标签:des style blog http color io os ar 使用
WebForms和WebServices作为.NET平台构建Web程序的两大利器,以其开发简单、易于部署的特点得到了广泛的应用,但殊不知微软公司在背后为我们做了大量的基础性工作,以至于我们开发人员只需简单地拖拖控件、写写一些页面级的代码就可以轻松地实现一些简单的应用程序。当然这种封装也不是没有好处的,至少从开发的角度而言它就可以极大地降低开发的难度,但是这种过度的封装使得我们开发人员当遇到有可能由底层引起的问题时就会束手无策,而且也会使得我们对知识的掌握和理解只停留在了表面而不得其内在本质。正是基于此,所以作者决定以一种探索的精神去试图解析和研究ASP.NET的内部运行机制,当然由于本人水平有限,也不可能对其各个方面理解很到位,姑且就当作本人的一家之言吧,有不对的地方还请各位同仁指正,这样大家可以共同学习提高。
一、IIS处理模型
从用户发出一个请求(一般而言就是在浏览器地址栏中键入一个URL),到这个请求到达服务器后,最先作出响应的就是IIS(本部分只关注ASP.NET部分,至于TCP/IP不在讨论范围),所以我们就先从这开始讲起。由于IIS有不同的版本,而且其处理模型也大相径庭,所以我会单独分别加以说明和解释。
IIS 5 处理模型
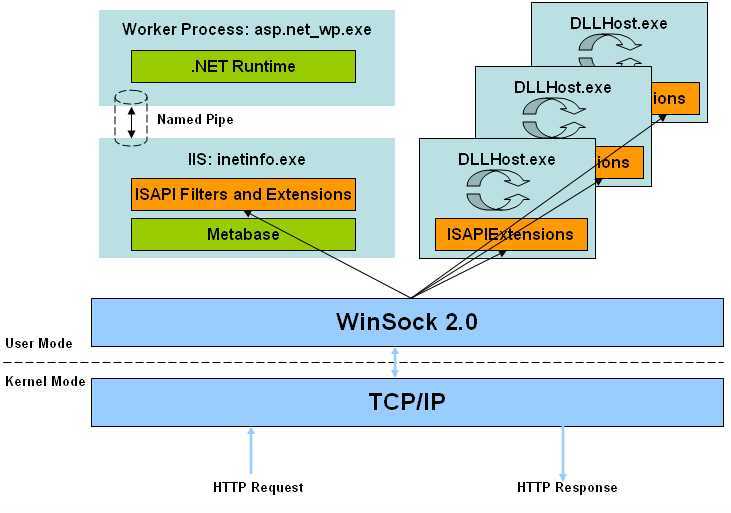
从上图我们可以清楚地知道,IIS在用户请求到达之后都做了哪些事情:
1.当用户请求到达后,工作在内核模式的TCP/IP驱动首先检测到请求,然后将其直接路由到inetinfo.exe进程;
3.用户请求由命名管道(为了提高性能,否则要在两个不同的进程间传递)从inetinfo.exe传给工作者进程aspnet_wp.exe;
4.aspnet_wp.exe将用户请求交由HTTP运行时即.NET Runtime处理(接下来的处理流程将会在后面讨论)。
IIS 6 处理模型
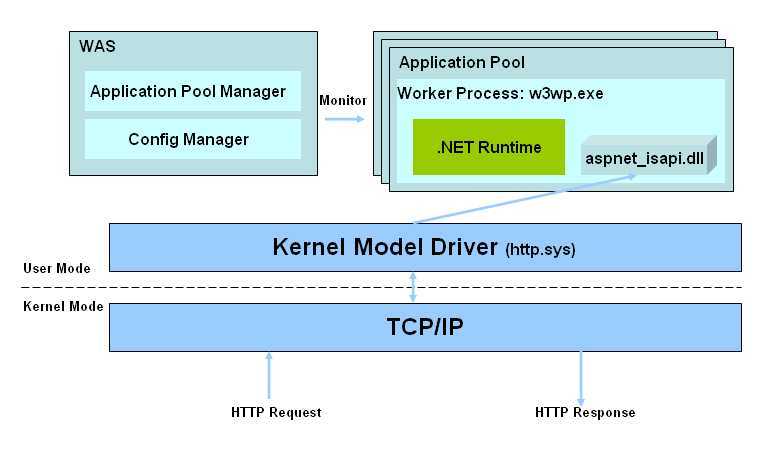
从上图来分析IIS 6架构的处理流程:
二、.NET运行时
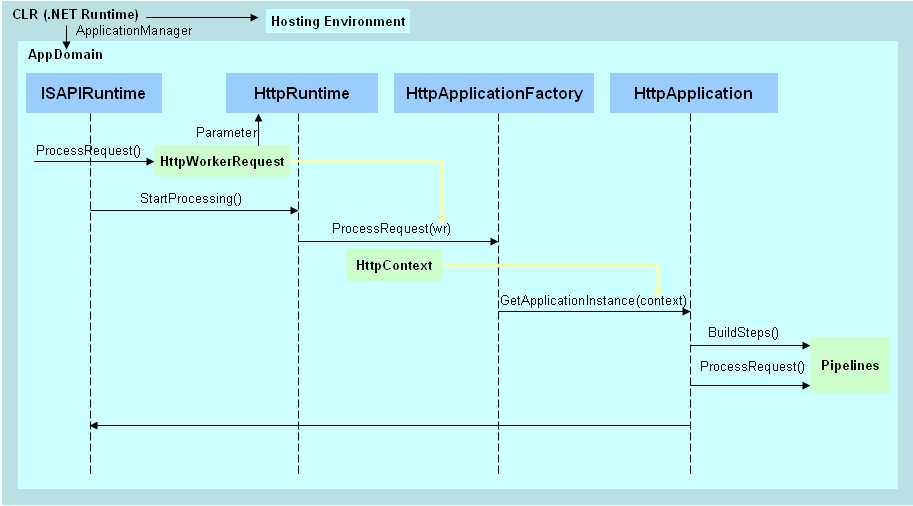
上面的图形简单描述了大概的处理流程,下面再用文字做些简单的说明:
1.当请求到达.NET Runtime后,接下来的处理操作就将在托管环境中完成。首先.NET Runtime做两个动作,一是准备Hosting Environment,二是由ApplicationManager创建一个AppDomain并且把处理权交由AppDomain继续完成;
2.在AppDomain中,由对象ISAPIRuntime启动操作,一方面经方法ProcessRequest()得到HttpWorkerRequest对象,另一方面由方法StartProcessing()生成HttpRuntime对象,接下来把处理权交给了HttpRuntime(HttpWorkerRequest对象将作为HttpRuntime方法中的参数被使用);
3.HttpRuntime中,方法ProcessRequest将处理请求:
[AspNetHostingPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Level=AspNetHostingPermissionLevel.Medium)]
public static void ProcessRequest(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{if (wr == null)
{throw new ArgumentNullException("wr");
}
if (UseIntegratedPipeline) {throw new PlatformNotSupportedException(System.Web.SR.GetString("Method_Not_Supported_By_Iis_Integrated_Mode", new object[] { "HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest" }));
}
ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr);
}
internal static void ProcessRequestNoDemand(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{RequestQueue queue = _theRuntime._requestQueue;
