标签:path Fix 文件比较 pattern 下载到本地 切换 实现原理 use 导入
在很多具体应用场景中,我们需要用到动态数据源的情况,比如多租户的场景,系统登录时需要根据用户信息切换到用户对应的数据库。又比如业务A要访问A数据库,业务B要访问B数据库等,都可以使用动态数据源方案进行解决。接下来,我们就来讲解如何实现动态数据源,以及在过程中剖析动态数据源背后的实现原理。
本教程案例基于 Spring Boot + Mybatis + MySQL 实现。
为方便我们初始化项目,Spring Boot给我们提供一个项目模板生成网站。
1. 打开浏览器,访问:https://start.spring.io/
2. 根据页面提示,选择构建工具,开发语言,项目信息等。
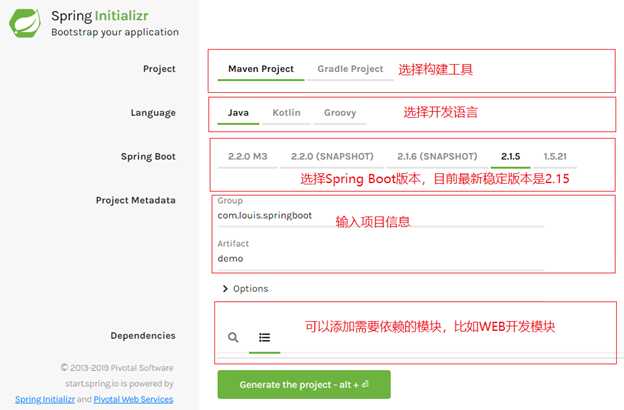
3. 点击 Generate the project,生成项目模板,生成之后会将压缩包下载到本地。
4. 使用IDE导入项目,我这里使用Eclipse,通过导入Maven项目的方式导入。
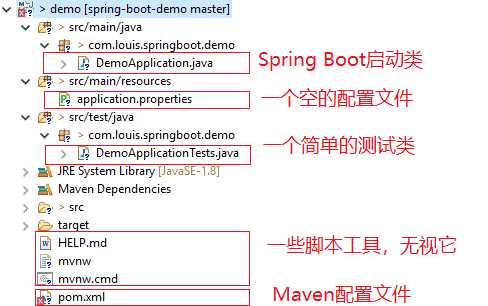
这里使用MySQL数据库,版本是8.0.16,在项目根目录下新建db目录,然后在其中编写一个数据库脚本文件。
在MySQL数据库新建一个master,slave数据库,然后在此数据库中执行下面的脚本创建项目用户表和用户数据。
脚本文件
SQL脚本内容
springboot.sql
-- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for sys_user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sys_user`; CREATE TABLE `sys_user` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ‘编号‘, `name` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘用户名‘, `nick_name` varchar(150) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘昵称‘, `avatar` varchar(150) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘头像‘, `password` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘密码‘, `salt` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘加密盐‘, `email` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘邮箱‘, `mobile` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘手机号‘, `status` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘状态 0:禁用 1:正常‘, `dept_id` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘机构ID‘, `create_by` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘创建人‘, `create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘创建时间‘, `last_update_by` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘更新人‘, `last_update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘更新时间‘, `del_flag` tinyint(4) DEFAULT ‘0‘ COMMENT ‘是否删除 -1:已删除 0:正常‘, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `name` (`name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=34 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT=‘用户管理‘; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of sys_user -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘1‘, ‘admin‘, ‘管理员‘, null, ‘bd1718f058d8a02468134432b8656a86‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘admin@qq.com‘, ‘13612345678‘, ‘1‘, ‘4‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-08-14 11:11:11‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-08-14 11:11:11‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘2‘, ‘liubei‘, ‘刘备‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘7‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:43:00‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2019-01-10 11:41:13‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘3‘, ‘zhaoyun‘, ‘赵云‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘7‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:43:44‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:43:52‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘4‘, ‘zhugeliang‘, ‘诸葛亮‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘7‘, ‘11‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:44:23‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:44:29‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘5‘, ‘caocao‘, ‘曹操‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘8‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:45:32‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2019-01-10 17:59:14‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘6‘, ‘dianwei‘, ‘典韦‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘10‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:45:48‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:45:57‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘7‘, ‘xiahoudun‘, ‘夏侯惇‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘8‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:46:09‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:46:17‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘8‘, ‘xunyu‘, ‘荀彧‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘10‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:46:38‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-11-04 