在JavaScript中,call、apply和bind是Function对象自带的三个方法,这三个方法的主要作用是改变函数中的this指向。
call、apply、bind方法的共同点和区别:apply 、 call 、bind 三者都是用来改变函数的this对象的指向的;apply 、 call 、bind 三者第一个参数都是this要指向的对象,也就是想指定的上下文(函数的每次调用都会拥有一个特殊值——本次调用的上下文(context)——这就是this关键字的值。);apply 、 call 、bind 三者都可以利用后续参数传参;bind 是返回对应函数,便于稍后调用;apply 、call 则是立即调用 。
一、call
call()
语法:
call([thisObj[,arg1[, arg2[, [,.argN]]]]])定义:调用一个对象的一个方法,以另一个对象替换当前对象。
说明: call 方法可以用来代替另一个对象调用一个方法。call 方法可将一个函数的对象上下文从初始的上下文改变为由 thisObj 指定的新对象。
thisObj的取值有以下4种情况:
(1) 不传,或者传null,undefined, 函数中的this指向window对象
(2) 传递另一个函数的函数名,函数中的this指向这个函数的引用
(3) 传递字符串、数值或布尔类型等基础类型,函数中的this指向其对应的包装对象,如 String、Number、Boolean
(4) 传递一个对象,函数中的this指向这个对象
function a(){ console.log(this); //输出函数a中的this对象 } function b(){} var c={name:"call"}; //定义对象c a.call(); //window a.call(null); //window a.call(undefined); //window a.call(1); //Number a.call(‘‘); //String a.call(true); //Boolean a.call(b); //function b(){} a.call(c); //Object
如果你不理解上面的,没关系,我们再来看一个例子:
function class1(){ this.name=function(){ console.log("我是class1内的方法"); } } function class2(){ class1.call(this); //此行代码执行后,当前的this指向了class1(也可以说class2继承了class1) } var f=new class2(); f.name(); //调用的是class1内的方法,将class1的name方法交给class2使用
常用例子:
(1)
function eat(x,y){ console.log(x+y); } function drink(x,y){ console.log(x-y); } eat.call(drink,3,2);
输出:5这个例子中的意思就是用 eat 来替换 drink,eat.call(drink,3,2) == eat(3,2) ,所以运行结果为:console.log(5);
注意:js 中的函数其实是对象,函数名是对 Function 对象的引用。
(2)
function Animal(){ this.name="animal"; this.showName=function(){ console.log(this.name); } } function Dog(){ this.name="dog"; } var animal=new Animal(); var dog=new Dog(); animal.showName.call(dog); 输出:dog
在上面的代码中,我们可以看到Dog里并没有showName方法,那为什么(this.name)的值是dog呢?
关键就在于最后一段代码(animal.showName.call(dog)),意思是把animal的方法放到dog上执行,也可以说,把animal 的showName()方法放到 dog上来执行,所以this.name 应该是 dog。
(3)继承
function Animal(name){ this.name=name; this.showName=function(){ console.log(this.name); } } function Dog(name){ Animal.call(this,name); } var dog=new Dog("Crazy dog"); dog.showName(); 输出:Crazy dog
Animal.call(this) 的意思就是使用 Animal对象代替this对象,那么Dog就能直接调用Animal的所有属性和方法。
二、apply()
语法:apply([thisObj[,argArray]])
定义:应用某一对象的一个方法,用另一个对象替换当前对象。
说明:
如果 argArray 不是一个有效的数组或者不是 arguments 对象,那么将导致一个 TypeError。
如果没有提供 argArray 和 thisObj 任何一个参数,那么 Global 对象将被用作 thisObj, 并且无法被传递任何参数。
call 和 apply的区别
对于 apply、call 二者而言,作用完全一样,只是接受参数的方式不太一样。
function class1(args1,args2){ this.name=function(){ console.log(args,args); } } function class2(){ var args1="1"; var args2="2"; class1.call(this,args1,args2); /*或*/ class1.apply(this,[args1,args2]); } var c=new class2(); c.name(); 输出:1 2
call 需要把参数按顺序传递进去,而 apply 则是把参数放在数组里。
既然两者功能一样,那该用哪个呢?
在JavaScript 中,某个函数的参数数量是不固定的,因此要说适用条件的话,当你的参数是明确知道数量时用 call ;而不确定的时候用 apply,然后把参数 push 进数组传递进去。当参数数量不确定时,函数内部也可以通过 arguments 这个数组来遍历所有的参数。
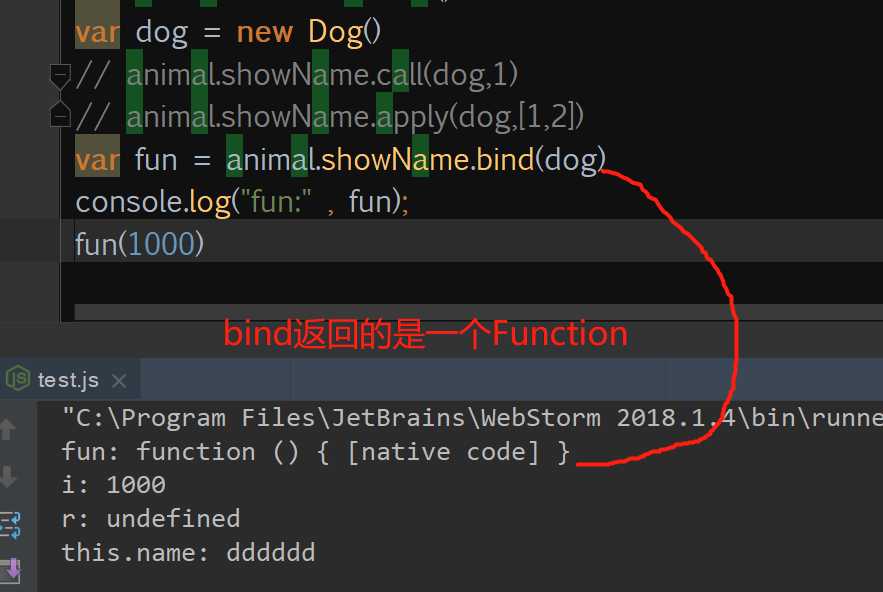
三、bindbind是在EcmaScript5中扩展的方法(IE6,7,8不支持)bind() 方法与 apply 和 call 很相似,也是可以改变函数体内 this 的指向。
MDN的解释是:bind()方法会创建一个新函数,称为绑定函数,当调用这个绑定函数时,绑定函数会以创建它时传入 bind()方法的第一个参数作为 this,传入 bind() 方法的第二个以及以后的参数加上绑定函数运行时本身的参数按照顺序作为原函数的参数来调用原函数。
注意:bind方法的返回值是函数
var bar=function(){ console.log(this.x); } var foo={ x:3 } bar(); bar.bind(foo)(); /*或*/ var func=bar.bind(foo); func(); 输出: undefined 3