标签:delete 获取 ext 不用 条件 jdbc原理 col sof upd
JDBC学过但又属于很容易忘记的那种,每次要用到,都要看下连接模式。每次找又很费时间,总之好麻烦呀呀呀,所以写篇博客,总结下原理和常用接口,要是又忘了可以直接来博客上看,嘿嘿。
一、什么是JDBC
1、JDBC全称是 Java DataBase Connectivity,可以为多种关系型数据库DBMS提供统一的访问方式,主要目的是用Java来操作数据库。
2、JDBC API主要负责三个功能:(1)与数据库建立连接(2)发送SQL语句给数据库(3)数据库将结果返回
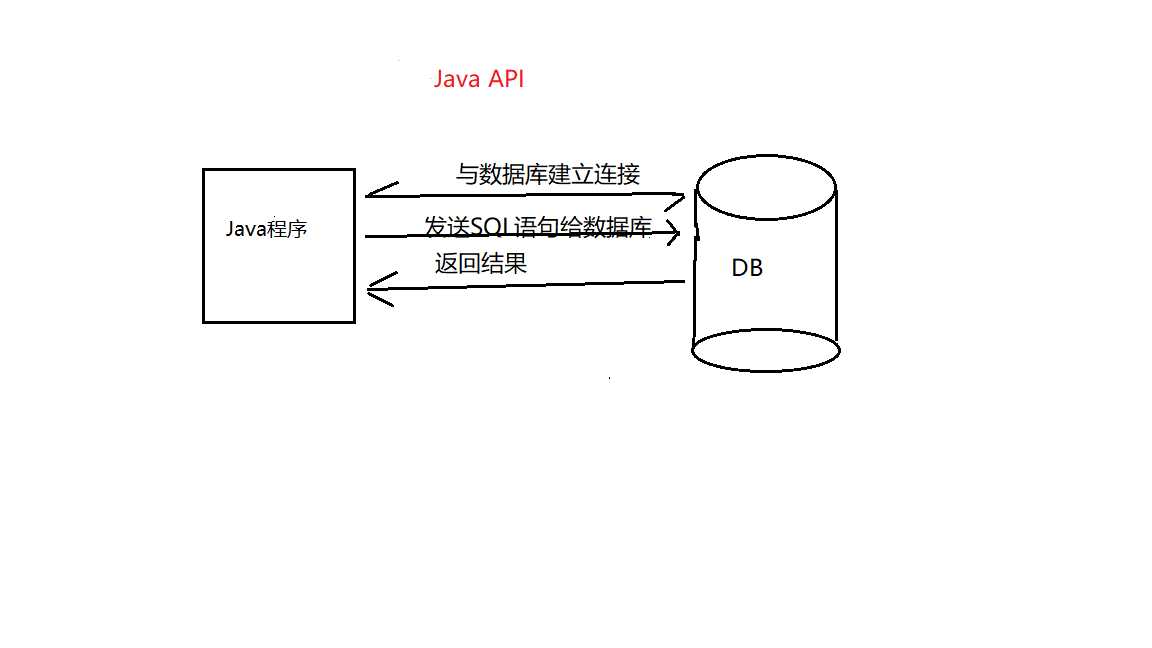
具体过程大致是这样子的:
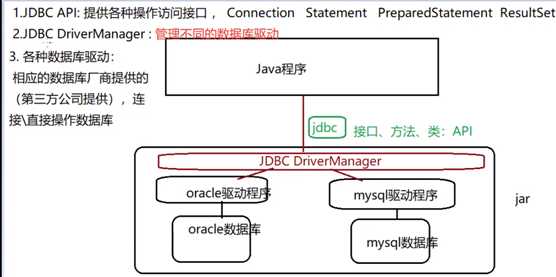
3、实现方法:(1)DriverManager:管理jdbc驱动(2)Connection 连接数据库(3)Statement(PreparedStatement)增删改查 CallableStatement 调用数据库的存储过程和存储函数 (4)ResultSet 结果集
4、实现步骤:(1)导入驱动,加载具体驱动类(2)与数据库建立连接(3)执行SQL语句(4)返回结果
5、常见数据库 oracle,mysql,SQLServer的加载驱动
oracle---具体驱动类:oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver 连接字符串:jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost(ip地址):1521:ORCL
mysql---具体驱动类:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 连接字符串:jdbc:mysql://localhost(ip地址):3306/数据库实名
SQLServer---具体驱动类:com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver 连接字符串:jdbc.microsoft.sqlserver:localhost(ip地址):1433;数据库实名
6、举个实例(以mysql数据库为例)实现对数据库增删改 查
建一个JDBCDemo
public class JDBCDemo { private String driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; private String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"; private String username="root"; private String password="root"; Connection conn=null; Statement statement=null; ResultSet set=null; public void updateSql(){ try{ //加载驱动类 Class.forName(driver); //与数据库建立连接 conn= DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); //发送SQL语句 statement=conn.createStatement(); //插入数据 String sql="insert into user(username,password) values(‘114‘,‘1234‘)"; //修改数据 //String sql="update user set password=‘1232‘ where id=2" //删除数据 //String sql= "delete from user where id=2"; //sql语句结果,一般进行 增删改 的SQL语句用excuteUpdate int count=statement.executeUpdate(sql); if(count>0){ System.out.println("操作成功"); }else{ System.out.println("操作失败"); } }catch(ClassNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if (statement == null) {//用判断来防止statement空异常 statement.close(); } if (conn == null) { conn.close(); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } public void querySql(){ try{ //加载驱动类 Class.forName(driver); //与数据库建立连接 conn= DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); //发送SQL语句 statement=conn.createStatement(); String sql="select * from user where username=‘111‘ and password=‘1234‘ "; //返回结果集 set=statement.executeQuery(sql); while(set.next()){
//用两种方式获取值,一种是根据列名,一种是所在的列数 String name=set.getString("username"); String pass=set.getString("password"); //String name=set.getString(2); // String pass=set.getString(3); System.out.println(name+","+pass); } }catch(ClassNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if (statement == null) {//用判断来防止statement空异常 statement.close(); } if (conn == null) { conn.close(); } }catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
上述代码主要使用Statement方式发送SQL,还有preparedStatement方式。他们之间有相同点,但是又不是一样,下面就来比较下Statement和PreparedStatement
二、Statement与PreparedStatement的比较
Statement:(1)产生方式:Connection.createStatement()(2)增删改 executeUpdate()(3)查询 executeQuery()(4)一般将SQL语句放在executeUpdate()中
PreparedStatement:(1)产生方式:Connection.prepareStatement()(2)增删改 executeUpdate()(3)查询 executeQuery()(4)一系列SetXXX方法(5)将SQL放在Connection.PrepareStatement(SQL)(6)需要预编译
查看PreparedStatement的源码 ,可知PreparedStatement继承Statement,Statement里有的方法PreparedStatement都有,但是PreparedStatement还有很多SetXXX方法
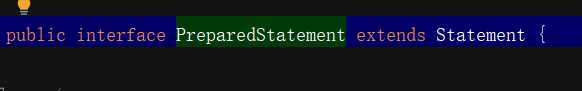
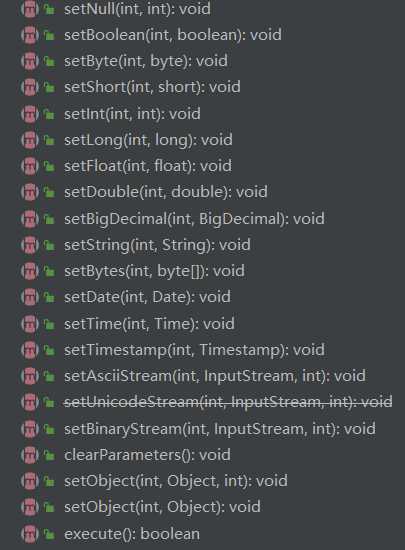
用代码直观的体现两者的区别:
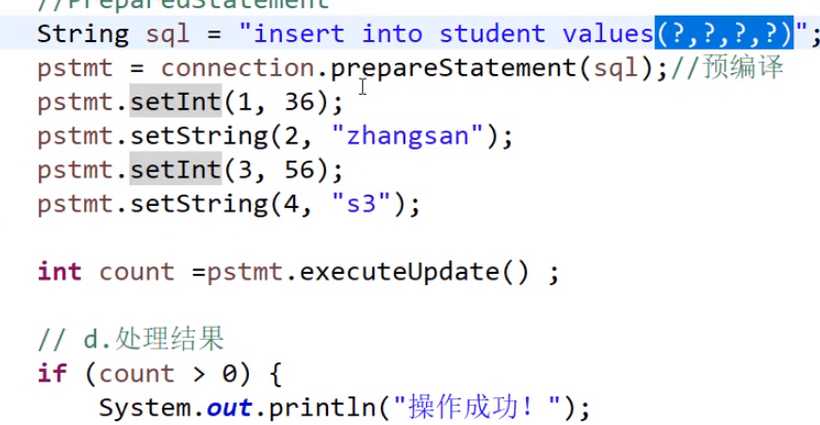
除了这部分之外,其他和上述代码一样,多了一步预编译。
三、PreparedStatement较Statement的优势
(1)编码更加简洁灵活:在PreparedStatement中SQL语句后的查询条件,插入的值可以用占位符(?)来表示,不用像Statement一样写具体的值,只需要调用PreparedStatement中的SetXXX方法赋值即可。
(2)提高性能:如果要执行一条SQL语句100回,Statement需要connection,createStatement(sql)语句编译SQL100次,PreparedStatemnet只需要编译SQL语句一回(即connection.PreparedStatement(sql)),重复执行100次preparedStatement.executeQuery();减少编译SQL次数,提高性能。
(3)安全性高,可以有效防止SQL注入的风险:Statement存在SQL注入的风险,PreparedStatement可以防止SQL注入的风险。
标签:delete 获取 ext 不用 条件 jdbc原理 col sof upd
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ym77/p/11316920.html