标签:不可 spl 大循环 成员 odi 长度 pen utf8 while
menu = { ‘北京‘:{ ‘海淀‘:{ ‘五道口‘:{ ‘soho‘:{}, ‘网易‘:{}, ‘google‘:{} }, ‘中关村‘:{ ‘爱奇艺‘:{}, ‘汽车之家‘:{}, ‘youku‘:{}, }, ‘上地‘:{ ‘百度‘:{}, }, }, ‘昌平‘:{ ‘沙河‘:{ ‘老男孩‘:{}, ‘北航‘:{}, }, ‘天通苑‘:{}, ‘回龙观‘:{}, }, ‘朝阳‘:{}, ‘东城‘:{}, }, ‘上海‘:{ ‘闵行‘:{ "人民广场":{ ‘炸鸡店‘:{} } }, ‘闸北‘:{ ‘火车战‘:{ ‘携程‘:{} } }, ‘浦东‘:{}, }, ‘山东‘:{}, }
exit_flag = False current_layer = menu #标志位,用于循环 layers = [menu] #用于存储循环后的list,记录最后一项的添加项。 while not exit_flag: for k in current_layer: #循环打印字典 print(k) choice = input(‘>>>‘).strip() if choice == ‘b‘: #退出 current_layer = layers[-1] #输出列表的最后一项 layers.pop() #删除列表的最后一项。用于返回上一级 elif choice in current_layer: #正确选择选项 layers.append(current_layer) #添加字典到列表最后一项 current_layer = current_layer[choice] #进入下一层 else: #输入错误 continue
(思路:使用标志位进行大循环。运用for进行循环打印,使用列表添加删除实现进入下一级和返回上一级)
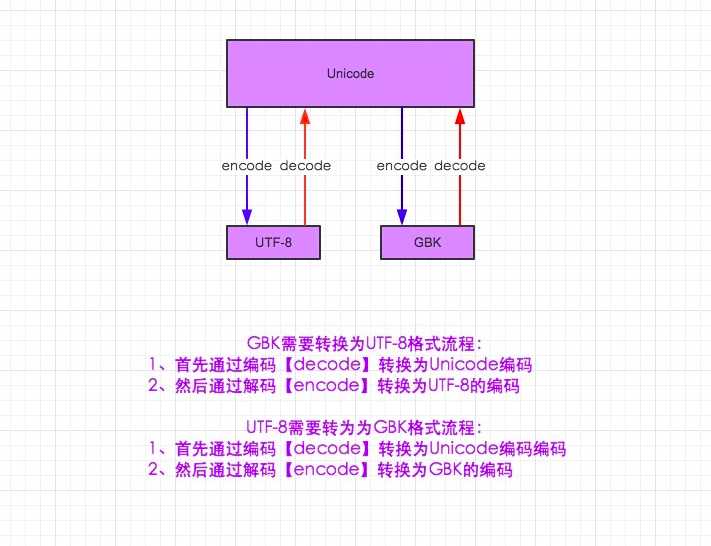
1.在python2默认编码是ASCII, python3里默认是unicode
2.unicode 分为 utf-32(占4个字节),utf-16(占两个字节),utf-8(占1-4个字节), so utf-16就是现在最常用的unicode版本, 不过在文件里存的还是utf-8,因为utf8省空间
3.在py3中encode,在转码的同时还会把string 变成bytes类型,decode在解码的同时还会把bytes变回string
集合是一个无序的,不重合的数据组合。
作用:

# s = set([1,23,45,6,"hello",(1,23,4)]) #创建一个数值集合,集合内的元素必须是不可哈希 # # (不可改变的){1, ‘hello‘, 6, 45, 23, (1, 23, 4)} # t = set(‘Hello‘) #创建一个唯一字符集合 {‘e‘, ‘l‘, ‘H‘, ‘o‘} # print(s,t) # s = set([1,2,3,4]) # t = set([3,4,5,6]) # a = s | t #s和t的并集 s.union(t) {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} # b = s & t #s和t的交集 s.intersection(t) {3, 4} # c = s ^ t #求对称差集(在s和t中共同存在以外的)s.symmetric_difference(t) {1, 2, 5, 6} # d = s - t #期差集 (s中存在,t中不存在的)s.difference(t) {1, 2} # print(a,b,c,d) # 基本操作 s = set([1,2,3,4]) t = set([1,2,3,4,5,6]) # s.add("x") #添加一项 # s.update([3,4,5,6,"YY"]) #添加多项 # s.remove(1) #移除集合中的某一项 # a=len(s) #len集合长度 # a = s in t #s是否是t的成员 # b = s not in t #s是否不是t的成员 # 测试是否 s 中的每一个元素都在 t 中 # b = t.issubset(s) # b = s <= t # 测试是否 t 中的每一个元素都在 s 中 # b = s.issuperset(t) # b = s >= t # s.copy() #集合的浅Copy{1, 2, 3, 4}
总结:1.集合的创建,列表中的元素必须是不可哈希的2.添加元素add、update,删除romover,长度len,复制s.copy。3.关系符:|、&、^、-、<=、>=
对文件的操作流程
1.打开文件,得到一个文件句柄并复制给一个变量
2.通过句柄对文件进行操作
3.关闭文件
# f = open(‘file‘) #打开文件 文件句柄 ,文件句柄 = open(‘文件路径‘, ‘模式‘) # first_line = f.readline() #读取文件第一行 # print(‘first_line:‘,first_line) # # print("我的分隔符".center(30,‘-‘)) # data = f.read() #读取剩下的,***文件大时误用*** # print(data) # f.close()
打开文件模式:
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
"b"表示处理二进制文件(如:FTP发送上传ISO镜像文件,linux可忽略,windows处理二进制文件时需标注)
# f = open(‘file‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) #只读模式,默认模式 # print(f.read()) # f.close() # f = open(‘file‘,‘w‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘)#w,只写模式【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则清空内容后添加】 # print(f.writelines(‘add‘)) #add # f.close() # f = open(‘file‘,‘a‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) #a,追加模式【可读;不存在则创建;存在则只追加内容;】 # print(f.write(‘add‘)) # f.close() # f = open(‘file‘,‘r+‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) # #print(f.write(‘pengdsdap‘)) # print(f.read()) # f.close()
高效读取方法:
# #高效读取方法: # f = open(‘file‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) # for line in f: # print(line.strip())
with语句
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下问:
# with open(‘file‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f: # print(f.read())
当with代码模块执行完毕,内部会自动关闭并释放文件资源。
Python2.7版本以后,with同时只多个文件的管理上下文:
# with open(‘file‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f,open(‘file2‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) as f2: # print(f2.read()) # print(f.read())
总结:1.文件的操作流程 2.打开文件的模式r、a、w和r+、w+、a+。3.读取方式:read、readline、高效读取方式。4.with语句打开文件忘记关闭5.seek、tell?
Python 三级菜单-字符编码和转码-集合的操作-文件的操作
标签:不可 spl 大循环 成员 odi 长度 pen utf8 while
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/070727sun/p/10795797.html