标签:linkage image add 开始 desc fas 需要 sed wiki
问题定义:给定数据$\vec{x}_1,\vec{x}_2,\cdots,\vec{x}_n$,将它们分到不同的$K$个簇(cluster)中。定义$\vec{c}=(c_1,c_2,\cdots,c_n),\text{ }c_i\in\{1,2,\cdots,K\}$,$c_i=k$表示$\vec{x}_i$被分到了第$k$个簇中。定义$\vec{\mu}_k$为第$k$个簇的中心(centroid),$k=1,2,\cdots,K$。K-means是一种基于距离的聚类算法,它的目标函数可以写为$$argmin_{\vec{c},\vec{\mu}_1,\cdots,\vec{\mu}_K}\sum\limits_{i=1}^n\sum\limits_{k=1}^KI(c_i=k)\lVert{\vec{x}_i-\vec{\mu}_k}\rVert_2^2$$
求解:使用坐标下降(Coordinate Descent)方法进行求解,将待求解的参数分为两个集合:$\vec{c}$以及$(\vec{\mu}_1,\cdots,\vec{\mu}_K)$。
由于目标函数是非凸的,因此最后的结果可能是局部最优值,实际应用时一般会运行多次上述求解过程(即对$(\vec{\mu}_1,\cdots,\vec{\mu}_K)$进行多次随机初始化),并选择使最终目标函数最小的那个结果。
DBSCAN是一种基于密度的聚类方法,它不需要预先指定簇的个数,但需要给定两个参数:MinPts以及eps,具体算法如下:

import numpy def MyDBSCAN(D, eps, MinPts): """ Cluster the dataset `D` using the DBSCAN algorithm. It will return a list of cluster labels. The label -1 means noise, and then the clusters are numbered starting from 1. """ labels = [0]*len(D) #Initially all labels are 0, 0 means the point hasn‘t been considered yet C = 0 #C is the ID of the current cluster. ### This outer loop is just responsible for picking new seed points--a point ### from which to grow a new cluster. for P in range(0, len(D)): if not (labels[P] == 0): continue NeighborPts = regionQuery(D, P, eps) #Find all of P‘s neighboring points. if len(NeighborPts) < MinPts: labels[P] = -1 else: C += 1 labels[P] = C #the label to our seed point. growCluster(D, labels, P, C, eps, MinPts) #Grow the cluster from the seed point. return labels def growCluster(D, labels, P, C, eps, MinPts): """ Grow a new cluster with label `C` from the seed point `P`. This function searches through the dataset to find all points that belong to this new cluster. When this function returns, cluster `C` is complete. """ ### SearchQueue is a FIFO queue of points to evaluate. It will only ever ### contain points which belong to cluster C SearchQueue = [P] i = 0 while i < len(SearchQueue): P = SearchQueue[i] NeighborPts = regionQuery(D, P, eps) #Find all the neighbors of P ### If the number of neighbors is below the minimum, then ### move to the next point in the queue. if len(NeighborPts) < MinPts: i += 1 continue ### Otherwise, For each of the neighbors... for Pn in NeighborPts: ### If Pn was labelled NOISE, claim it as part of cluster C if labels[Pn] == -1: labels[Pn] = C #Add Pn to cluster C ### Otherwise, if Pn hasn‘t been considered yet, claim it as part of ### C and add it to the search queue. elif labels[Pn] == 0: labels[Pn] = C #Add Pn to cluster C SearchQueue.append(Pn) #Add Pn to the SearchQueue i += 1 #Advance to the next point in the queue. return def regionQuery(D, P, eps): """ Find all points in dataset `D` within distance `eps` of point `P`. This function calculates the distance between a point P and every other point in the dataset, and then returns only those points which are within a threshold distance `eps`. """ neighbors = [] for Pn in range(0, len(D)): if numpy.linalg.norm(D[P] - D[Pn]) < eps: neighbors.append(Pn) return neighbors
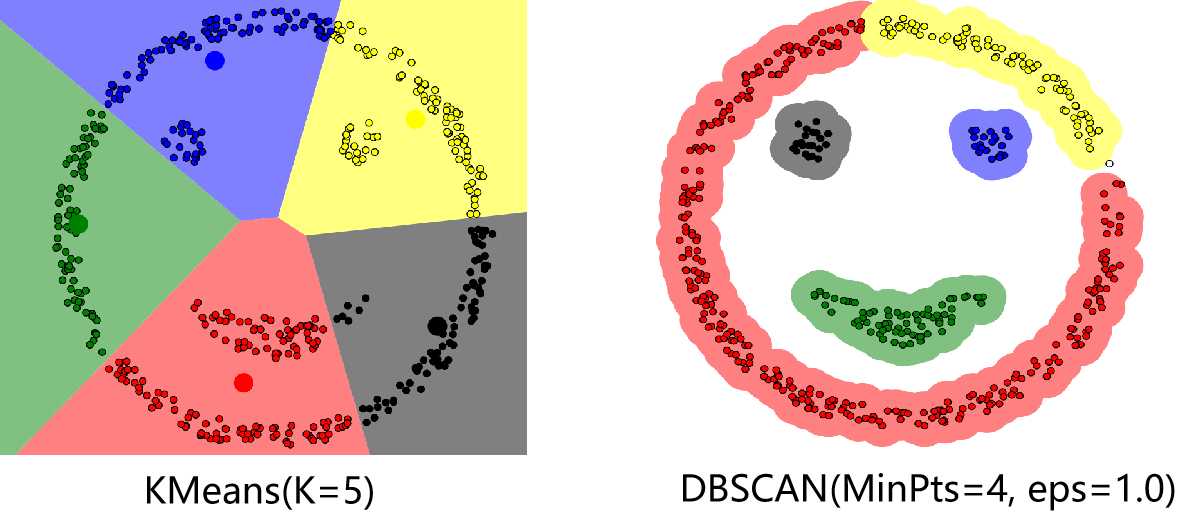
代码部分主要参考了文章DBSCAN Clustering Tutorial。若最终有数据点未被分到任何簇中(噪音点),则可将这些点视为异常点。下图分别是K均值算法以及DBSCAN算法对一个数据集的聚类结果,可以看出相比于K均值算法,DBSCAN算法可以有任意形状的簇,并且找到了数据中的异常点(右图中的空心点)。在实际应用中应对MinPts以及eps这两个参数仔细加以调试,特别是eps在不同的数据集中变化较大,具有较大的调试难度。
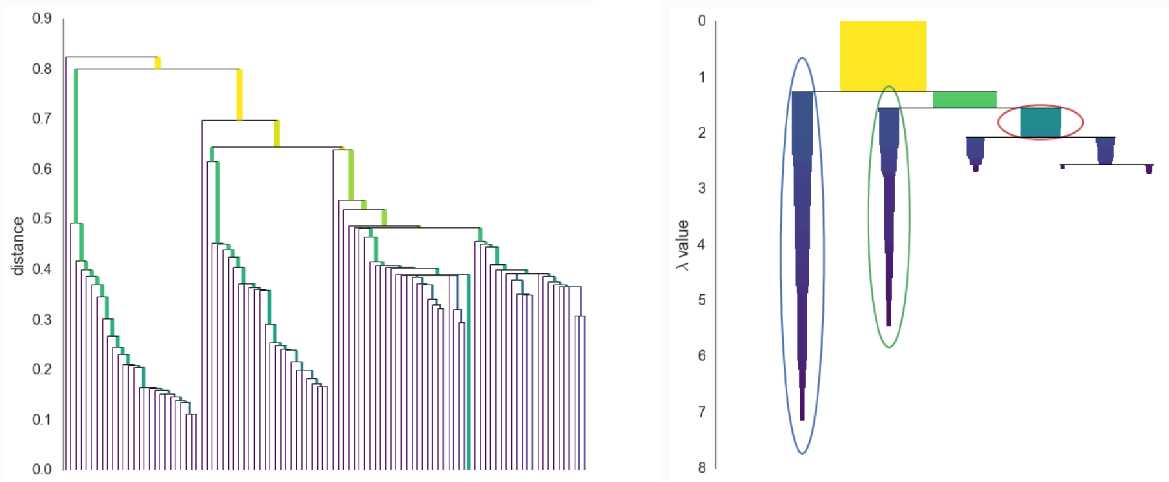
DBSCAN的一个改进算法为HDBSCAN,它也是一种基于密度的聚类方法,主要有两个参数$k$(也可记为$min\_samples$)以及$min\_cluster\_size$。DBSCAN通过一个数据点$\vec{x}$的半径为eps的邻域内是否有至少MinPts个点来判定该点是局地稠密还是稀疏的;而HDBSCAN通过一个数据点$\vec{x}$距它的第$k$个近邻点的距离$core_k(\vec{x})$来定量表征该点的局地密度,显然距离越大局地密度越小,在此基础上定义两个数据点之间的距离为:$$d(\vec{x}_1,\vec{x}_2)=\max{(core_k(\vec{x}_1),core_k(\vec{x}_2),\lVert{\vec{x}_1-\vec{x}_2}\rVert_2)}$$
标签:linkage image add 开始 desc fas 需要 sed wiki
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunwq06/p/10844745.html