if (queue != null)
{wr = queue.GetRequestToExecute(wr);
}
if (wr != null)
{CalculateWaitTimeAndUpdatePerfCounter(wr);
wr.ResetStartTime();
ProcessRequestNow(wr);
}
}
internal static void ProcessRequestNow(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{_theRuntime.ProcessRequestInternal(wr);
}
ProcessRequestInternal
private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{HttpContext context;
try {context = new HttpContext(wr, false);
}
catch { wr.SendStatus(400, "Bad Request"); wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8");byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Bad Request</body></html>");
wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes, bytes.Length);
wr.FlushResponse(true);wr.EndOfRequest();
return;}
wr.SetEndOfSendNotification(this._asyncEndOfSendCallback, context);Interlocked.Increment(ref this._activeRequestCount);
HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount();
try { try { this.EnsureFirstRequestInit(context);}
catch { if (!context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) { throw;}
}
context.Response.InitResponseWriter();
IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context);
if (applicationInstance == null)
{throw new HttpException(System.Web.SR.GetString("Unable_create_app_object"));
}
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, context.WorkerRequest, applicationInstance.GetType().FullName, "Start");}
if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
{IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
context.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;
handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this._handlerCompletionCallback, context);}
else {applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(context);
this.FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null);
}
}
catch (Exception exception) {context.Response.InitResponseWriter();
this.FinishRequest(wr, context, exception);}
}
4.下面我们来看看HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context)到底做了什么?
