字段级。在MVC Web应用中,它们将String类型转换或格式化成另一种Java类型,如java.time.LocalDate。验证器则作用于对象级。它决定某一个对象中的所有字段是否均是有效的,以及是否遵循某些规则。一个典型的Spring MVC应用会同时应用到Formatter(或Converter)和Validator。
如果一个应用程序既使用了Formatter,又有了Validator,那么,应用中的事件顺序是这样的:在调用Controller的请求处理方式时,将会有一个或者多个Formatter,试图将输入字符串转换成domain对象中的属性(或者说字段)值,一旦格式化成功,验证器就会介入。
例如:Order对象有一个shippingDate属性(其类型为LocalDate),它的值绝对不可能早于今天的日期。当调用OrderController时,LocalDateFormatter会将字符串转换成LocalDate,并将它赋予Order对象的shippingDate属性。如果转换失败,用户就会被转回到前一个表单;如果转换成功,则会调用验证器,查看shippingDate是否早于今天的日期。
现在,你或许会问,将验证逻辑转移到LocalDateFormatter中是否更加明智?
因为比较一下日期并非难事,但答案却是肯定的。首先,LocalDateFormatter还可以用于将其它字符串格式化成日期,如birthDate或者purchaseDate。这两个日期的规则都不同于shippingDate,事实上,比如,员工的出生日期绝对不可能晚于今日。
其次,校验器可以检查两个或更多字段之间的关系,各字段均受不同的Formatter支持。例如,假设Employee对象有birthDate属性和startDate属性,验证器就可以设定规则,使任何员工的入职日期均不可能早于他的出生日期。因此,有效的Employee对象必须让它的birthDate属性值早于其startDate值,这就是验证器的任务。
从一开始,Spring就设计了输入验证,甚至早于JSR 303(Java验证规范)。因此,Spring的Validation框架至今都很普遍,对于新项目,一般建议使用JSR 303验证器。
为了创建Spring验证器,要实现org.springframework.validation.Validator接口,这个接口的源码如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.validation; /** * A validator for application-specific objects. * * <p>This interface is totally divorced from any infrastructure * or context; that is to say it is not coupled to validating * only objects in the web tier, the data-access tier, or the * whatever-tier. As such it is amenable to being used in any layer * of an application, and supports the encapsulation of validation * logic as a first-class citizen in its own right. * * <p>Find below a simple but complete {@code Validator} * implementation, which validates that the various {@link String} * properties of a {@code UserLogin} instance are not empty * (that is they are not {@code null} and do not consist * wholly of whitespace), and that any password that is present is * at least {@code ‘MINIMUM_PASSWORD_LENGTH‘} characters in length. * * <pre class="code"> public class UserLoginValidator implements Validator { * * private static final int MINIMUM_PASSWORD_LENGTH = 6; * * public boolean supports(Class clazz) { * return UserLogin.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz); * } * * public void validate(Object target, Errors errors) { * ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "userName", "field.required"); * ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "password", "field.required"); * UserLogin login = (UserLogin) target; * if (login.getPassword() != null * && login.getPassword().trim().length() < MINIMUM_PASSWORD_LENGTH) { * errors.rejectValue("password", "field.min.length", * new Object[]{Integer.valueOf(MINIMUM_PASSWORD_LENGTH)}, * "The password must be at least [" + MINIMUM_PASSWORD_LENGTH + "] characters in length."); * } * } * }</pre> * * <p>See also the Spring reference manual for a fuller discussion of * the {@code Validator} interface and its role in an enterprise * application. * * @author Rod Johnson * @see SmartValidator * @see Errors * @see ValidationUtils */ public interface Validator { /** * Can this {@link Validator} {@link #validate(Object, Errors) validate} * instances of the supplied {@code clazz}? * <p>This method is <i>typically</i> implemented like so: * <pre class="code">return Foo.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);</pre> * (Where {@code Foo} is the class (or superclass) of the actual * object instance that is to be {@link #validate(Object, Errors) validated}.) * @param clazz the {@link Class} that this {@link Validator} is * being asked if it can {@link #validate(Object, Errors) validate} * @return {@code true} if this {@link Validator} can indeed * {@link #validate(Object, Errors) validate} instances of the * supplied {@code clazz} */ boolean supports(Class<?> clazz); /** * Validate the supplied {@code target} object, which must be * of a {@link Class} for which the {@link #supports(Class)} method * typically has (or would) return {@code true}. * <p>The supplied {@link Errors errors} instance can be used to report * any resulting validation errors. * @param target the object that is to be validated * @param errors contextual state about the validation process * @see ValidationUtils */ void validate(Object target, Errors errors); }
这个接口需要实现两个方法:supports()和validate()。
如果验证器可以处理指定的Class,supports()方法将返回true。只有当supports()方法的返回结果为true的时候,validate()方法才会被调用来验证目标对象,并将验证错误填入Errors对象。
Errors对象是org.springframework.validation.Errors接口的一个实现类。Errors接口的源代码如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.validation; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessor; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; /** * Stores and exposes information about data-binding and validation * errors for a specific object. * * <p>Field names can be properties of the target object (e.g. "name" * when binding to a customer object), or nested fields in case of * subobjects (e.g. "address.street"). Supports subtree navigation * via {@link #setNestedPath(String)}: for example, an * {@code AddressValidator} validates "address", not being aware * that this is a subobject of customer. * * <p>Note: {@code Errors} objects are single-threaded. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @see #setNestedPath * @see BindException * @see DataBinder * @see ValidationUtils */ public interface Errors { /** * The separator between path elements in a nested path, * for example in "customer.name" or "customer.address.street". * <p>"." = same as the * {@link org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessor#NESTED_PROPERTY_SEPARATOR nested property separator} * in the beans package. */ String NESTED_PATH_SEPARATOR = PropertyAccessor.NESTED_PROPERTY_SEPARATOR; /** * Return the name of the bound root object. */ String getObjectName(); /** * Allow context to be changed so that standard validators can validate * subtrees. Reject calls prepend the given path to the field names. * <p>For example, an address validator could validate the subobject * "address" of a customer object. * @param nestedPath nested path within this object, * e.g. "address" (defaults to "", {@code null} is also acceptable). * Can end with a dot: both "address" and "address." are valid. */ void setNestedPath(String nestedPath); /** * Return the current nested path of this {@link Errors} object. * <p>Returns a nested path with a dot, i.e. "address.", for easy * building of concatenated paths. Default is an empty String. */ String getNestedPath(); /** * Push the given sub path onto the nested path stack. * <p>A {@link #popNestedPath()} call will reset the original * nested path before the corresponding * {@code pushNestedPath(String)} call. * <p>Using the nested path stack allows to set temporary nested paths * for subobjects without having to worry about a temporary path holder. * <p>For example: current path "spouse.", pushNestedPath("child") -> * result path "spouse.child."; popNestedPath() -> "spouse." again. * @param subPath the sub path to push onto the nested path stack * @see #popNestedPath */ void pushNestedPath(String subPath); /** * Pop the former nested path from the nested path stack. * @throws IllegalStateException if there is no former nested path on the stack * @see #pushNestedPath */ void popNestedPath() throws IllegalStateException; /** * Register a global error for the entire target object, * using the given error description. * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as a message key */ void reject(String errorCode); /** * Register a global error for the entire target object, * using the given error description. * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as a message key * @param defaultMessage fallback default message */ void reject(String errorCode, String defaultMessage); /** * Register a global error for the entire target object, * using the given error description. * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as a message key * @param errorArgs error arguments, for argument binding via MessageFormat * (can be {@code null}) * @param defaultMessage fallback default message */ void reject(String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage); /** * Register a field error for the specified field of the current object * (respecting the current nested path, if any), using the given error * description. * <p>The field name may be {@code null} or empty String to indicate * the current object itself rather than a field of it. This may result * in a corresponding field error within the nested object graph or a * global error if the current object is the top object. * @param field the field name (may be {@code null} or empty String) * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as a message key * @see #getNestedPath() */ void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode); /** * Register a field error for the specified field of the current object * (respecting the current nested path, if any), using the given error * description. * <p>The field name may be {@code null} or empty String to indicate * the current object itself rather than a field of it. This may result * in a corresponding field error within the nested object graph or a * global error if the current object is the top object. * @param field the field name (may be {@code null} or empty String) * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as a message key * @param defaultMessage fallback default message * @see #getNestedPath() */ void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage); /** * Register a field error for the specified field of the current object * (respecting the current nested path, if any), using the given error * description. * <p>The field name may be {@code null} or empty String to indicate * the current object itself rather than a field of it. This may result * in a corresponding field error within the nested object graph or a * global error if the current object is the top object. * @param field the field name (may be {@code null} or empty String) * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as a message key * @param errorArgs error arguments, for argument binding via MessageFormat * (can be {@code null}) * @param defaultMessage fallback default message * @see #getNestedPath() */ void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage); /** * Add all errors from the given {@code Errors} instance to this * {@code Errors} instance. * <p>This is a convenience method to avoid repeated {@code reject(..)} * calls for merging an {@code Errors} instance into another * {@code Errors} instance. * <p>Note that the passed-in {@code Errors} instance is supposed * to refer to the same target object, or at least contain compatible errors * that apply to the target object of this {@code Errors} instance. * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to merge in */ void addAllErrors(Errors errors); /** * Return if there were any errors. */ boolean hasErrors(); /** * Return the total number of errors. */ int getErrorCount(); /** * Get all errors, both global and field ones. * @return a list of {@link ObjectError} instances */ List<ObjectError> getAllErrors(); /** * Are there any global errors? * @return {@code true} if there are any global errors * @see #hasFieldErrors() */ boolean hasGlobalErrors(); /** * Return the number of global errors. * @return the number of global errors * @see #getFieldErrorCount() */ int getGlobalErrorCount(); /** * Get