标签:messages demo 限制 call cer 介绍 空字符串 guest 调用
abbitMQ是一个消息代理。它的核心原理非常简单:接收和发送消息。你可以把它想像成一个邮局:你把信件放入邮箱,邮递员就会把信件投递到你的收件人处。在这个比喻中,RabbitMQ是一个邮箱、邮局、邮递员。RabbitMQ和邮局的主要区别是,它处理的不是纸,而是接收、存储和发送二进制的数据——消息。一般提到RabbitMQ和消息,都用到一些专有名词。




我们第一个程序send.php会发送一个消息到队列中。首先要做的事情就是建立一个到RabbitMQ服务器的连接。
$connection = new AMQPConnection(array(‘host‘ =>‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘port‘ =>‘5672‘, ‘vhost‘ =>‘/‘, ‘login‘ =>‘guest‘, ‘password‘ => ‘guest‘));
现在我们已经连接上服务器了,那么,在发送消息之前我们需要确认队列是存在的。如果我们把消息发送到一个不存在的队列,RabbitMQ会丢弃这条消息。我门先创建一个名为hello的队列,然后把消息发送到这个队列中。
$queue = new AMQPQueue($channel); $queue->setName($queueName);
这时候我们就可以发送消息了,我们第一条消息只包含了 Hello World!字符串,我们打算把它发送到我们的hello队列。
在RabbitMQ中,消息是不能直接发送到队列,它需要发送到交换器(exchange)中。我们不打算在这里深入讨论它——你可以通过教程第三部分了解更多。现在我们所需要了解的是如何使用默认的交换器(exchange),它使用一个空字符串来标识。交换器允许我们指定某条消息需要投递到哪个队列,$$routeKey参数必须指定为队列的名称:
$exchange->publish($message, $routeKey); var_dump("[x] Sent ‘Hello World!‘");
在退出程序之前,我们需要确认网络缓冲已经被刷写、消息已经投递到RabbitMQ。完成这些事情(正确的关闭连接)是很简单的。
$connection->disconnect();

我们的第二个程序receive.php,将会从队列中获取消息并打印消息。
这次我们还是先要连接到RabbitMQ服务器。连接服务器的代码和之前是一样的。
下一步也和之前一样,我们需要确认队列是存在的。使用$queue->declare(),新版为$queue->declareQueue()创建一个队列,我们可以运行这个命令很多次,但是只有一个队列会创建。
$queue = new AMQPQueue($channel); $queue->setName($queueName); //$queue->declare(); $queue->declareQueue();
你也许要问为什么重复声明了队列——我们已经在前面的代码中声明了它。如果我们确定了队列是已经存在的,那么我们可以不这么做。比如先运行send.php程序。可是我们并不确定哪个程序先运行,这种情况的话再程序中重复声明是好的做法。
从队列中获取消息相对来说稍显复杂。需要为队列定义一个回调(callback)函数。当我们获取到消息的时候,Pika库就会调用这个回调(callback)函数。我们的这个回调函数将会但因消息的内容到屏幕上。
function callback($envelope, $queue) { $msg = $envelope->getBody(); var_dump(" [x] Received:" . $msg); $queue->nack($envelope->getDeliveryTag()); }
下一步,我们需要告诉RabbitMQ这个回调函数将会从hello队列中接收消息:
$queue->consume(‘callback‘);
要成功运行这些命令,我们必须保证队列是存在的,我们之前已经使用创建了一个队列queue_declare。
$queue->nack()//函数稍后会介绍。
最后,我们输入一个无限循环来等待消息数据并确运行回调函数。
var_dump(‘[*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C‘); while (TRUE) { $queue->consume(‘callback‘); }
receive.php
<?php $exchangeName = ‘demo‘; $queueName = ‘hello‘; $routeKey = ‘hello‘; $connection = new AMQPConnection(array(‘host‘ => ‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘port‘ => ‘5672‘, ‘vhost‘ => ‘/‘, ‘login‘ => ‘guest‘, ‘password‘ => ‘guest‘)); $connection->connect() or die("Cannot connect to the broker!\n"); $channel = new AMQPChannel($connection); $exchange = new AMQPExchange($channel); $exchange->setName($exchangeName); $exchange->setType(AMQP_EX_TYPE_DIRECT); //$queue->declare(); $exchange->declareExchange(); $queue = new AMQPQueue($channel); $queue->setName($queueName); //$queue->declare(); $queue->declareQueue(); $queue->bind($exchangeName, $routeKey); var_dump(‘[*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C‘); while (TRUE) { $queue->consume(‘callback‘); } $connection->disconnect(); function callback($envelope, $queue) { $msg = $envelope->getBody(); var_dump(" [x] Received:" . $msg); $queue->nack($envelope->getDeliveryTag()); }
send.php
<?php $exchangeName = ‘demo‘; $queueName = ‘hello‘; $routeKey = ‘hello‘; $message = ‘Hello World!‘; $connection = new AMQPConnection(array(‘host‘ => ‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘port‘ => ‘5672‘, ‘vhost‘ => ‘/‘, ‘login‘ => ‘guest‘, ‘password‘ => ‘guest‘)); $connection->connect() or die("Cannot connect to the broker!\n"); try { $channel = new AMQPChannel($connection); $exchange = new AMQPExchange($channel); $exchange->setName($exchangeName); $queue = new AMQPQueue($channel); $queue->setName($queueName); $exchange->publish($message, $routeKey); var_dump("[x] Sent ‘Hello World!‘"); } catch (AMQPConnectionException $e) { var_dump($e); exit(); } $connection->disconnect();
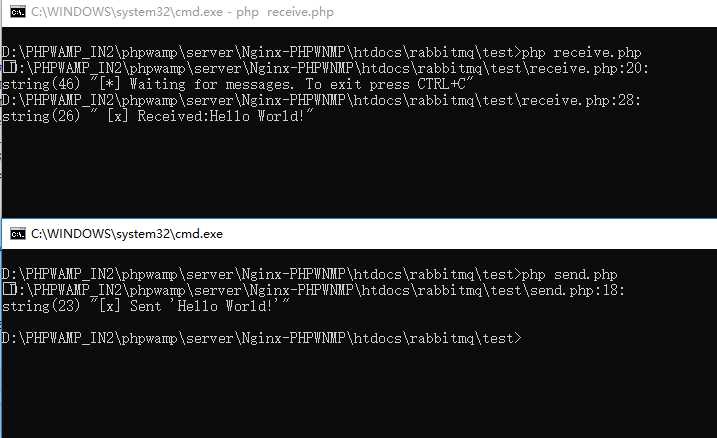
使用方法:先运行receive.php,再运行send.php
效果截图:
RabbitMQ 入门教程(PHP版) 第一部分:Hello World
标签:messages demo 限制 call cer 介绍 空字符串 guest 调用
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/-mrl/p/11102336.html