标签:multi 夏令时 输入 sam creat 切片 额外 mktime 方式
#### 对某某项目进行一个标准化的开发,进行规范化.
#bin : 启动项目程序的主入口
#conf : 项目的配置文件
#core : 主要逻辑(业务逻辑)
#db : 存放数据()
#lib : 辅助文件(存放公共的一些方法)
#README : 项目文档说明? 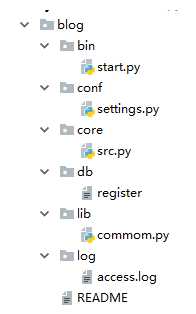
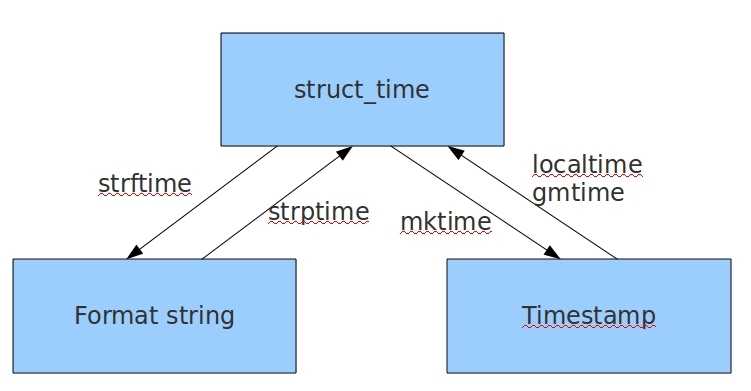
? 1.时间戳 ,用于计时 (始于1970年,Unix的诞生.)
? 2.格式化时间 ,
? 3.元组结构化时间, 元组则是用来操作时间的.(作为一种中间介质,用于转换)
### 1.时间戳 ,从1970年到现在的一个时间戳,秒为单位
print(time.time())
### 2.格式化时间
# 字符串类型 ,参数 :%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S ,不能包含Unicode的编码
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
#不能包含Unicode的编码
print(time.strftime('%Y{}%m{}%d{} %H:%M:%S').format('年','月','日'))
### 3.结构化时间
print(time.localtime())
### 时间转换
# 时间戳转换成结构化时间
ret=time.time() # 时间戳
st_time=time.localtime(ret) # 时间戳转换成 结构化时间
print(st_time)
# 结构化时间转换成格式化时间
ft=time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',st_time) # 将结构化时间转换成格式化时间
print(ft)
# 格式化时间转换成结构化时间,
ft=time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # 格式化时间.
st=time.strptime(ft,'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # 格式化时间转换成 结构化时间,
print(st)
# 结构化时间转换成时间戳,
timestamp=time.mktime(st) # 结构化时间转换成时间戳
print(timestamp)
## 突发奇想: 算一算 从1970到2019-06-28现在一共同多少天
count=0
for i in range(1970,2019):
ret=time.strptime(f'{i}-12-31','%Y-%m-%d')
count+=int(ret.tm_yday)
res=time.strptime('2019-06-28','%Y-%m-%d')
print(res)
print(res.tm_yday+count)
## 用户输入一个格式化的时间如:2019-06-28,给返回这一天在这一年中是第几天
def user_time(times_us):
ret = time.strptime(times_us,'%Y-%m-%d')
return ret.tm_yday
print(user_time(input('请输入年-月-日:>>').strip()))
## 计算博客园园龄
# 将指定时间转换成时间戳
bok_time='2019-05-20 00:00:00'
#先转换成结构化时间,在由结构化时间转换成时间戳
t2=time.mktime(time.strptime(bok_time,'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
create_time=now_time-t2 # 获得一个时间戳.当前时间戳 - 创建时的时间戳
# gmtime(sec) 计算 从1970时间 到现在已经过了多少时间函数将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time,可选的参数sec表示从1970-1-1以来的秒数。(返回结构tm 代表目前UTC 时间。)
# localtime() 是格式本地当前时间,(会把差值+时区一起算)(返回结构tm 代表目前的当地时间)
time_struct=time.gmtime(create_time)
print(f'现在已经过去了{time_struct.tm_year-1970}年,{time_struct.tm_mon-1}月,{time_struct.tm_mday-1}天,{time_struct.tm_hour}小时,{time_struct.tm_min}分,{time_struct.tm_sec}秒,夏令时:{time_struct.tm_isdst}')
import datetime
### 现在的时间
now_datetime=datetime.datetime.now()
print(now_datetime) # 2019-06-28 15:29:38.478080
### 在当前时间上,为其增减时间(时,分,秒,天,周)
now_time=datetime.datetime.now()
# 现在的时间加上增删的时间
print(now_time+datetime.timedelta(weeks=3)) # 三周后
print(now_time+datetime.timedelta(weeks=-3)) # 三周前
