标签:存在 数据 代码实现 后序遍历 rip 结构 bsp OLE 结果
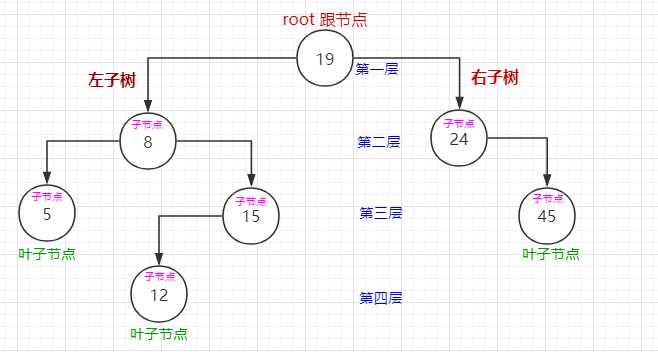
1.由一系列节点组成,具有层级结构。每个节点的特性包含有节点值、关系指针。节点之间存在对应关系。
2.树中存在一个没有父节点的节点,叫做根节点。树的末尾存在一系列没有子节点的节点,称为叶子节点。其他可以叫做中间节点。
3.树的根节点位于第一层,层级数越大,节点位置越深,层级数也叫做树高。
1.节点分为左右子树。
2.在不为空的情况下,左子树子节点的值都小于父节点的值。
3.在不为空的情况下,右子树子节点的值都大于父节点的值。
4.每个节点的左右子树都按照上述规则排序。
如图:
 (打错字了..)
(打错字了..)
1.节点用对象来描述,节点特性用对象属性来描述。
1 class Node { 2 constructor(key) { 3 this.key = key;// 节点值 4 this.left = null;// 左指针 5 this.right = null;// 右指针 6 } 7 }
2.二叉树结构用对象来描述。
1 // 二叉树 2 class BinaryTree { 3 constructor() { 4 this.root = null;// 根节点 5 } 6 insert(key) {// api--插入 7 const newNode = new Node(key); 8 if (this.root === null) {// 设置根节点 9 this.root = newNode; 10 } 11 method.insertNode(this.root, newNode); 12 } 13 }
相关方法:
1 // method 2 method = { 3 insertNode(root, newNode) { 4 if (newNode.key < root.key) {// 进入左子树 5 if (root.left === null) {// 左子树为空 6 root.left = newNode; 7 } else {// 左子树已存在 8 method.insertNode(root.left, newNode); 9 } 10 } else if (newNode.key > root.key) {// 进入右子树 11 if (root.right === null) {// 右子树为空 12 root.right = newNode; 13 } else {// 右子树已存在 14 method.insertNode(root.right, newNode); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 };
具体用法:
1 // 实例化二叉树 2 const binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); 3 4 // key值 5 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5]; 6 7 // 生成排序二叉树 8 keys.forEach(key => binaryTree.insert(key));
结果:
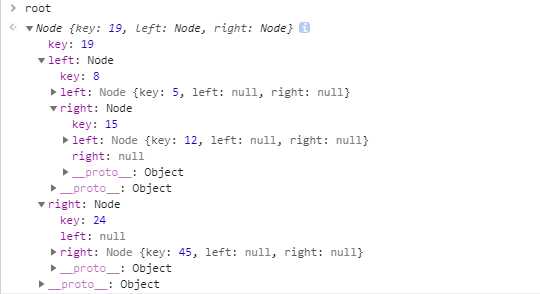
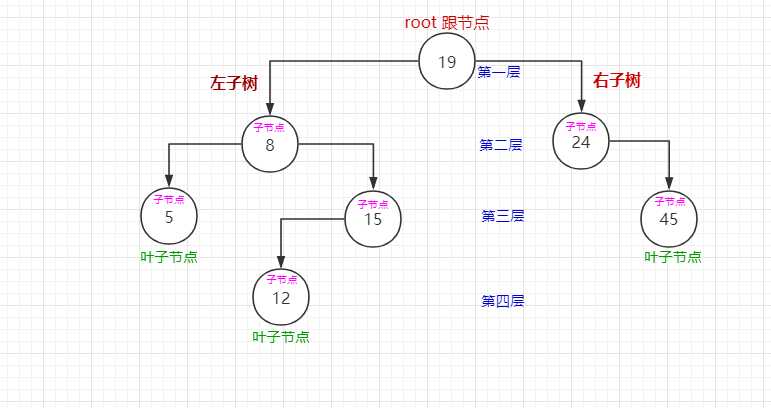
(1)以上图为例,中序遍历顺序为: 5 - 8 - 12 - 15 - 19 - 24 - 45。
(2)总是先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,接着遍历右子树。
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 // callback为访问节点时执行的操作 4 inorderTraversal(callback) {// api--中序遍历 5 method.inorderTraversalNode(this.root, callback); 6 } 7 } 8 9 method = { 10 ... 11 12 inorderTraversalNode(node, callback) { 13 if (node) {// 当前节点 14 method.inorderTraversalNode(node.left, callback);// 遍历左子树 15 callback(node);// 访问节点 16 method.inorderTraversalNode(node.right, callback);// 遍历右子树 17 } 18 }, 19 }; 20 21 // 中序遍历 22 binaryTree.inorderTraversal(node => console.log(node.key));