15:33:17‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘9‘, ‘sunquan‘, ‘孙权‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘10‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:46:54‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:47:03‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘0‘, ‘zhouyu‘, ‘周瑜‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘11‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:47:28‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:48:04‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘11‘, ‘luxun‘, ‘陆逊‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘11‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:47:44‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:47:58‘, ‘0‘); INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (‘12‘, ‘huanggai‘, ‘黄盖‘, null, ‘fd80ebd493a655608dc893a9f897d845‘, ‘YzcmCZNvbXocrsz9dm8e‘, ‘test@qq.com‘, ‘13889700023‘, ‘1‘, ‘11‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:48:38‘, ‘admin‘, ‘2018-09-23 19:49:02‘, ‘0‘);
需要添加Spring Boot,Spring Aop,Mybatis,MySQL,Swagger相关依赖。Swagger方便用来测试接口。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.louis.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- spring boot -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring aop -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- swagger -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!-- 打包时拷贝MyBatis的映射文件 -->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/sqlmap/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
修改配置文件,添加两个数据源,可以是同一个主机地址的两个数据库master,slave,也可是两个不同主机的地址,根据实际情况配置。
application.yml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
master:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/master?useUnicode=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 123456
slave:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/slave?useUnicode=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 123456
在config包中添加一个swagger 配置类,在工程下新建 config 包并添加一个 SwaggerConfig 配置类。
SwaggerConfig.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("SpringBoot API Doc")
.description("This is a restful api document of Spring Boot.")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
启动类添加 exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}, 以禁用数据源默认自动配置。
数据源默认自动配置会读取 spring.datasource.* 的属性创建数据源,所以要禁用以进行定制。
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.louis.springboot") 是扫描范围,都知道不用多说。
DemoApplication.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) // 禁用数据源自动配置
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.louis.springboot")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
创建一个数据源配置类,主要做以下几件事情:
1. 配置 dao,model,xml mapper文件的扫描路径。
2. 注入数据源配置属性,创建master、slave数据源。
3. 创建一个动态数据源,并装入master、slave数据源。
4. 将动态数据源设置到SQL会话工厂和事务管理器。
如此,当进行数据库操作时,就会通过我们创建的动态数据源去获取要操作的数据源了。
package com.louis.springboot.demo.config;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.config.dds.DynamicDataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.louis.**.dao"}) // 扫描DAO
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean("master")
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource master() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("slave")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slave() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("dynamicDataSource")
public DataSource dynamicDataSource() {
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>(2);
dataSourceMap.put("master", master());
dataSourceMap.put("slave", slave());
// 将 master 数据源作为默认指定的数据源
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultDataSource(master());
// 将 master 和 slave 数据源作为指定的数据源
dynamicDataSource.setDataSources(dataSourceMap);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
// 配置数据源,此处配置为关键配置,如果没有将 dynamicDataSource作为数据源则不能实现切换
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource());
sessionFactory.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.louis.**.model"); // 扫描Model
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
sessionFactory.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath*:**/sqlmap/*.xml")); // 扫描映射文件
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
// 配置事务管理, 使用事务时在方法头部添加@Transactional注解即可
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dynamicDataSource());
