标签:延时 scale 顺序 amp view wip end console span
一、前言
本文主要涉及:
二、主要内容
(1)常见的touch事件
touch事件是移动端的触摸事件 并且是一组事件。
touchstart 当手指触摸到屏幕的时候会触发
touchmove 当手指在屏幕上来回滑动的时候会触发
touchend 当手指离开屏幕的时候会触发
touchcancel 当被迫终止滑动的时候触发
(2)分析常用的事件对象
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <title>Title</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box{ width: 200px; height: 200px; background: pink; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <script> window.onload = function () { var box = document.querySelector(‘.box‘); box.addEventListener(‘touchstart‘,function (e) { console.log(‘start‘); console.log(e); //打印出触摸开始的事件对象 }); box.addEventListener(‘touchmove‘,function (e) { console.log(‘move‘); console.log(e);//打印出触摸过程中的事件对象 }); box.addEventListener(‘touchend‘,function (e) { console.log(‘end‘); console.log(e);//打印出触摸结束的事件对象 }); /*box.addEventListener(‘click‘,function (e) { console.log(‘click‘); console.log(e); });*/ } </script> </body> </html>
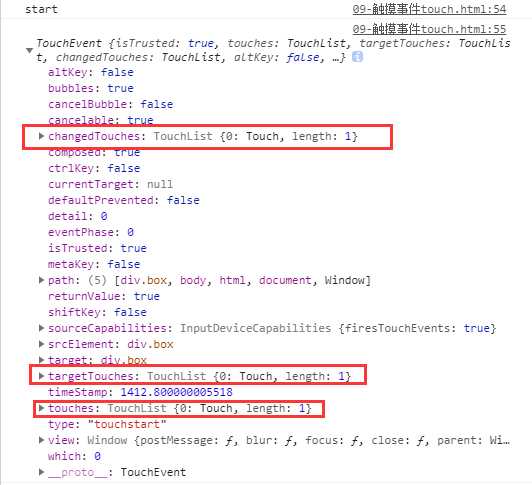
start:
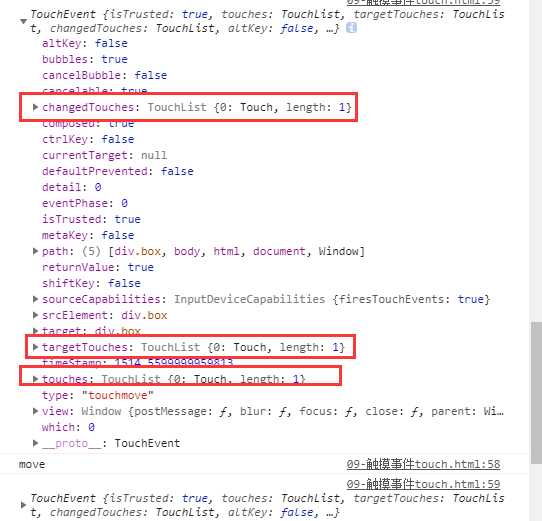
move:
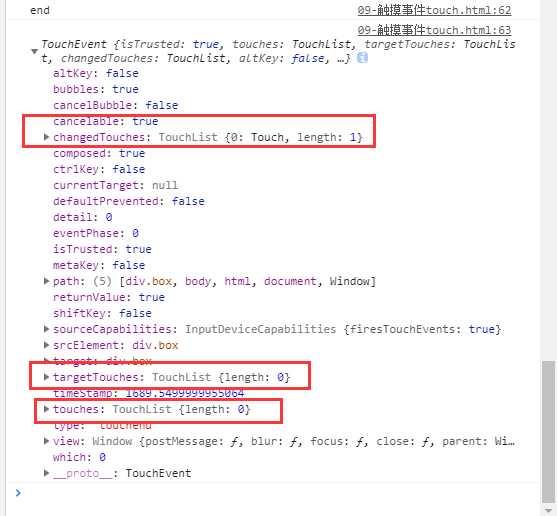
end
(3)触摸事件涉及到的事件对象
| TouchList | 触摸点(一个手指触摸就是一个触发点,和屏幕的接触点的个数)的集合 |
| changedTouches | 改变后的触摸点集合 |
| targetTouches | 当前元素的触发点集合 |
| touches | 页面上所有触发点集合 |
(1)分析:滑动实现的原理就是让触摸的元素随着手指的滑动做位置的改变。置的改变需要当前手指的坐标。每个触摸点中会记录当前触摸点的坐标 e.touches[0]
(2)移动端的手势事件具体实现
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <title>Title</title> <style> body { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background: pink; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <script> window.onload = function () { /*1. 理解移动端的手势事件*/ /*2. swipe swipeLeft swipeRight swipeUp swipeDown */ /*3. 左滑和右滑手势怎么实现*/ var bindSwipeEvent = function (dom,leftCallback,rightCallback) { /*手势的条件*/ /*1.必须滑动过*/ /*2.滑动的距离50px*/ var isMove = false; var startX = 0; var distanceX = 0; dom.addEventListener(‘touchstart‘,function (e) { startX = e.touches[0].clientX; }); dom.addEventListener(‘touchmove‘,function (e) { isMove = true; var moveX = e.touches[0].clientX; distanceX = moveX - startX; }); dom.addEventListener(‘touchend‘,function (e) { /*滑动结束*/ if(isMove && Math.abs(distanceX) > 50){ if(distanceX > 0){ rightCallback && rightCallback.call(this,e); }else{ leftCallback && leftCallback.call(this,e); } } /*重置参数*/ isMove = false; startX = 0; distanceX = 0; }); } bindSwipeEvent(document.querySelector(‘.box‘),function (e) { console.log(this); console.log(e); console.log(‘左滑手势‘); },function (e) { console.log(this); console.log(e); console.log(‘右滑手势‘); }); } </script> </body> </html>