internal static IHttpHandler GetApplicationInstance(HttpContext context)
{if (_customApplication != null)
{ return _customApplication;}
if (context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) {return new HttpDebugHandler();
}
_theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited();
_theApplicationFactory.EnsureAppStartCalled(context);
return _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context);}
private HttpApplication GetNormalApplicationInstance(HttpContext context){ HttpApplication application = null;lock (this._freeList)
{if (this._numFreeAppInstances > 0)
{ application = (HttpApplication) this._freeList.Pop(); this._numFreeAppInstances--;if (this._numFreeAppInstances < this._minFreeAppInstances)
{this._minFreeAppInstances = this._numFreeAppInstances;
}
}
}
if (application == null)
{ application = (HttpApplication) HttpRuntime.CreateNonPublicInstance(this._theApplicationType);using (new ApplicationImpersonationContext())
{application.InitInternal(context, this._state, this._eventHandlerMethods);
}
}
return application;}
通过上面的方法我们最终获得了HttpApplication对象;
5.如果我们继续追踪代码application.InitInternal(context, this._state, this._eventHandlerMethods);看会获得什么?
InitInternal
internal void InitInternal(HttpContext context, HttpApplicationState state, MethodInfo[] handlers)
{ this._state = state;PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.PIPELINES);
try { try { this._initContext = context;this._initContext.ApplicationInstance = this;
context.ConfigurationPath = context.Request.ApplicationPathObject;
using (new HttpContextWrapper(context))
{ if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { try { context.HideRequestResponse = true;this._hideRequestResponse = true;
this.InitIntegratedModules(); goto Label_006B;}
finally { context.HideRequestResponse = false;this._hideRequestResponse = false;
}
}
this.InitModules();Label_006B:
if (handlers != null)
{ this.HookupEventHandlersForApplicationAndModules(handlers);}
this._context = context;if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline && (this._context != null))
{this._context.HideRequestResponse = true;
}
this._hideRequestResponse = true;
try { this.Init();}
catch (Exception exception) { this.RecordError(exception);}
}
if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline && (this._context != null))
{this._context.HideRequestResponse = false;
}
this._hideRequestResponse = false;
this._context = null;
this._resumeStepsWaitCallback = new WaitCallback(this.ResumeStepsWaitCallback);
if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) {this._stepManager = new PipelineStepManager(this);
}
else {this._stepManager = new ApplicationStepManager(this);
}
this._stepManager.BuildSteps(this._resumeStepsWaitCallback);
}
finally {this._initInternalCompleted = true;
context.ConfigurationPath = null;this._initContext.ApplicationInstance = null;
this._initContext = null;
}
}
catch { throw;}
}
请注意方法的这些地方
this.InitModules();初始化所有的Modules,包含用户自定义的HttpModules
private void InitModules()
{ this._moduleCollection = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().HttpModules.CreateModules(); this.InitModulesCommon();}
private void InitModulesCommon()
{int count = this._moduleCollection.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{this._currentModuleCollectionKey = this._moduleCollection.GetKey(i);
this._moduleCollection[i].Init(this);
}
this._currentModuleCollectionKey = null;
this.InitAppLevelCulture();}
this._stepManager.BuildSteps(this._resumeStepsWaitCallback);
internal override void BuildSteps(WaitCallback stepCallback)
{ ArrayList steps = new ArrayList(); HttpApplication app = base._application;bool flag = false;
UrlMappingsSection urlMappings = RuntimeConfig.GetConfig().UrlMappings;
flag = urlMappings.IsEnabled && (urlMappings.UrlMappings.Count > 0);
steps.Add(new HttpApplication.ValidatePathExecutionStep(app)); if (flag) { steps.Add(new HttpApplication.UrlMappingsExecutionStep(app));}
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventBeginRequest, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventAuthenticateRequest, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventDefaultAuthentication, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostAuthenticateRequest, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventAuthorizeRequest, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostAuthorizeRequest, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventResolveRequestCache, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostResolveRequestCache, steps);