all global errors. * @return a list of {@link ObjectError} instances */ List<ObjectError> getGlobalErrors(); /** * Get the <i>first</i> global error, if any. * @return the global error, or {@code null} */ @Nullable ObjectError getGlobalError(); /** * Are there any field errors? * @return {@code true} if there are any errors associated with a field * @see #hasGlobalErrors() */ boolean hasFieldErrors(); /** * Return the number of errors associated with a field. * @return the number of errors associated with a field * @see #getGlobalErrorCount() */ int getFieldErrorCount(); /** * Get all errors associated with a field. * @return a List of {@link FieldError} instances */ List<FieldError> getFieldErrors(); /** * Get the <i>first</i> error associated with a field, if any. * @return the field-specific error, or {@code null} */ @Nullable FieldError getFieldError(); /** * Are there any errors associated with the given field? * @param field the field name * @return {@code true} if there were any errors associated with the given field */ boolean hasFieldErrors(String field); /** * Return the number of errors associated with the given field. * @param field the field name * @return the number of errors associated with the given field */ int getFieldErrorCount(String field); /** * Get all errors associated with the given field. * <p>Implementations should support not only full field names like * "name" but also pattern matches like "na*" or "address.*". * @param field the field name * @return a List of {@link FieldError} instances */ List<FieldError> getFieldErrors(String field); /** * Get the first error associated with the given field, if any. * @param field the field name * @return the field-specific error, or {@code null} */ @Nullable FieldError getFieldError(String field); /** * Return the current value of the given field, either the current * bean property value or a rejected update from the last binding. * <p>Allows for convenient access to user-specified field values, * even if there were type mismatches. * @param field the field name * @return the current value of the given field */ @Nullable Object getFieldValue(String field); /** * Return the type of a given field. * <p>Implementations should be able to determine the type even * when the field value is {@code null}, for example from some * associated descriptor. * @param field the field name * @return the type of the field, or {@code null} if not determinable */ @Nullable Class<?> getFieldType(String field); }
Errors对象中包含了一个FieldError类型的集合和一个ObjectError类型的集合:
FieldError类的源码如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.validation; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils; /** * Encapsulates a field error, that is, a reason for rejecting a specific * field value. * * <p>See the {@link DefaultMessageCodesResolver} javadoc for details on * how a message code list is built for a {@code FieldError}. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 10.03.2003 * @see DefaultMessageCodesResolver */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class FieldError extends ObjectError { private final String field; @Nullable private final Object rejectedValue; private final boolean bindingFailure; /** * Create a new FieldError instance. * @param objectName the name of the affected object * @param field the affected field of the object * @param defaultMessage the default message to be used to resolve this message */ public FieldError(String objectName, String field, String defaultMessage) { this(objectName, field, null, false, null, null, defaultMessage); } /** * Create a new FieldError instance. * @param objectName the name of the affected object * @param field the affected field of the object * @param rejectedValue the rejected field value * @param bindingFailure whether this error represents a binding failure * (like a type mismatch); else, it is a validation failure * @param codes the codes to be used to resolve this message * @param arguments the array of arguments to be used to resolve this message * @param defaultMessage the default message to be used to resolve this message */ public FieldError(String objectName, String field, @Nullable Object rejectedValue, boolean bindingFailure, @Nullable String[] codes, @Nullable Object[] arguments, @Nullable String defaultMessage) { super(objectName, codes, arguments, defaultMessage); Assert.notNull(field, "Field must not be null"); this.field = field; this.rejectedValue = rejectedValue; this.bindingFailure = bindingFailure; } /** * Return the affected field of the object. */ public String getField() { return this.field; } /** * Return the rejected field value. */ @Nullable public Object getRejectedValue() { return this.rejectedValue; } /** * Return whether this error represents a binding failure * (like a type mismatch); otherwise it is a validation failure. */ public boolean isBindingFailure() { return this.bindingFailure; } @Override public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) { if (this == other) { return true; } if (!super.equals(other)) { return false; } FieldError otherError = (FieldError) other; return (getField().equals(otherError.getField()) && ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(getRejectedValue(), otherError.getRejectedValue()) && isBindingFailure() == otherError.isBindingFailure()); } @Override public int hashCode() { int hashCode = super.hashCode(); hashCode = 29 * hashCode + getField().hashCode(); hashCode = 29 * hashCode + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(getRejectedValue()); hashCode = 29 * hashCode + (isBindingFailure() ? 1 : 0); return hashCode; } @Override public String toString() { return "Field error in object ‘" + getObjectName() + "‘ on field ‘" + this.field + "‘: rejected value [" + ObjectUtils.nullSafeToString(this.rejectedValue) + "]; " + resolvableToString(); } }