}
}
我们上一步把这个动态数据源设置到了SQL会话工厂和事务管理器,这样在操作数据库时就会通过动态数据源类来获取要操作的数据源了。
动态数据源类集成了Spring提供的AbstractRoutingDataSource类,AbstractRoutingDataSource 中获取数据源的方法就是 determineTargetDataSource,而此方法又通过 determineCurrentLookupKey 方法获取查询数据源的key。
所以如果我们需要动态切换数据源,就可以通过以下两种方式定制:
1. 覆写 determineCurrentLookupKey 方法
通过覆写 determineCurrentLookupKey 方法,从一个自定义的 DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey() 获取数据源key值,这样在我们想动态切换数据源的时候,只要通过 DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(key) 的方式就可以动态改变数据源了。这种方式要求在获取数据源之前,要先初始化各个数据源到 DynamicDataSource 中,我们案例就是采用这种方式实现的,所以在 MybatisConfig 中把master和slave数据源都事先初始化到DynamicDataSource 中。
2. 可以通过覆写 determineTargetDataSource,因为数据源就是在这个方法创建并返回的,所以这种方式就比较自由了,支持到任何你希望的地方读取数据源信息,只要最终返回一个 DataSource 的实现类即可。比如你可以到数据库、本地文件、网络接口等方式读取到数据源信息然后返回相应的数据源对象就可以了。
DynamicDataSource.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.config.dds;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
/**
* 动态数据源实现类
* @author Louis
* @date Jun 17, 2019
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
/**
* 如果不希望数据源在启动配置时就加载好,可以定制这个方法,从任何你希望的地方读取并返回数据源
* 比如从数据库、文件、外部接口等读取数据源信息,并最终返回一个DataSource实现类对象即可
*/
@Override
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
return super.determineTargetDataSource();
}
/**
* 如果希望所有数据源在启动配置时就加载好,这里通过设置数据源Key值来切换数据,定制这个方法
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey();
}
/**
* 设置默认数据源
* @param defaultDataSource
*/
public void setDefaultDataSource(Object defaultDataSource) {
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(defaultDataSource);
}
/**
* 设置数据源
* @param dataSources
*/
public void setDataSources(Map<Object, Object> dataSources) {
super.setTargetDataSources(dataSources);
// 将数据源的 key 放到数据源上下文的 key 集合中,用于切换时判断数据源是否有效
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.addDataSourceKeys(dataSources.keySet());
}
}
动态数据源的切换主要是通过调用这个类的方法来完成的。在任何想要进行切换数据源的时候都可以通过调用这个类的方法实现切换。比如系统登录时,根据用户信息调用这个类的数据源切换方法切换到用户对应的数据库。
主要方法介绍:
1. 切换数据源
在任何想要进行切换数据源的时候都可以通过调用这个类的方法实现切换。
/**
* 切换数据源
* @param key
*/
public static void setDataSourceKey(String key) {
contextHolder.set(key);
}
2. 重置数据源
将数据源重置回默认的数据源。默认数据源通过 DynamicDataSource.setDefaultDataSource(ds) 进行设置。
/**
* 重置数据源
*/
public static void clearDataSourceKey() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
3. 获取当前数据源key
/**
* 获取数据源
* @return
*/
public static String getDataSourceKey() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
完整代码如下
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.config.dds;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 动态数据源上下文
* @author Louis
* @date Jun 17, 2019
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>() {
/**
* 将 master 数据源的 key作为默认数据源的 key
*/
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
return "master";
}
};
/**
* 数据源的 key集合,用于切换时判断数据源是否存在
*/
public static List<Object> dataSourceKeys = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 切换数据源
* @param key
*/
public static void setDataSourceKey(String key) {
contextHolder.set(key);
}
/**
* 获取数据源
* @return
*/
public static String getDataSourceKey() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
/**
* 重置数据源
*/
public static void clearDataSourceKey() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
/**
* 判断是否包含数据源
* @param key 数据源key
* @return
*/
public static boolean containDataSourceKey(String key) {
return dataSourceKeys.contains(key);
}
/**
* 添加数据源keys
* @param keys
* @return
*/
public static boolean addDataSourceKeys(Collection<? extends Object> keys) {
return dataSourceKeys.addAll(keys);
}
}
到这里,在任何想要动态切换数据源的时候,只要调用 DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(key) 就可以完成了。
接下来我们实现通过注解的方式来进行数据源的切换,原理就是添加注解(如@DataSource(value="master")),然后实现注解切面进行数据源切换。
创建一个动态数据源注解,拥有一个value值,用于标识要切换的数据源的key。
DataSource.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.config.dds;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 动态数据源注解
* @author Louis
* @date Jun 17, 2019
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DataSource {
/**
* 数据源key值
* @return
*/
String value();
}
创建一个AOP切面,拦截带 @DataSource 注解的方法,在方法执行前切换至目标数据源,执行完成后恢复到默认数据源。
DynamicDataSourceAspect.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.config.dds;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 动态数据源切换处理器
* @author Louis
* @date Jun 17, 2019
*/
@Aspect