steps.Add(new HttpApplication.MapHandlerExecutionStep(app));app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostMapRequestHandler, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventAcquireRequestState, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostAcquireRequestState, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPreRequestHandlerExecute, steps);
steps.Add(new HttpApplication.CallHandlerExecutionStep(app));app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostRequestHandlerExecute, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventReleaseRequestState, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostReleaseRequestState, steps);
steps.Add(new HttpApplication.CallFilterExecutionStep(app));app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventUpdateRequestCache, steps);
app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventPostUpdateRequestCache, steps);
this._endRequestStepIndex = steps.Count;app.CreateEventExecutionSteps(HttpApplication.EventEndRequest, steps);
steps.Add(new HttpApplication.NoopExecutionStep());this._execSteps = new HttpApplication.IExecutionStep[steps.Count];
steps.CopyTo(this._execSteps); this._resumeStepsWaitCallback = stepCallback;}
你看到什么?对,这就是我们常说的管道事件序列(具体的Pipelines也会在下一部分介绍)
我们继续深入代码来看看CreateEventExecutionSteps()和CallHandlerExecutionStep()
private void CreateEventExecutionSteps(object eventIndex, ArrayList steps)
{ AsyncAppEventHandler handler = this.AsyncEvents[eventIndex];if (handler != null)
{ handler.CreateExecutionSteps(this, steps);}
EventHandler handler2 = (EventHandler) this.Events[eventIndex];if (handler2 != null)
{Delegate[] invocationList = handler2.GetInvocationList();
for (int i = 0; i < invocationList.Length; i++)
{steps.Add(new SyncEventExecutionStep(this, (EventHandler) invocationList[i]));
}
}
}
internal CallHandlerExecutionStep(HttpApplication app){ this._application = app;this._completionCallback = new AsyncCallback(this.OnAsyncHandlerCompletion);
}
6.接下来就是开始HttpApplication的BeginProcessRequest()方法了
handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this._handlerCompletionCallback, context)
IAsyncResult IHttpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext context, AsyncCallback cb, object extraData){ this._context = context;this._context.ApplicationInstance = this;
this._stepManager.InitRequest(); this._context.Root(); HttpAsyncResult result = new HttpAsyncResult(cb, extraData); this.AsyncResult = result;if (this._context.TraceIsEnabled)
{ HttpRuntime.Profile.StartRequest(this._context);}
this.ResumeSteps(null);
return result;}
ResumeSteps
[DebuggerStepperBoundary]
internal override void ResumeSteps(Exception error)
{bool flag = false;
bool completedSynchronously = true;
HttpApplication application = base._application;HttpContext context = application.Context;
HttpApplication.ThreadContext context2 = null;AspNetSynchronizationContext syncContext = context.SyncContext;
lock (base._application)
{ try {context2 = application.OnThreadEnter();
}
catch (Exception exception) {if (error == null)
{error = exception;
}
}
try { try {Label_0040:
if (syncContext.Error != null)
{error = syncContext.Error;
syncContext.ClearError();
}
if (error != null)
{application.RecordError(error);
error = null;}
if (syncContext.PendingOperationsCount > 0) { syncContext.SetLastCompletionWorkItem(this._resumeStepsWaitCallback);}
else {if ((this._currentStepIndex < this._endRequestStepIndex) && ((context.Error != null) || base._requestCompleted))
{context.Response.FilterOutput();
this._currentStepIndex = this._endRequestStepIndex;
}
else { this._currentStepIndex++;}
if (this._currentStepIndex >= this._execSteps.Length)
{ flag = true;}
else { this._numStepCalls++;context.SyncContext.Enable();
error = application.ExecuteStep(this._execSteps[this._currentStepIndex], ref completedSynchronously);
if (completedSynchronously) { this._numSyncStepCalls++; goto Label_0040;}
}
}
}
finally {if (context2 != null)
{ try {context2.Leave();
}
catch {}
}
}
}
catch { throw;}
}