ObjectError类的源码如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.validation; import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * Encapsulates an object error, that is, a global reason for rejecting * an object. * * <p>See the {@link DefaultMessageCodesResolver} javadoc for details on * how a message code list is built for an {@code ObjectError}. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 10.03.2003 * @see FieldError * @see DefaultMessageCodesResolver */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class ObjectError extends DefaultMessageSourceResolvable { private final String objectName; @Nullable private transient Object source; /** * Create a new instance of the ObjectError class. * @param objectName the name of the affected object * @param defaultMessage the default message to be used to resolve this message */ public ObjectError(String objectName, String defaultMessage) { this(objectName, null, null, defaultMessage); } /** * Create a new instance of the ObjectError class. * @param objectName the name of the affected object * @param codes the codes to be used to resolve this message * @param arguments the array of arguments to be used to resolve this message * @param defaultMessage the default message to be used to resolve this message */ public ObjectError( String objectName, @Nullable String[] codes, @Nullable Object[] arguments, @Nullable String defaultMessage) { super(codes, arguments, defaultMessage); Assert.notNull(objectName, "Object name must not be null"); this.objectName = objectName; } /** * Return the name of the affected object. */ public String getObjectName() { return this.objectName; } /** * Preserve the source behind this error: possibly an {@link Exception} * (typically {@link org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessException}) * or a Bean Validation {@link javax.validation.ConstraintViolation}. * <p>Note that any such source object is being stored as transient: * that is, it won‘t be part of a serialized error representation. * @param source the source object * @since 5.0.4 */ public void wrap(Object source) { if (this.source != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Already wrapping " + this.source); } this.source = source; } /** * Unwrap the source behind this error: possibly an {@link Exception} * (typically {@link org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessException}) * or a Bean Validation {@link javax.validation.ConstraintViolation}. * <p>The cause of the outermost exception will be introspected as well, * e.g. the underlying conversion exception or exception thrown from a setter * (instead of having to unwrap the {@code PropertyAccessException} in turn). * @return the source object of the given type * @throws IllegalArgumentException if no such source object is available * (i.e. none specified or not available anymore after deserialization) * @since 5.0.4 */ public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> sourceType) { if (sourceType.isInstance(this.source)) { return sourceType.cast(this.source); } else if (this.source instanceof Throwable) { Throwable cause = ((Throwable) this.source).getCause(); if (sourceType.isInstance(cause)) { return sourceType.cast(cause); } } throw new IllegalArgumentException("No source object of the given type available: " + sourceType); } /** * Check the source behind this error: possibly an {@link Exception} * (typically {@link org.springframework.beans.PropertyAccessException}) * or a Bean Validation {@link javax.validation.ConstraintViolation}. * <p>The cause of the outermost exception will be introspected as well, * e.g. the underlying conversion exception or exception thrown from a setter * (instead of having to unwrap the {@code PropertyAccessException} in turn). * @return whether this error has been caused by a source object of the given type * @since 5.0.4 */ public boolean contains(Class<?> sourceType) { return (sourceType.isInstance(this.source) || (this.source instanceof Throwable && sourceType.isInstance(((Throwable) this.source).getCause()))); } @Override public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) { if (this == other) { return true; } if (other == null || other.getClass() != getClass() || !super.equals(other)) { return false; } ObjectError otherError = (ObjectError) other; return getObjectName().equals(otherError.getObjectName()); } @Override public int hashCode() { return super.hashCode() * 29 + getObjectName().hashCode(); } @Override public String toString() { return "Error in object ‘" + this.objectName + "‘: " + resolvableToString(); } }
编写验证器时,不需要直接创建Error对象,并且实例化FieldError和ObjectError花费了大量的编程精力。这是因为ObjectError类有两个构造函数,其中一个需要2个参数,另一个需要4个参数:FieldError类的构造器也有2个,其中一个需要3个参数,另一个需要7个参数。
但是我们可以通过调用rejectValue()方法向Errors对象中添加被验证对象的字段错误信息,该方法实际上是创建一个FieldError对象,并添加Errors该对象的List<FieldError>集合中。
通过调用reject()方法向Errors对象中添加被验证对象错误信息,该方法实际上是创建一个ObjectError对象,并添加到Errors对象的List<ObjectError>中。
下面是reject()和rejectValue的部分方法重载:
void reject(String errorCode); void reject(String errorCode, String defaultMessage); void reject(String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage); void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode); void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage); void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage);
大多数时候,只给reject()或者rejectValue()方法传入一个错误码,Spring就会在属性文件中查找错误码,获取相应的错误消息。还可以传入一个默认消息,当没有找到指定的错误码时,就会使用默认消息。
Errors对象中的错误消息,可以利用表单标签库的Errors标签显示在HTML页面中,错误消息可以通过Spring支持的国际化特性本地化。