@Order(-1) // 该切面应当先于 @Transactional 执行
@Component
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
/**
* 切换数据源
* @param point
* @param dataSource
*/
@Before("@annotation(dataSource))")
public void switchDataSource(JoinPoint point, DataSource dataSource) {
if (!DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.containDataSourceKey(dataSource.value())) {
System.out.println("DataSource [{}] doesn‘t exist, use default DataSource [{}] " + dataSource.value());
} else {
// 切换数据源
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(dataSource.value());
System.out.println("Switch DataSource to [" + DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey()
+ "] in Method [" + point.getSignature() + "]");
}
}
/**
* 重置数据源
* @param point
* @param dataSource
*/
@After("@annotation(dataSource))")
public void restoreDataSource(JoinPoint point, DataSource dataSource) {
// 将数据源置为默认数据源
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.clearDataSourceKey();
System.out.println("Restore DataSource to [" + DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey()
+ "] in Method [" + point.getSignature() + "]");
}
}
到这里,动态数据源相关的处理代码就完成了。
由于手动编写MyBatis的Model、DAO、XML映射文件比较繁琐,通常都会通过一些生成工具来生成。MyBatis官方也提供了生成工具(MyBaits Generator),另外还有一些基于官方基础上改进的第三方工具,比如MyBatis Plus就是国内提供的一款非常优秀的开源工具,网上相关教程比较多,这里就不再赘述了。
这里提供一些资料作为参考。
Mybatis Generator 官网:http://www.mybatis.org/generator/index.html
Mybatis Generator 教程:https://blog.csdn.net/testcs_dn/article/details/77881776
MyBatis Plus 官网: http://mp.baomidou.com/#/
MyBatis Plus 官网: http://mp.baomidou.com/#/quick-start
代码生成好之后,分別将MODEL、DAO、XML映射文件拷贝到相应的包里。
生成的用户类代码如下面所示。
SysUser.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.model;
import java.util.Date;
public class SysUser {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String nickName;
private String avatar;
private String password;
private String salt;
private String email;
private String mobile;
private Byte status;
private Long deptId;
private String createBy;
private Date createTime;
private String lastUpdateBy;
private Date lastUpdateTime;
private Byte delFlag;
// 省略setter和getter
}
接下来在SysUserMapper中添加一个查询全部的方法。
SysUserMapper.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser;
public interface SysUserMapper {
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Long id);
int insert(SysUser record);
int insertSelective(SysUser record);
SysUser selectByPrimaryKey(Long id);
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(SysUser record);
int updateByPrimaryKey(SysUser record);
/**
* 查询全部用户
* @return
*/
List<SysUser> selectAll();
}
然后在SysUserMapper.xml中实现查询全部方法的SQL语句。
SysUserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.louis.springboot.demo.dao.SysUserMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser">
<id column="id" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="id" />
<result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" />
<result column="nick_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="nickName" />
<result column="avatar" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="avatar" />
<result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" />
<result column="salt" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="salt" />
<result column="email" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="email" />
<result column="mobile" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="mobile" />
<result column="status" jdbcType="TINYINT" property="status" />
<result column="dept_id" jdbcType="BIGINT" property="deptId" />
<result column="create_by" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="createBy" />
<result column="create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="createTime" />
<result column="last_update_by" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="lastUpdateBy" />
<result column="last_update_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" property="lastUpdateTime" />
<result column="del_flag" jdbcType="TINYINT" property="delFlag" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id, name, nick_name, avatar, password, salt, email, mobile, status, dept_id, create_by,
create_time, last_update_by, last_update_time, del_flag
</sql>
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Long" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from sys_user
