标签:value 数据结构 nio 创建 今天 insert server 英语 就是
对于行列转换的数据,通常也就是在做报表的时候用的比较多,之前也零零散散的看了一些,今天就来总结一下。
先创建一个用于演示的临时表:
create table #temp
(
年份 nvarchar(10) null,
月份 nvarchar(10) null,
数量 int null
)
insert into #temp(年份,月份,数量)
select ‘2015‘,‘1‘,‘5645‘ union
select ‘2015‘,‘2‘,‘1234‘ union
select ‘2015‘,‘3‘,‘7982‘ union
select ‘2016‘,‘1‘,‘6465‘ union
select ‘2016‘,‘2‘,‘7942‘ union
select ‘2016‘,‘3‘,‘8453‘ union
select ‘2017‘,‘1‘,‘4653‘ union
select ‘2017‘,‘2‘,‘1358‘ union
select ‘2017‘,‘3‘,‘7842‘
select * from #temp
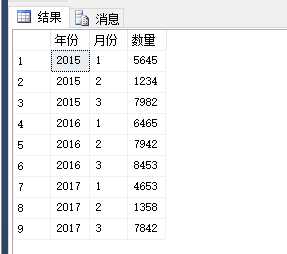
下面来实现一些需求:
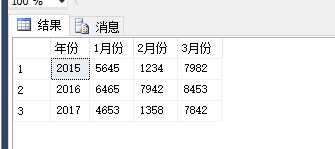
需求一,按年份分组,不同的月份为一列。
-- 按年份分组,不同的月份为一列 select t.年份, sum(case t.月份 when ‘1‘ then t.数量 end) ‘1月份‘, sum(case t.月份 when ‘2‘ then t.数量 end) ‘2月份‘, sum(case t.月份 when ‘3‘ then t.数量 end) ‘3月份‘ from #temp t group by t.年份
另外两种方法:
-- 使用左外连接查询 select t.年份,t1.数量 ‘1月份‘,t2.数量 ‘2月份‘,t3.数量 ‘3月份‘ from #temp t left join (select 年份,数量 from #temp where 月份=‘1‘) t1 on t.年份=t1.年份 left join (select 年份,数量 from #temp where 月份=‘2‘) t2 on t.年份=t2.年份 left join (select 年份,数量 from #temp where 月份=‘3‘) t3 on t.年份=t3.年份 group by t.年份,t1.数量,t2.数量,t3.数量 -- 使用自连接查询 select t.年份,t1.数量 ‘1月份‘,t2.数量 ‘2月份‘,t3.数量 ‘3月份‘ from #temp t, (select 年份,数量 from #temp where 月份=‘1‘) t1, (select 年份,数量 from #temp where 月份=‘2‘) t2, (select 年份,数量 from #temp where 月份=‘3‘) t3 where t.年份=t1.年份 and t.年份=t2.年份 and t.年份=t3.年份 group by t.年份,t1.数量,t2.数量,t3.数量
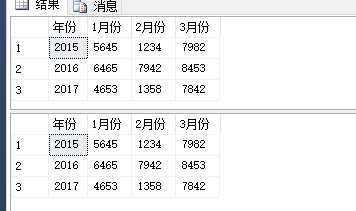
返回的结果都是一样的,可以看见这几种方法都是可以实现的(当然,可能还有更多的方法待发掘),不过比起第一种方法,后面这两种方法也太低效了吧,比如一年有12个月份的数据,有个七八年的,那得写多少个子查询、表连接的,而且第一种方法也不是我们想要的。那么就需要用到 Pivot 这种方法了。
Pivot 语法:
table_source -- 表名称,即数据源
PIVOT(
聚合函数(value_column) -- value_column 要转换为 列值 的列名
FOR pivot_column -- pivot_column 指定要转换的列
IN(<column_list>) -- column_list 自定义的目标列名
)
因为这里列名不允许指定为数字,真是无语。。。我重建了一个数据结构一模一样的表。
create table #temp
(
Name nvarchar(10) null,
Course nvarchar(10) null,
Score int null
)
insert into #temp(Name,Course,Score)
select ‘小李‘,‘语文‘,‘88‘ union
select ‘小李‘,‘数学‘,‘79‘ union
select ‘小李‘,‘英语‘,‘85‘ union
select ‘小明‘,‘语文‘,‘79‘ union
select ‘小明‘,‘数学‘,‘89‘ union
select ‘小明‘,‘英语‘,‘87‘ union
select ‘小红‘,‘语文‘,‘84‘ union
select ‘小红‘,‘数学‘,‘76‘ union
select ‘小红‘,‘英语‘,‘92‘
select * from #temp
go