org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils类是一个工具,源码如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.validation; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * Utility class offering convenient methods for invoking a {@link Validator} * and for rejecting empty fields. * * <p>Checks for an empty field in {@code Validator} implementations can become * one-liners when using {@link #rejectIfEmpty} or {@link #rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace}. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Dmitriy Kopylenko * @since 06.05.2003 * @see Validator * @see Errors */ public abstract class ValidationUtils { private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ValidationUtils.class); /** * Invoke the given {@link Validator} for the supplied object and * {@link Errors} instance. * @param validator the {@code Validator} to be invoked * @param target the object to bind the parameters to * @param errors the {@link Errors} instance that should store the errors * @throws IllegalArgumentException if either of the {@code Validator} or {@code Errors} * arguments is {@code null}, or if the supplied {@code Validator} does not * {@link Validator#supports(Class) support} the validation of the supplied object‘s type */ public static void invokeValidator(Validator validator, Object target, Errors errors) { invokeValidator(validator, target, errors, (Object[]) null); } /** * Invoke the given {@link Validator}/{@link SmartValidator} for the supplied object and * {@link Errors} instance. * @param validator the {@code Validator} to be invoked * @param target the object to bind the parameters to * @param errors the {@link Errors} instance that should store the errors * @param validationHints one or more hint objects to be passed to the validation engine * @throws IllegalArgumentException if either of the {@code Validator} or {@code Errors} * arguments is {@code null}, or if the supplied {@code Validator} does not * {@link Validator#supports(Class) support} the validation of the supplied object‘s type */ public static void invokeValidator( Validator validator, Object target, Errors errors, @Nullable Object... validationHints) { Assert.notNull(validator, "Validator must not be null"); Assert.notNull(target, "Target object must not be null"); Assert.notNull(errors, "Errors object must not be null"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking validator [" + validator + "]"); } if (!validator.supports(target.getClass())) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Validator [" + validator.getClass() + "] does not support [" + target.getClass() + "]"); } if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(validationHints) && validator instanceof SmartValidator) { ((SmartValidator) validator).validate(target, errors, validationHints); } else { validator.validate(target, errors); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (errors.hasErrors()) { logger.debug("Validator found " + errors.getErrorCount() + " errors"); } else { logger.debug("Validator found no errors"); } } } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code if the value is empty. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null} or * the empty string "". * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key */ public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode) { rejectIfEmpty(errors, field, errorCode, null, null); } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code and default message * if the value is empty. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null} or * the empty string "". * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode error code, interpretable as message key * @param defaultMessage fallback default message */ public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage) { rejectIfEmpty(errors, field, errorCode, null, defaultMessage); } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code and error arguments * if the value is empty. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null} or * the empty string "". * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key * @param errorArgs the error arguments, for argument binding via MessageFormat * (can be {@code null}) */ public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, Object[] errorArgs) { rejectIfEmpty(errors, field, errorCode, errorArgs, null); } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code, error arguments * and default message if the value is empty. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null} or * the empty string "". * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key * @param errorArgs the error arguments, for argument binding via MessageFormat * (can be {@code null}) * @param defaultMessage fallback default message */ public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage) { Assert.notNull(errors, "Errors object must not be null"); Object value = errors.getFieldValue(field); if (value == null || !StringUtils.hasLength(value.toString())) { errors.rejectValue(field, errorCode, errorArgs, defaultMessage); } } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code if the value is empty * or just contains whitespace. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null}, * the empty string "", or consisting wholly of whitespace. * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key */ public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode) { rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, field, errorCode, null, null); } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code and default message * if the value is empty or just contains whitespace. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null}, * the empty string "", or consisting wholly of whitespace. * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key * @param defaultMessage fallback default message */ public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace( Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage) { rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, field, errorCode, null, defaultMessage); } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code and error arguments * if the value is empty or just contains whitespace. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null}, * the empty string "", or consisting wholly of whitespace. * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key * @param errorArgs the error arguments, for argument binding via MessageFormat * (can be {@code null}) */ public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace( Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs) { rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, field, errorCode, errorArgs, null); } /** * Reject the given field with the given error code, error arguments * and default message if the value is empty or just contains whitespace. * <p>An ‘empty‘ value in this context means either {@code null}, * the empty string "", or consisting wholly of whitespace. * <p>The object whose field is being validated does not need to be passed * in because the {@link Errors} instance can resolve field values by itself * (it will usually hold an internal reference to the target object). * @param errors the {@code Errors} instance to register errors on * @param field the field name to check * @param errorCode the error code, interpretable as message key * @param errorArgs the error arguments, for argument binding via MessageFormat * (can be {@code null}) * @param defaultMessage fallback default message */ public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace( Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage) { Assert.notNull(errors, "Errors object must not be null"); Object value = errors.getFieldValue(field); if (value == null ||!StringUtils.hasText(value.toString())) { errors.rejectValue(field, errorCode, errorArgs, defaultMessage); } } }
ValidationUtils类有助于编写Spring验证器,比如检测一个name属性是否为null或者是“”字符串,不需要像下面这样编写:
if(name== null || name.isEmpty()){ errors.rejectValue("name","name.required"); }
而是可以利用类的rejectIfEmpty()方法,像下面这样:
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors,"name","name.required");
其中,"name"是属性名,"name.required"是错误代码。
或者下面这样的代码:
if(name== null || name.trim().isEmpty()){ errors.rejectValue("name","name.required"); }
可以编写成:
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace("name");
下面是ValidationUtils中rejectIfEmpty()和rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace()方法的方法重载:
public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode) { rejectIfEmpty(errors, field, errorCode, null, null); } public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage) { rejectIfEmpty(errors, field, errorCode, null, defaultMessage); } public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, Object[] errorArgs) { rejectIfEmpty(errors, field, errorCode, errorArgs, null); } public static void rejectIfEmpty(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage) { Assert.notNull(errors, "Errors object must not be null"); Object value = errors.getFieldValue(field); if (value == null || !StringUtils.hasLength(value.toString())) { errors.rejectValue(field, errorCode, errorArgs, defaultMessage); } } public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(Errors errors, String field, String errorCode) { rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, field, errorCode, null, null); } public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace( Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage) { rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, field, errorCode, null, defaultMessage); } public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace( Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs) { rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, field, errorCode, errorArgs, null); } public static void rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace( Errors errors, String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage) { Assert.notNull(errors, "Errors object must not be null"); Object value = errors.getFieldValue(field); if (value == null ||!StringUtils.hasText(value.toString())) { errors.rejectValue(field, errorCode, errorArgs, defaultMessage); } }
此外,ValidationUtils还有一个invokeValidator()方法,用来代用验证器:
public static void invokeValidator( Validator validator, Object target, Errors errors, @Nullable Object... validationHints) { Assert.notNull(validator, "Validator must not be null"); Assert.notNull(target, "Target object must not be null"); Assert.notNull(errors, "Errors object must not be null"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking validator [" + validator + "]"); } if (!validator.supports(target.getClass())) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Validator [" + validator.getClass() + "] does not support [" + target.getClass() + "]"); } if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(validationHints) && validator instanceof SmartValidator) { ((SmartValidator) validator).validate(target, errors, validationHints); } else { validator.validate(target, errors); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (errors.hasErrors()) { logger.debug("Validator found " + errors.getErrorCount() + " errors"); } else { logger.debug("Validator found no errors"); } } }
接下来将通过范例来介绍如何使用这个工具。