where id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</select>
<delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
delete from sys_user
where id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</delete>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser">
insert into sys_user (id, name, nick_name,
avatar, password, salt,
email, mobile, status,
dept_id, create_by, create_time,
last_update_by, last_update_time, del_flag
)
values (#{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{nickName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{avatar,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{salt,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{mobile,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{status,jdbcType=TINYINT},
#{deptId,jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{createBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
#{lastUpdateBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{lastUpdateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP}, #{delFlag,jdbcType=TINYINT}
)
</insert>
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser">
insert into sys_user
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
id,
</if>
<if test="name != null">
name,
</if>
<if test="nickName != null">
nick_name,
</if>
<if test="avatar != null">
avatar,
</if>
<if test="password != null">
password,
</if>
<if test="salt != null">
salt,
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email,
</if>
<if test="mobile != null">
mobile,
</if>
<if test="status != null">
status,
</if>
<if test="deptId != null">
dept_id,
</if>
<if test="createBy != null">
create_by,
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time,
</if>
<if test="lastUpdateBy != null">
last_update_by,
</if>
<if test="lastUpdateTime != null">
last_update_time,
</if>
<if test="delFlag != null">
del_flag,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
#{id,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="name != null">
#{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="nickName != null">
#{nickName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="avatar != null">
#{avatar,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="password != null">
#{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="salt != null">
#{salt,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="email != null">
#{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="mobile != null">
#{mobile,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="status != null">
#{status,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
<if test="deptId != null">
#{deptId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="createBy != null">
#{createBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
#{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="lastUpdateBy != null">
#{lastUpdateBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="lastUpdateTime != null">
#{lastUpdateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="delFlag != null">
#{delFlag,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser">
update sys_user
<set>
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="nickName != null">
nick_name = #{nickName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="avatar != null">
avatar = #{avatar,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="password != null">
password = #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="salt != null">
salt = #{salt,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email = #{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="mobile != null">
mobile = #{mobile,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="status != null">
status = #{status,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
<if test="deptId != null">
dept_id = #{deptId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="createBy != null">
create_by = #{createBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time = #{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="lastUpdateBy != null">
last_update_by = #{lastUpdateBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="lastUpdateTime != null">
last_update_time = #{lastUpdateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="delFlag != null">