1 // key值 2 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5];
输入结果:5 - 8 - 12 - 15 - 19 - 24 - 45
(1)以上图为例,前序遍历顺序为: 19 - 8 - 5 - 15 - 12 - 24 - 45。
(2)总是先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,接着遍历右子树。
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 preOrderTraversal(callback) {// api--前序遍历 4 method.preOrderTraversalNode(this.root, callback); 5 } 6 } 7 8 method = { 9 ... 10 preOrderTraversalNode(node, callback) { 11 if (node) {// 当前节点 12 callback(node);// 访问节点 13 method.preOrderTraversalNode(node.left, callback);// 遍历左子树 14 method.preOrderTraversalNode(node.right, callback);// 遍历右子树 15 } 16 } 17 }; 18 19 // 前序遍历 20 binaryTree.preOrderTraversal(node => console.log(node.key));
1 // key值 2 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5];
输入结果:19 - 8 - 5 - 15 - 12 - 24 - 45
(1)以上图为例,后序遍历顺序为: 5 - 12 - 15 - 8 - 45 - 24 - 19。
(2)先遍历左子树,接着遍历右子树,最后访问根节点。
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 postOrderTraversal(callback) {// api--后序遍历 4 method.postOrderTraversalNode(this.root, callback); 5 } 6 } 7 8 method = { 9 ... 10 postOrderTraversalNode(node, callback) { 11 if (node) {// 当前节点 12 method.postOrderTraversalNode(node.left, callback);// 遍历左子树 13 method.postOrderTraversalNode(node.right, callback);// 遍历右子树 14 callback(node);// 访问节点 15 } 16 } 17 }; 18 19 // 后序遍历 20 binaryTree.postOrderTraversal(node => console.log(node.key));
1 // key值 2 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5];
输入结果:5 - 12 - 15 - 8 - 45 - 24 - 19
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 max() { 4 return method.maxNode(this.root); 5 } 6 } 7 8 method = { 9 ... 10 maxNode(node) { 11 if (node) { 12 while(node.right !== null) {// 右子树不为空时 13 node = node.right; 14 } 15 return node.key; 16 } 17 return null; 18 } 19 };
1 // key值 2 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5];
结果: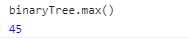
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 min() { 4 return method.minNode(this.root); 5 } 6 } 7 8 method = { 9 ... 10 minNode(node) { 11 if (node) { 12 while(node.left!== null) {// 左子树不为空时 13 node = node.left; 14 } 15 return node.key; 16 } 17 return null; 18 } 19 };