(1)出现的原因:移动端的tap事件 轻触 轻击响应时间快。但是在移动端也有滑动事件,为了区别手指在移动端是滑动事件还是点击事件。当点击后会有300ms延时来区分到底用户要做的是滑动事件还是点击事件。这样会影响用户体验。
(2)解决方案
方案一:使用tap事件(不是移动端原生事件,通过touch相关事件衍生过来)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <title>Title</title> <style> body { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background: pink; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <script> window.onload = function () { /*使用tap事件*/ /*1. 响应的速度比click要快 150ms */ /*2. 不能滑动*/ var bindTapEvent = function (dom, callback) { /*事件的执行顺序*/ /*在谷歌浏览器模拟看不到300ms的效果*/ /*在真机上面才能看看到延时效果*/ var startTime = 0; var isMove = false; dom.addEventListener(‘touchstart‘, function () { startTime = Date.now();//获取到手指刚放下去的事件 }); dom.addEventListener(‘touchmove‘, function () { //console.log(‘touchmove‘); isMove = true; //滑动的时候置为true }); dom.addEventListener(‘touchend‘, function (e) { //console.log(‘touchend‘); console.log((Date.now() - startTime)); //当滑动的时间小于150ms, 并且isMove=false的时候,为点击 if ((Date.now() - startTime) < 150 && !isMove) { callback && callback.call(this, e); } startTime = 0; isMove = false; }); /*dom.addEventListener(‘click‘,function () { //console.log(‘click‘); });*/ } bindTapEvent(document.querySelector(‘.box‘), function (e) { console.log(this); console.log(e); console.log(‘tap事件‘) }); } </script> </body> </html>
方案二:使用插件fastclick.min.js
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <title>Title</title> <style> body { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background: pink; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <!-- 1. tap事件 轻击 轻触 (响应速度快) 2. 移动端也有click事件 (在移动为了区分是滑动还是点击,click点击延时300ms) 3. 影响用户体验 响应太慢了。 4. 解决方案: 4.1 使用tap事件(不是移动端原生事件,通过touch相关事件衍生过来) (zepto.js tap事件)了解其原理 4.2 使用一个叫:fastclick.js 提供移动端click响应速度的 4.2.1 下载:https://cdn.bootcss.com/fastclick/1.0.6/fastclick.min.js 4.2.2 使用: --> <script src="../js/fastclick.min.js"></script> <script> /*当页面的dom元素加载完成*/ document.addEventListener(‘DOMContentLoaded‘, function() { /*初始化方法*/ FastClick.attach(document.body); }, false); /*正常使用click事件就可以了*/ </script> </body> </html>
三、总结
web移动端_移动端的左右手势以及tap事件(解决移动端点击时出现的300ms毫秒延时问题)
标签:延时 scale 顺序 amp view wip end console span
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xxm980617/p/11207355.html