del_flag = #{delFlag,jdbcType=TINYINT},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser">
update sys_user
set name = #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
nick_name = #{nickName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
avatar = #{avatar,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
password = #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
salt = #{salt,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
email = #{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
mobile = #{mobile,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
status = #{status,jdbcType=TINYINT},
dept_id = #{deptId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
create_by = #{createBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
create_time = #{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
last_update_by = #{lastUpdateBy,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
last_update_time = #{lastUpdateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
del_flag = #{delFlag,jdbcType=TINYINT}
where id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</update>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from sys_user
</select>
</mapper>
接着编写一个服务接口,添加一个查询全部的方法。
SysUserService.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser;
public interface SysUserService {
/**
* 查找所有用户
* @return
*/
List<SysUser> findAll();
}
继续编写服务实现类,并通过调用DAO来完成查询方法。
package com.louis.springboot.demo.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.dao.SysUserMapper;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.model.SysUser;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.service.SysUserService;
@Service
public class SysUserServiceImpl implements SysUserService {
@Autowired
private SysUserMapper sysUserMapper;
@Override
public List<SysUser> findAll() {
return sysUserMapper.selectAll();
}
}
最后编写一个控制器,包含两个查询方法,分别注解 master 和 slave 数据源。
SysUserController.java
package com.louis.springboot.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.config.dds.DataSource;
import com.louis.springboot.demo.service.SysUserService;
/**
* 用户控制器
* @author Louis
* @date Jun 17, 2019
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class SysUserController {
@Autowired
private SysUserService sysUserService;
@DataSource(value="master")
@PostMapping(value="/findAll")
public Object findAll() {
return sysUserService.findAll();
}
@DataSource(value="slave")
@PostMapping(value="/findAll2")
public Object findAll2() {
return sysUserService.findAll();
}
}
到这里,相关代码就完成了,接下来,我们来测试一下接口。
1. 右键项目 -> Run as -> Maven install,开始执行Maven构建,第一次会下载Maven依赖,可能需要点时间,如果出现如下信息,就说明项目编译打包成功了。
2. 右键文件 DemoApplication.java -> Run as -> Java Application,开始启动应用,当出现如下信息的时候,就说明应用启动成功了,默认启动端口是8080。
3. 打开浏览器,访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html,进入swagger接口文档界面。
为了区分master和slave的数据,我们把slave数据库的管理员记录的昵称修改为超级管理员。
然后我们首先测试findAll接口,最终返回结果如下,管理员记录昵称为“管理员“,说明查询的是master数据库。
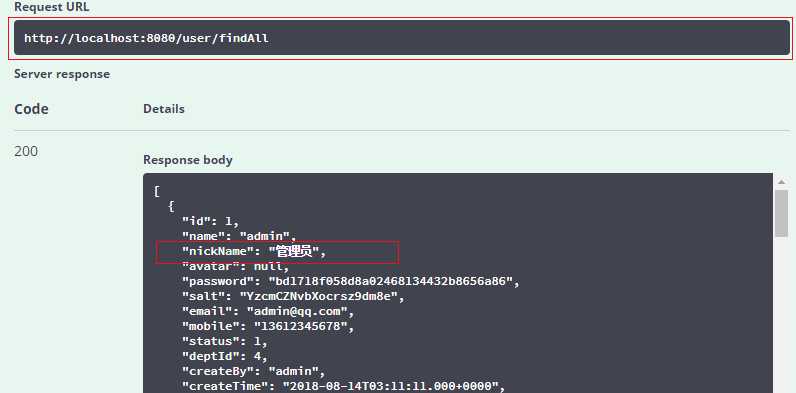
接着我们测试findAll2接口,最终返回结果如下,可以看到管理员记录昵称为“超级管理员“,说明查询的是slave数据库。
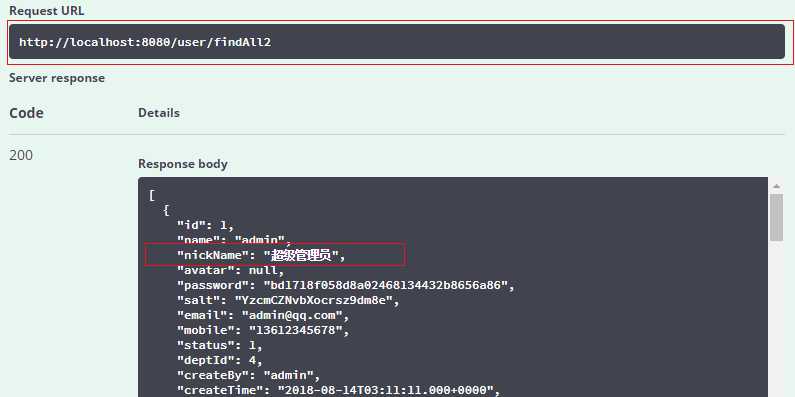
现在我们来整体分析一下动态数据源的实现流程,整个过程大概是这样的。
首先,我们在配置文件中配置了我们需要的两个数据源,当然你也可以配多个。
application.yml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
master:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/master?useUnicode=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 123456
slave:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/slave?useUnicode=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 123456
然后我们在MybatisConfig配置类中,加载了我们的数据源,并通过dynamicDataSource.setDataSources(dataSourceMap)将我们的数据源里边保存起来。
MybatisConfig.java
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.louis.**.dao"}) // 扫描DAO
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean("master")
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource master() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("slave")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slave() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("dynamicDataSource")
public DataSource dynamicDataSource() {
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>(2);
dataSourceMap.put("master", master());
dataSourceMap.put("slave", slave());
// 将 master 数据源作为默认指定的数据源
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultDataSource(master());