本节将会创建一个spring-validator应用,该应用包含一个名为ProductValidator的验证器,用于验证Product对象。
package domain; import java.io.Serializable; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.time.LocalDate; public class Product implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String name; private String description; private BigDecimal price; private LocalDate productionDate; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public BigDecimal getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) { this.price = price; } public LocalDate getProductionDate() { return productionDate; } public void setProductionDate(LocalDate productionDate) { this.productionDate = productionDate; } }
为了使ProductForm.jsp页面中表单输入的日期可以使用不同于当前语言区域的日期样式,,我们创建了一个LocalDateFormatter 类:
package formatter; import java.text.ParseException; import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import java.time.format.DateTimeParseException; import java.util.Locale; import org.springframework.format.Formatter; public class LocalDateFormatter implements Formatter<LocalDate> { private DateTimeFormatter formatter; private String datePattern; // 设定日期样式 public LocalDateFormatter(String datePattern) { this.datePattern = datePattern; formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(datePattern); } //利用指定的Locale将一个LocalDate解析成String类型 @Override public String print(LocalDate date, Locale locale) { return date.format(formatter); } //利用指定的Locale将一个String解析成LocalDate类型 @Override public LocalDate parse(String s, Locale locale) throws ParseException { try { //使用指定的formatter从字符串中获取一个LocalDate对象 如果字符串不符合formatter指定的样式要求,转换会失败 return LocalDate.parse(s, DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(datePattern)); } catch (DateTimeParseException e) { // the error message will be displayed in <form:errors> throw new IllegalArgumentException( "invalid date format. Please use this pattern\"" + datePattern + "\""); } } }
LocalDateFormatter 类的parse()方法,它利用传给构造器的日期样式,将一个String转换成LocalDate。
如果输入的日期格式有问题,将会抛出IllegalArgumentException异常,这表明以下代码中input标签绑定到表单支持对象的birthDate属性出现错误:
<p> <label for="productionDate">*Production Date (MM-dd-yyyy): </label> <form:input id="productionDate" path="productionDate" tabindex="4"/> </p>
在/save-product页面对应的请求处理方法saveEmployee()中,bindingResult参数将会记录到这个绑定错误,即类型转换错误。
该应用包含一个名为ProductValidator的验证器:
package validator; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.time.LocalDate; import org.springframework.validation.Errors; import org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils; import org.springframework.validation.Validator; import domain.Product; public class ProductValidator implements Validator { @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> klass) { //支持Product类? return Product.class.isAssignableFrom(klass); } //将目标对象target的错误注册到errors对象中 @Override public void validate(Object target, Errors errors) { //强制类型转换 Product product = (Product) target; //如果目标对象的name属性为null,或者为""字符串,则将错误注册到errors对象 ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors, "name", "productName.required"); //如果目标对象的price属性为null,或者为""字符串,则将错误注册到errors对象中 ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors, "price", "price.required"); //如果目标对象的productionDate属性为null,或者为""字符串,则将错误注册到errors对象中 ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors, "productionDate", "productionDate.required"); BigDecimal price = product.getPrice(); //如果价格为负数 则将错误注册到errors对象中 if (price != null && price.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) < 0) { errors.rejectValue("price", "price.negative"); } //如果产品日期在今天之后 则将错误注册到errors对象中 LocalDate productionDate = product.getProductionDate(); if (productionDate != null) { if (productionDate.isAfter(LocalDate.now())) { errors.rejectValue("productionDate", "productionDate.invalid"); } } } }
ProductValidator验证器是一个非常简单的验证器。它的validate()方法会检验Product是否有名称和价格,并且价格是否不为负数,它还会确保生产日期不晚于今天。
在Controller类中通过实例化validator类,可以使用Spring验证器。
package controller; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult; import org.springframework.validation.FieldError; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import domain.Product; import validator.ProductValidator; @Controller public class ProductController { private static final Log logger = LogFactory .getLog(ProductController.class); @RequestMapping(value = "/add-product") public String inputProduct(Model model) { model.addAttribute("product", new Product()); return "ProductForm"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/save-product") public String saveProduct(@ModelAttribute Product product, BindingResult bindingResult, Model model) { ProductValidator productValidator = new ProductValidator(); productValidator.validate(product, bindingResult); if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) { FieldError fieldError = bindingResult.getFieldError(); logger.debug("Code:" + fieldError.getCode() + ", field:" + fieldError.getField()); return "ProductForm"; } // save product here //model.addAttribute("product", product); return "ProductDetails"; } }
ProductController类的saveProduct()方法,有三个参数:
注意:BindingResult接口是Errors接口的子类,在请求处理方法的签名中使用了BindingResult参数,就是告诉Spring关于表单对象数据校验的错误将由我们自己来处理,否则Spring会直接抛出异常。
该方法创建一个ProductValidator,并调用其validate()方法校验Product对象,并将验证错误填入bindingResult中。
ProductValidator productValidator = new ProductValidator(); productValidator.validate(product, bindingResult);
为了检验该验证器是否生成错误消息,需要在BindingResult中调用hasErrors()方法:
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) { FieldError fieldError = bindingResult.getFieldError(); logger.debug("Code:" + fieldError.getCode() + ", field:" + fieldError.getField()); return "ProductForm"; }
如果存在表单绑定错误或者是输入验证错误,将会打印出错误相关的字段,并重定位到ProductForm.jsp页面。
如果表单输入的数据均合法,则会重定位到ProductDetails.jsp页面。