1 // key值 2 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5];
结果: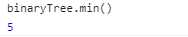
根据排序二叉树的特点,比较给定值与节点值,小于时进入节点左子树。大于时进入节点右子树。等于时返回真。层层对比,最后如果子树为空,则表示没有找到。
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 search(key) { 4 return method.searchNode(this.root, key); 5 } 6 } 7 8 method = { 9 ... 10 searchNode(node, key) { 11 if (node === null) {// 没有找到 12 return false; 13 } 14 if (key < node.key) {// 进入左子树 15 return method.searchNode(node.left, key); 16 } else if (key > node.key) {// 进入右子树 17 return method.searchNode(node.right, key); 18 } else {// 找到了 19 return true; 20 } 21 } 22 };
1 // key值 2 const keys = [19, 8, 15, 24, 45, 12, 5];
结果: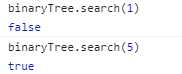
当删除的节点为叶子节点时,直接把叶子节点设置成空。如图:删除值为5的节点。
原:
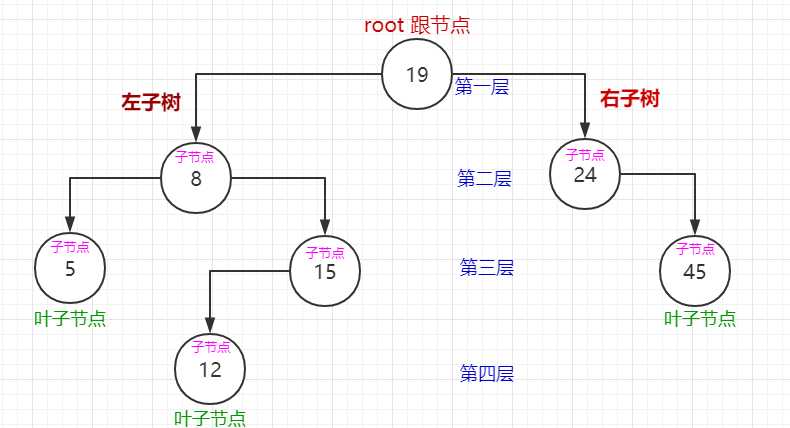
现:
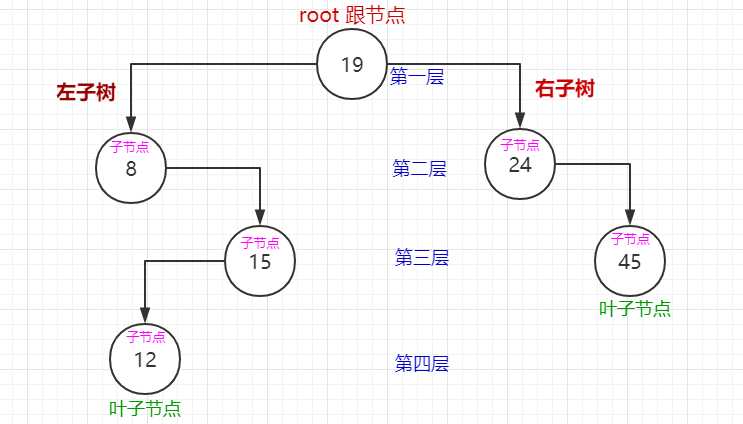
当删除的节点存在左子树时,把父节点的关系指针直接指向左子树。如图:删除值为15的节点。存在右子树时同理。
原:

现:
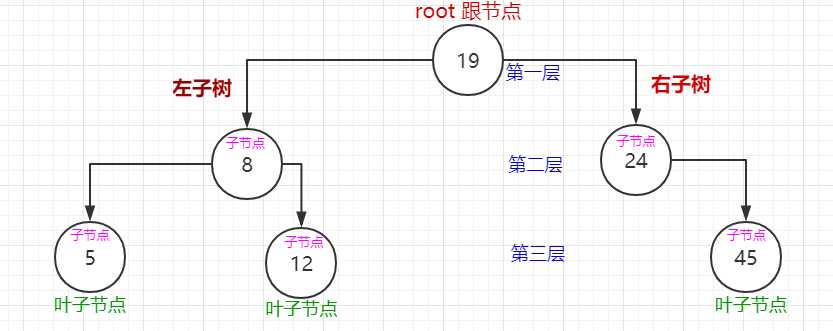
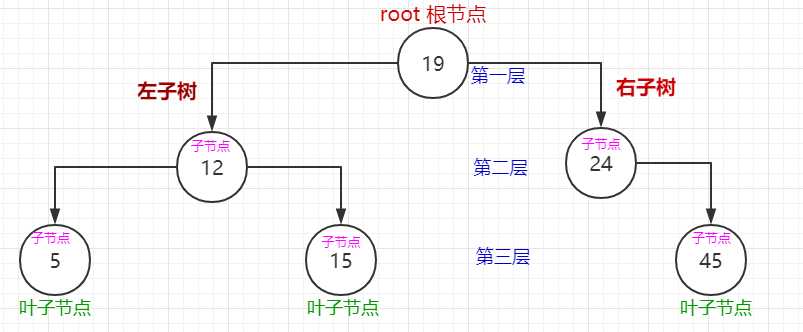
当节点存在左右子树时,先去右子树里找到最小值,然后用最小值替换节点值,最后进入右子树删除最小值对应的节点。如图:删除值为8的节点。
原:

现:
代码实现:
1 class BinaryTree { 2 ... 3 remove(key) { 4 this.root = method.removeNode(this.root, key); 5 } 6 } 7 8 method = { 9 ... 10 removeNode(node, key) { 11 if(node === null) {// 没有找到值对应的节点 12 return null; 13 } 14 if (key < node.key) {// 给定值小于当前节点值 15 node.left = method.removeNode(node.left, key); 16 return node; 17 } else if (key > node.key) {// 给定值大于当前节点值 18 node.right = method.removeNode(node.right, key); 19 return node; 20 } else {// 找到给定值对应的节点 21 if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {// 节点为叶子节点 22 node = null; 23 return node; 24 } 25 26 if (node.left === null) {// 节点存在右子树 27 node = node.right; 28 return node; 29 } else if (node.right === null) {// 节点存在左子树 30 node = node.left; 31 return node; 32 } 33 34 // 节点存在左右子树时,先去右子树里找到最小值,然后用最小值替换节点值,最后进入右子树删除最小值对应的节点。 35 const minKey = method.minNode(node.right); 36 node.key = minKey; 37 method.removeNode(node.right, minKey); 38 return node; 39 } 40 } 41 };
结果:
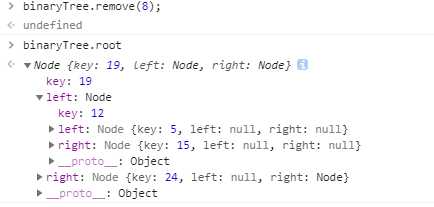

累死我了。。。
javascript/js实现 排序二叉树数据结构 学习随笔
标签:存在 数据 代码实现 后序遍历 rip 结构 bsp OLE 结果
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/caimuguodexiaohongmao/p/11123933.html