// 将 master 和 slave 数据源作为指定的数据源
dynamicDataSource.setDataSources(dataSourceMap);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
// 配置数据源,此处配置为关键配置,如果没有将 dynamicDataSource作为数据源则不能实现切换
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource());
sessionFactory.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.louis.**.model"); // 扫描Model
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
sessionFactory.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath*:**/sqlmap/*.xml")); // 扫描映射文件
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
// 配置事务管理, 使用事务时在方法头部添加@Transactional注解即可
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dynamicDataSource());
}
}
其实在使用了AbstractRoutingDataSource之后,代码执行数据库操作时,是通过AbstractRoutingDataSource的determineTargetDataSource方法来获取要访问的数据源的,而determineTargetDataSource又会通过determineCurrentLookupKey来获取数据源key,然后根据这个key去查找数据源。所以这里就衍生了两种动态切换数据源的方法,一种是直接覆盖determineTargetDataSource方法,返回自己需要的数据源,或者通过覆盖determineCurrentLookupKey来获取自定义的key,然后通过key去获取数据源。我们这里就采用第二种方法,并且我们把key保存到上下文中,通过DynamicDataSourceContextHolder来设置和获取,这样,只要我们在需要的时候调用DynamicDataSourceContextHolder的设置方法动态改变key值,就可以达到动态读取数据源的目的了。
DynamicDataSource.java
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
/**
* 如果不希望数据源在启动配置时就加载好,可以定制这个方法,从任何你希望的地方读取并返回数据源
* 比如从数据库、文件、外部接口等读取数据源信息,并最终返回一个DataSource实现类对象即可
*/
@Override
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
return super.determineTargetDataSource();
}
/**
* 如果希望所有数据源在启动配置时就加载好,这里通过设置数据源Key值来切换数据,定制这个方法
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey();
}
/**
* 设置默认数据源
* @param defaultDataSource
*/
public void setDefaultDataSource(Object defaultDataSource) {
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(defaultDataSource);
}
/**
* 设置数据源
* @param dataSources
*/
public void setDataSources(Map<Object, Object> dataSources) {
super.setTargetDataSources(dataSources);
// 将数据源的 key 放到数据源上下文的 key 集合中,用于切换时判断数据源是否有效
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.addDataSourceKeys(dataSources.keySet());
}
}
通过上面讲解我们已经知道只要在需要切换数据源的时候通过DynamicDataSourceContextHolder设置一下key值就可以了,那么如何可以实现指定不同方法可以不同数据库呢,我们这里添加了一个名为DataSource的注解,只要在需要制定数据源的方法上加上@DataSource(value="数据源名称")就可以了。如我们的SysUserController分别指定了findAll访问master数据源,findAll2访问slave数据源。
SysUserController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class SysUserController {
@Autowired
private SysUserService sysUserService;
@DataSource(value="master")
@PostMapping(value="/findAll")
public Object findAll() {
return sysUserService.findAll();
}
@DataSource(value="slave")
@PostMapping(value="/findAll2")
public Object findAll2() {
return sysUserService.findAll();
}
}
之所以加了数据源注解就能使用数据源切换,是因为我们通过Spring AOP实现了一个DynamicDataSourceAspect切面,这个切面能够在添加有数据源注解的方法执行的时候,先行把数据源切换到注解提供的目标数据源,并且如果有需要的话,在数据访问执行完毕后清理和切换回先前的数据源。
DynamicDataSourceAspect.java
@Aspect
@Order(-1) // 该切面应当先于 @Transactional 执行
@Component
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
/**
* 切换数据源
* @param point
* @param dataSource
*/
@Before("@annotation(dataSource))")
public void switchDataSource(JoinPoint point, DataSource dataSource) {
if (!DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.containDataSourceKey(dataSource.value())) {
System.out.println("DataSource [{}] doesn‘t exist, use default DataSource [{}] " + dataSource.value());
} else {
// 切换数据源
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(dataSource.value());
System.out.println("Switch DataSource to [" + DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey()
+ "] in Method [" + point.getSignature() + "]");
}
}
/**
* 重置数据源
* @param point
* @param dataSource
*/
@After("@annotation(dataSource))")
public void restoreDataSource(JoinPoint point, DataSource dataSource) {
// 将数据源置为默认数据源
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.clearDataSourceKey();
System.out.println("Restore DataSource to [" + DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey()
+ "] in Method [" + point.getSignature() + "]");
}
}
MyBatis 官网:http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
MyBatis Generator 官网:http://www.mybatis.org/generator/index.html
MyBatis Plus 官网: http://mp.baomidou.com/#/quick-start
标签:path Fix 文件比较 pattern 下载到本地 切换 实现原理 use 导入
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/7788IT/p/11143480.html