标签:png return include 调用 names 产品 int 参数 静态成员函数
一.友元函数友元的介绍
1.友元是C++中的一种关系
2.友元关系发生在函数与类之间或者类与类之间
3.友元关系是单项的,不能传递
友元的用法
1.在类中以friend关键字声明友元
2.类的友元可以是其它类或者具体函数
3.友元不是类的一部分
4.友元不受类中访问级别的限制
5.友元可以直接访问具体类的所有成员
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
class Point
{
double x;
double y;
public:
Point(double x, double y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
double getX()
{
return x;
}
double getY()
{
return y;
}
};
double func(Point& p1, Point& p2)
{
double ret = 0;
ret = (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) * (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) +
(p2.getX() - p1.getX()) * (p2.getX() - p1.getX());
ret = sqrt(ret);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
Point p1(1, 2);
Point p2(10, 20);
printf("p1(%f, %f)\n", p1.getX(), p1.getY());
printf("p2(%f, %f)\n", p2.getX(), p2.getY());
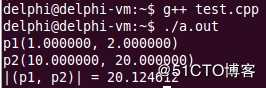
printf("|(p1, p2)| = %f\n", func(p1, p2));
return 0;
}
该示例主要是想求两个坐标点之间的距离,但是由于x,y是私有成员变量,所以不能直接调用,必须提高功能函数getX(),getY()进行调用,但是需要8次的调用导致使其没有效率。但是,friend函数可以解决此问题
改正以及运行结果图
友元的缺点
1.友元是为兼顾C语言的高效二诞生的
2.友元直接破坏了面对对象的封装性
3.友元在实际产品中的高效是得不偿失的
4.友元在现代软件工程中已经逐渐被遗忘
注意事项
1.友元关系不具备传递性
2.类的友元可以是其它类的成员函数
3.类的友元可以是某个完整的类--所有的成员函数都是友元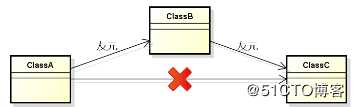
函数重载
1.函数重载的本质为相互独立的不同函数
2.C++中通过函数名和函数参数确定函数调用
3.无法直接通过函数名得到重载函数的入口地址
4.函数重载必然发生在同一个作用域中
类中的重载
1.构造函数的重载
2.普通成员函数的重载
3.静态成员函数的重载
Q:全局函数,普通成员函数以及静态成员函数之间是否可以构成重载?
示例分析
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int i;
public:
Test()
{
cout<<"Test::Test()"<<endl;
this->i = 0;
}
Test(int i)
{
cout<<"Test::Test(int i)"<<endl;
this->i = i;
}
Test(const Test& obj)
{
cout<<"Test(const Test& obj)"<<endl;
this->i = obj.i;
}
static void func()
{
cout<<"void Test::func()"<<endl;
}
void func(int i)
{
cout<<"void Test::func(int i)="<<i<<endl;
}
int getI()
{
return i;
}
};
void func()
{
cout<<"void func()"<<endl;
}
void func(int i)
{
cout<<"void func(int i)="<<i<<endl;
}
int main()
{
func();
func(1);
//void func()
//void func(int i)=1
Test t; // Test::Test()
Test t1(1); // Test::Test(int i)
Test t2(t1); // Test(const Test& obj)
func(); // void func()
Test::func(); // void Test::func()
func(2); // void func(int i), i = 2;
t1.func(2); // void Test::func(int i), i = 2
t1.func(); // void Test::func()
return 0;
}在出现结果之前,对每个函数进行结果分析
运行结果如如图所示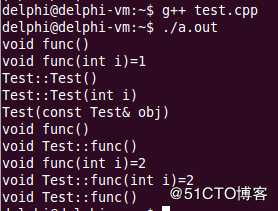
重载的意义
1.通过函数名对函数功能进行提示
2.通过参数列表对函数用法进行提示
3.扩展系统中已经存在的函数功能
标签:png return include 调用 names 产品 int 参数 静态成员函数
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/13475106/2410547