使用Spring验证器的另一种方法是:在Controller中编写initBinder()方法,并将验证器传到WebDataBinder,并调用其validate()方法:
@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder){ //this will apply the Validator to all request-handling methods binder.setValidator(new ProductValidator)(); binder.validate(); }
将验证器传到WebDataBinder,会使该验证器应用于Controller类中的所有请求处理的方法。
或者利用@javax.validation.Valid对要验证的对象参数进行注解,例如:
public String saveProduct(@Valid @ModelAttribute Product product, BindingResult bindingResult, Model model) {
Valid注解类型是在JSR 303中定义的,关于JSR 303的相关西你想,后面介绍。
spring-validator应用包含三个视图文件:
ProductForm.jsp:
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <title>Add Product Form</title> <style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style> </head> <body> <div id="global"> <form:form modelAttribute="product" action="save-product" method="post"> <fieldset> <legend>Add a product</legend> <p class="errorLine"> <form:errors path="name" cssClass="error"/> </p> <p> <label for="name">*Product Name: </label> <form:input id="name" path="name" tabindex="1"/> </p> <p> <label for="description">Description: </label> <form:input id="description" path="description" tabindex="2"/> </p> <p class="errorLine"> <form:errors path="price" cssClass="error"/> </p> <p> <label for="price">*Price: </label> <form:input id="price" path="price" tabindex="3"/> </p> <p class="errorLine"> <form:errors path="productionDate" cssClass="error"/> </p> <p> <label for="productionDate">*Production Date (MM-dd-yyyy): </label> <form:input id="productionDate" path="productionDate" tabindex="4"/> </p> <p id="buttons"> <input id="reset" type="reset" tabindex="5"> <input id="submit" type="submit" tabindex="6" value="Add Product"> </p> </fieldset> </form:form> </div> </body> </html>
在ProductForm.jsp视图中我们使用到了表单标签,并且使用了errors标签。下面详细介绍errors的用途:
如果想要从某个属性文件中获取错误消息,则需要通过声明messageSource.bean。告诉Spring要去哪里查找这个文件。下面是springmvc-config.xml中的messageSource.bean:
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basename" value="/WEB-INF/resource/messages" /> </bean>
这个bean实际上是说,错误码和错误信息可以在/WEB-INF/resource/messages.properties文件中找到:
productName.required.product.name=Please enter a product name
price.required=Please enter a price
price.negative=Price cannot be less than 0
productionDate.required=Please enter a production date
productionDate.invalid=Please ensure the production date is not later than today
typeMismatch.productionDate=Invalid production date
每一行代表一个错误,格式为:
errorCode=defaultMessage
如果是验证错误(validator),错误码一般就是errors.rejectValue()方法中errorCode参数;如果是类型转换错误,错误码一般就是:typeMismatch.属性名。
ProductDetails.jsp:

<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <title>Save Product</title> <style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style> </head> <body> <div id="global"> <h4>The product has been saved.</h4> <p> <h5>Details:</h5> Product Name: ${product.name}<br/> Description: ${product.description}<br/> Price: $${product.price} </p> </div> </body> </html>
ProductView.jsp(没用到):

<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <title>View Product</title> <style type="text/css">@import url("<c:url value="/css/main.css"/>");</style> </head> <body> <div id="global"> <h4>${message}</h4> <p> <h5>Details:</h5> Product Name: ${product.name}<br/> Description: ${product.description}<br/> Price: $${product.price} </p> </div> </body> </html>
main.css:

#global { text-align: left; border: 1px solid #dedede; background: #efefef; width: 560px; padding: 20px; margin: 100px auto; } form { font:100% verdana; min-width: 500px; max-width: 600px; width: 560px; } form fieldset { border-color: #bdbebf; border-width: 3px; margin: 0; } legend { font-size: 1.3em; } form label { width: 250px; display: block; float: left; text-align: right; padding: 2px; } #buttons { text-align: right; } #errors, li { color: red; } .error { color: red; font-size: 9pt; } .errorLine { text-align: center; }
下面给出springmvc-config.xml文件的所有内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="controller" /> <context:component-scan base-package="formatter" /> <mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService" /> <mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/" /> <mvc:resources mapping="/*.html" location="/" /> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basename" value="/WEB-INF/resource/messages" /> </bean> <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean"> <property name="formatters"> <set> <bean class="formatter.LocalDateFormatter"> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="MM-dd-yyyy" /> </bean> </set> </property> </bean> </beans>
部署描述符(web.xml文件):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="3.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc-config.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
部署项目,并在浏览器输入:
http://localhost:8008/spring-validator/add-product
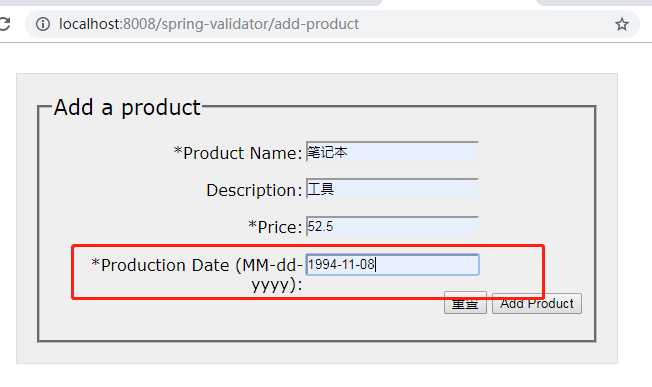
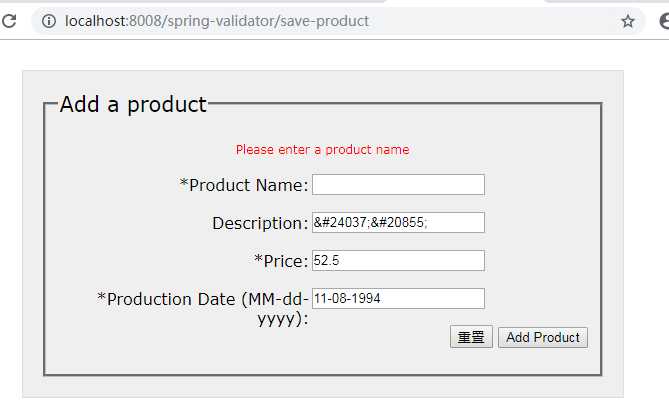
试着输入一个无效的日期,将会跳转到/save--product,但是表单内容不会丢失,并且会在表单中看到错误的消息:
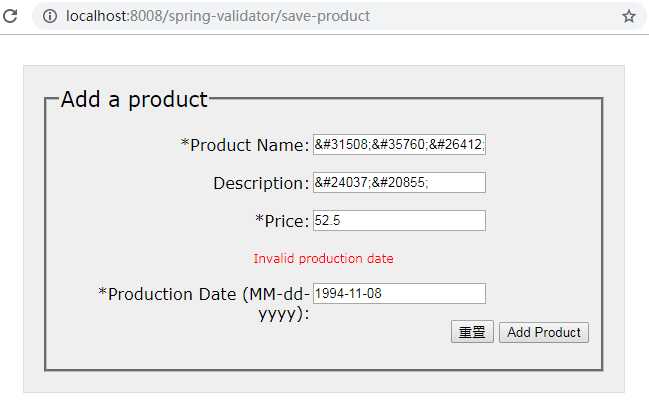
可以看到由于输入的日期没有按照MM-dd-yyyy的格式,所以将String转换LocalDate类型时,将会发生typeMismatch.productionDate错误,Errors标签将会将messages.properties中设置的errorCode对应的错误消息显示出来。
但是如果将Spring MVC配置文件中声明的messageSource bean删除,将会提示错误码typeMismatch.productionDate对应的默认系统错误消息。
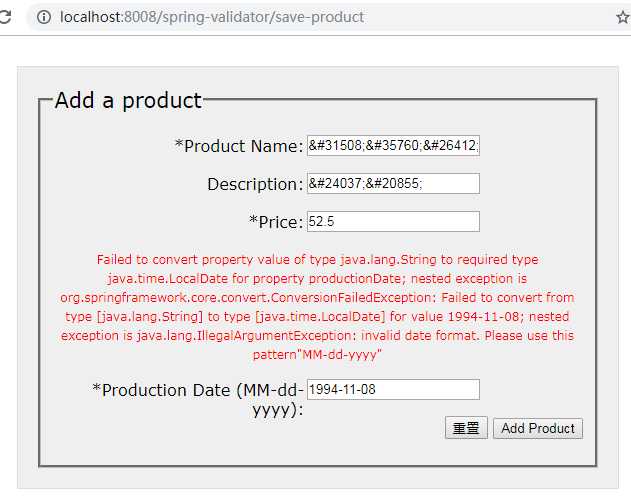
但是针对验证器中我们自己设定的errorCode,我们必须在messages.properties指定其对应的错误消息,并配置messageSource bean.
JSR 303 是 JAVA EE 6 中的一项子规范,叫做 Bean Validation。 JSR 303 用于对 Java Bean 中的字段的值进行验证。
当前,JSR只是一个规范文档,本身用处不大,除了编写了它的实现。用于实现JSR Bean Validation,目前有两个实现:
参考文章
[1]从源码分析java.lang.String.isEmpty()
[3]Spring MVC学习指南
标签:label lock eva xtend iss when result 入职 padding
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zyly/p/10842678.html