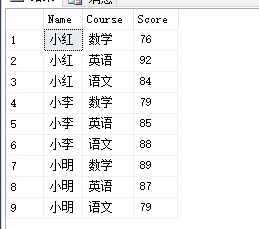
select Name 姓名, max(case Course when ‘语文‘ then Score end) 语文, max(case Course when ‘数学‘ then Score end) 数学, max(case Course when ‘英语‘ then Score end) 英语, sum(Score) 课程总分, cast(avg(Score) as decimal(18,2)) 课程平均分 from #temp group by Name
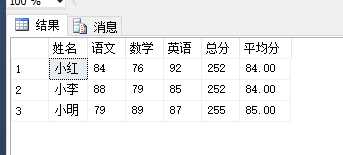
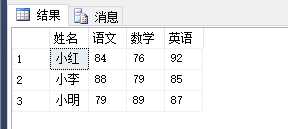
使用 Pivot 进行 行转列:
select a.Name 姓名,a.语文,a.数学,a.英语
from #temp
pivot
(
max(Score) -- 指定作为转换的列的值 的列名
for Course -- 指定要转换的列的列名
in(语文,数学,英语) -- 自定义的目标列名,即要转换列的不同的值作为列
)a
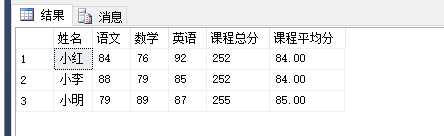
select a.Name 姓名,a.语文,a.数学,a.英语,b.SumScore 课程总分,b.AvgScore 课程平均分
from #temp
pivot
(
max(Score) -- 指定作为转换的列的值 的列名
for Course -- 指定要转换的列的列名
in(语文,数学,英语) -- 自定义的目标列名,即要转换列的不同的值作为列
)a,
(
select t.Name,sum(t.Score) SumScore,cast(avg(t.Score) as decimal(18,2)) AvgScore
from #temp t
group by t.Name
)b
where a.Name=b.Name
UnPivot 语法:
table_source -- 表名称,即数据源
UNPIVOT(
value_column -- value_column 要转换为 行值 的列名
FOR pivot_column -- pivot_column 指定要转换为指定的列
IN(<column_list>) -- column_list 目标列名
)
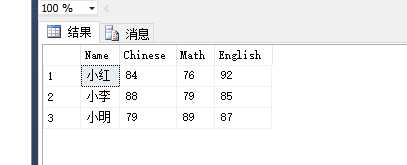
create table #temp
(
Name nvarchar(10) null,
Chinese int null,
Math int null,
English int null
)
insert into #temp(Name,Chinese,Math,English)
select ‘小李‘,‘88‘,‘79‘,‘85‘ union
select ‘小明‘,‘79‘,‘89‘,‘87‘ union
select ‘小红‘,‘84‘,‘76‘,‘92‘
select * from #temp
go
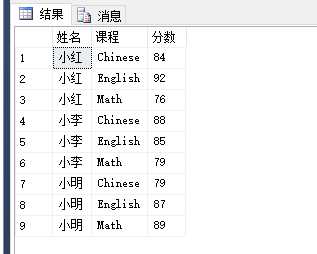
select t.Name 姓名,t.Course 课程,t.Score 分数 from (select t.Name,Course=‘Chinese‘,Score=Chinese from #temp t union all select t.Name,Course=‘Math‘,Score=Math from #temp t union all select t.Name,Course=‘English‘,Score=English from #temp t) t order by t.Name,t.Course
select t.Name 姓名,t.Course 课程,t.Score 分数 from (select t.Name,‘Chinese‘ Course,Chinese Score from #temp t union all select t.Name,‘Math‘,Math from #temp t union all select t.Name,‘English‘,English from #temp t) t order by t.Name,t.Course
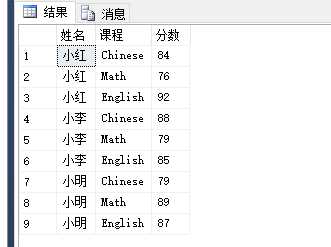
使用 UnPivot 进行 列转行:
select t.Name 姓名,t.Course 课程,t.Score 分数
from #temp
unpivot
(
Score for Course
in(Chinese,Math,English)
)t
SQL Server 使用 Pivot 和 UnPivot 实现行列转换
标签:value 数据结构 nio 创建 今天 insert server 英语 就是
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/shoshana-kong/p/11140092.html