标签:出现 int start color end substring eve pre 对象 ever
String由多个字符组成的一串数据
字符串其本质是一个字符数组
字符串是常量,一旦被赋值就不能改变
String s1 = new String("hello"); //构造方法 String s2 = "hello"; //直接赋值方式
其中的区别
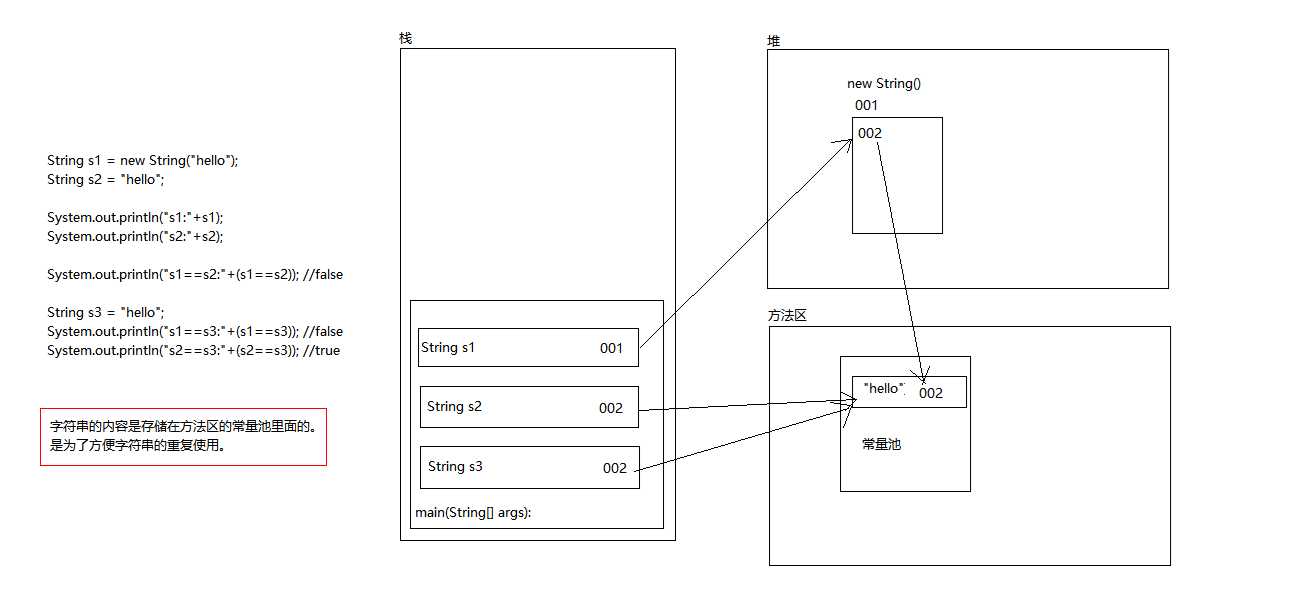
== 的意义:
基本数据类型:比较的是基本数据类型的值是否相同
引用数据类型:比较的是引用数据类型的地址值是否相同
equals( ) 比较字符串内容是否相同
equalsIgnoreCase( )比较字符串的内容是否相同忽略大小写
startsWith( String s ) 判断字符串对象是否以 s 开头
endsWith( String s ) 判断字符串对象是否以 s 结尾
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "hello"; String s3 = "Hello"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); System.out.println(s3.startsWith("hell")); System.out.println(s1.endsWith("llo")); }
运行结果:
true true false true
length( )获取字符串的长度,也就是字符的个数
charAt( int index ) 获取指定索引处的字符
indexOf(String s ) 获取s在字符串对象中第一次出现的索引
substring(int start):从start开始截取字符串
substring(int start,int end):从start开始,到end结束截取字符串。【start,end)
public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "hello world"; System.out.println(s.length()); System.out.println("--------------"); System.out.println(s.charAt(4)); System.out.println(s.indexOf("l")); System.out.println(s.substring(7,9)); System.out.println(s.substring(5)); }
运行结果:
11 o 2 or world
char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组
String toLowerCase():把字符串转换为小写字符串
String toUpperCase():把字符串转换为大写字符串
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "abcde"; //char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组 char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); for(int x=0; x<chs.length; x++) { System.out.println(chs[x]); } System.out.println("-----------"); //String toLowerCase():把字符串转换为小写字符串 System.out.println("HelloWorld".toLowerCase()); //String toUpperCase():把字符串转换为大写字符串 System.out.println("HelloWorld".toUpperCase()); }
运行结果:
a b c d e ----------- helloworld HELLOWORLD
String trim() 去除字符串两端空格
String[] split(String str) 按照指定符号分割字符串
区别:1、在这方面运行速度快慢为:StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String
String最慢的原因:String为字符串常量,而StringBuilder和StringBuffer均为字符串变量
2、在线程安全上,StringBuilder是线程不安全的,而StringBuffer是线程安全的
3、String:适用于少量的字符串操作的情况
StringBuilder:适用于单线程下在字符缓冲区进行大量操作的情况
StringBuffer:适用多线程下在字符缓冲区进行大量操作的情况
capacity():返回当前容量 (理论值)
length():返回长度(已经存储的字符个数)
append(任意类型):添加数据,并返回自身对象
reverse() 反转字符串功能
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建对象 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); System.out.println("sb:"+sb); System.out.println("sb.capacity():"+sb.capacity()); System.out.println("sb.length():"+sb.length()); }
运行结果:
sb: sb.capacity():16 sb.length():0
添加数据以及反转字符串
public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("hello"); sb.append("wordld"); //链式编程(因为sb返回的是个对象所以可以继续.方法) //sb.append("hello").append("world").append(true).append(100); System.out.println(sb); sb.reverse(); System.out.println(sb); }
运行结果:
hellowordld
dldrowolleh
StringBuilder -- String
public String toString():通过toString()就可以实现把StringBuilder转成String
String -- StringBuilder
StringBuilder(String str):通过构造方法就可以实现把String转成StringBuilder
标签:出现 int start color end substring eve pre 对象 ever
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/viperqy/p/11273625.html