if (flag) {context.Unroot();
application.AsyncResult.Complete(this._numStepCalls == this._numSyncStepCalls, null, null);
application.ReleaseAppInstance();
}
}
ExecuteStep
internal Exception ExecuteStep(IExecutionStep step, ref bool completedSynchronously)
{ Exception exception = null; try { try { if (step.IsCancellable) { this._context.BeginCancellablePeriod(); try {step.Execute();
}
finally { this._context.EndCancellablePeriod();}
this._context.WaitForExceptionIfCancelled();}
else {step.Execute();
}
if (!step.CompletedSynchronously) { completedSynchronously = false;return null;
}
}
catch (Exception exception2) {exception = exception2;
if (ImpersonationContext.CurrentThreadTokenExists) {exception2.Data["ASPIMPERSONATING"] = string.Empty;
}
if ((exception2 is ThreadAbortException) && ((Thread.CurrentThread.ThreadState & System.Threading.ThreadState.AbortRequested) == System.Threading.ThreadState.Running))
{ exception = null; this._stepManager.CompleteRequest();}
}
catch {}
}
catch (ThreadAbortException exception3) {if ((exception3.ExceptionState != null) && (exception3.ExceptionState is CancelModuleException))
{CancelModuleException exceptionState = (CancelModuleException) exception3.ExceptionState;
if (exceptionState.Timeout) {exception = new HttpException(System.Web.SR.GetString("Request_timed_out"), null, 0xbb9);
PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.REQUESTS_TIMED_OUT);
}
else { exception = null; this._stepManager.CompleteRequest();}
Thread.ResetAbort();
}
}
completedSynchronously = true; return exception;}
void HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.Execute(){string str = null;
if (this._handler != null)
{ if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 2)) { str = this._handler.Method.ReflectedType.ToString(); EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_PIPELINE_ENTER, this._application.Context.WorkerRequest, str);}
this._handler(this._application, this._application.AppEvent);
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 2)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_PIPELINE_LEAVE, this._application.Context.WorkerRequest, str);}
}
}
HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.Execute
void HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.Execute(){ HttpContext context = this._application.Context;IHttpHandler handler = context.Handler;
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(4, 4)) {EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_ENTER, context.WorkerRequest);
}
if ((handler != null) && HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline)
{ IIS7WorkerRequest workerRequest = context.WorkerRequest as IIS7WorkerRequest;if ((workerRequest != null) && workerRequest.IsHandlerExecutionDenied())
{this._sync = true;
HttpException exception = new HttpException(0x193, System.Web.SR.GetString("Handler_access_denied"));
exception.SetFormatter(new PageForbiddenErrorFormatter(context.Request.Path, System.Web.SR.GetString("Handler_access_denied")));
throw exception;}
}
if (handler == null)
{this._sync = true;
}
else if (handler is IHttpAsyncHandler)
{IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) handler;
this._sync = false;
this._handler = handler2;IAsyncResult result = handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this._completionCallback, null);
if (result.CompletedSynchronously) {this._sync = true;
this._handler = null;
try {handler2.EndProcessRequest(result);
}
finally {context.Response.GenerateResponseHeadersForHandler();
}
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(4, 4)) {EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_LEAVE, context.WorkerRequest);
}
}
}
else {this._sync = true;
context.SyncContext.SetSyncCaller();
try {handler.ProcessRequest(context);
}
finally {context.SyncContext.ResetSyncCaller();
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(4, 4)) {EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_LEAVE, context.WorkerRequest);
}
context.Response.GenerateResponseHeadersForHandler();
}
}
}
三、管道事件序列Pipelines
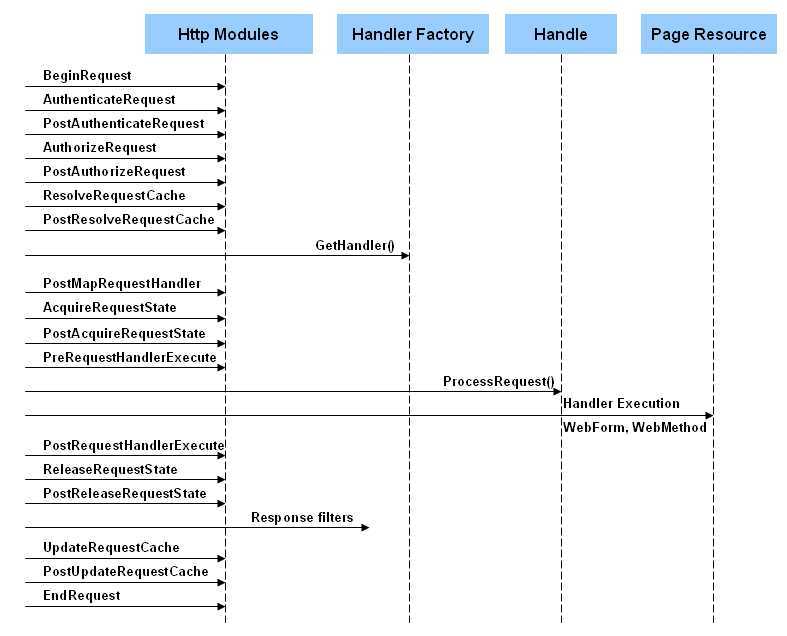
MSDN上的链接http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.web.httpapplication(v=vs.80).aspx
标签:des style blog http color io os ar 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jx270/p/4042334.html