### 指定调整 年月日时分秒等
now_time2=datetime.datetime.now()
print(now_time2.replace(year=1949)) # 指定年
print(now_time2.replace(year=1997,month=11,day=16,hour=12,minute=0,second=0)) # 指定年 , 月, 日
### 将时间戳转换成格式化时间
print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(3125456312))import random
# 获得一个 大于0,且小于1 ,随机小数
print(random.random())
# 1到7之间, 随机小数
print(random.uniform(1,7))
# 随机整数 顾头也顾尾
print(random.randint(1,5))
# 随机切片 顾头不顾尾
print(random.randrange(1,10,2))
# 随机选择一个返回
print(random.choice([1,'22',3,4]))
# 随机选择多个
print(random.sample([1,2,3,4,5,6,7]))
# 打乱列表次序
item=[i for i in range(10)]
random.shuffle(item) # 对原列表 打乱顺序
print(item)### 内置数据类型 (dict, list,set ,tuple) 基础上: Counter,deque,defaultdict,namedtuple和OrderedDict等
# 1.namedtuple: 生成可以使用名字来访问元素内容的tuple 元组
from collections import namedtuple
# 表示一个二维坐标点
Point=namedtuple('Point',['X','Y'])
p=Point(1,2)
print(p.X,p.Y)
#坐标和半径表示一个圆
Circle = namedtuple('Circle', ['x', 'y', 'r'])
c=Circle(1,2,3)
### 2.deque: 双端队列,可以快速的从另外一侧追加和推出对象 ,
# list 插入和删除元素慢,是线性存储,数据量大的时候,插入和删除效率很低。
#了高效实现插入和删除操作的双向列表,适合用于队列和栈:
from collections import deque
q=deque(['a','b','c'])
q.append('x') # 末尾插入
q.appendleft('y') # 列头插入
print(q.pop()) # 默认删除末尾元素,并返回删除元素
print(q.popleft()) # 默认删除头元素
print(q)
### 3.Counter: 计数器,主要用来计数 ###很吊!!!!
# 它是一个无序的容器类型,以字典的键值对形式存储,其中元素作为key,其计数作为value。
# 计数值可以是任意的Interger(包括0和负数)。
# Counter类和其他语言的bags或multisets很相似。
import random
from collections import Counter
c=Counter('nopqrsydefgst')
print(c)
num_li=[random.randint(1,20) for i in range(20)]
c2=Counter(num_li)
print(c2)
# 4.OrderedDict: 有序字典
from collections import OrderedDict
d=dict([('e', 2), ('b', 2), ('c', 3)]) # 字典推导式 将可迭代对象默认循环得到一个元组,
print(d)
od = OrderedDict([('e', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 3)])
print(od)
od['z'] = 1 # 添加元素 只会往末尾添加
od['x'] = 2 #
od['y'] = 3 #
print(od,type(od))
print(od.keys())
### 5.defaultdict: 带有默认值的字典
# 放置数据类型作为字典的值类型
from collections import defaultdict
values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
my_dict = defaultdict(list)
for value in values:
if value>66:
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
print(my_dict)
# 当键不存在 执行lambda 函数
from collections import defaultdict
dd=defaultdict(lambda :'N/A')
dd['key1']='abc'
print(dd)
print(dd['key1'])
print(dd['key2']) # key2不存在,返回默认值 'N/A'
Python进阶(十)----规范化格式目录, time模块, datatime模块,random模块,collection模块(python额外数据类型)
标签:multi 夏令时 输入 sam creat 切片 额外 mktime 方式
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dengl/p/11104952.html