标签:语言 code 父类 walk ack xml文件 head instance 设计
反射是框架设计的灵魂
当程序要使用某个类时,如果该类还未被加载到内存中,系统会通过加载,连接,初始化三步来实现对这个类进行初始化。
负责将 .class文件加载到内存中,并为之生成对应的Class对象。
虽然我们不需要关心类加载机制,但是了解这个机制我们就能更好的理解程序的运行。
(1)根类加载器
(2)扩展类加载器
(3)系统类加载器
在运行时能够获取JavaBean当中的属性名称和get与set方法
| 类名 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| Class类 | 代表类的实体,在运行的Java应用程序中表示类和接口 |
| Field类 | 代表类的成员变量(成员变量也称为类的属性) |
| Method类 | 代表类的方法 |
| Constructor类 | 代表类的构造方法 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| forName(String className) | 根据类名返回类的对象 |
| getName() | 获得类的完整路径名字 |
| newInstance() | 创建类的实例 |
| getPackage() | 获得类的包 |
| getSimpleName() | 获得类的名字 |
| getSuperclass() | 获得当前类继承的父类的名字 |
| getInterfaces() | 获得当前类实现的类或是接口 |
| asSubclass(Class clazz) | 把传递的类的对象转换成代表其子类的对象 |
| Cast | 把对象转换成代表类或是接口的对象 |
| getClassLoader() | 获得类的加载器 |
| getClasses() | 返回一个数组,数组中包含该类中所有公共类和接口类的对象 |
| getDeclaredClasses() | 返回一个数组,数组中包含该类中所有类和接口类的对象 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getField(String name) | 获得某个公有的属性对象 |
| getFields() | 获得所有公有的属性对象 |
| getDeclaredField(String name) | 获得某个属性对象 |
| getDeclaredFields() | 获得所有属性对象 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getAnnotation(Class annotationClass) | 返回该类中与参数类型匹配的公有注解对象 |
| getAnnotations() | 返回该类所有的公有注解对象 |
| getDeclaredAnnotation(Class annotationClass) | 返回该类中与参数类型匹配的所有注解对象 |
| getDeclaredAnnotations() | 返回该类所有的注解对象 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getConstructor(Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类中与参数类型匹配的公有构造方法 |
| getConstructors() | 获得该类的所有公有构造方法 |
| getDeclaredConstructor(Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类中与参数类型匹配的构造方法 |
| getDeclaredConstructors() | 获得该类所有构造方法 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getMethod(String name, Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类某个公有的方法 |
| getMethods() | 获得该类所有公有的方法 |
| getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类某个方法 |
| getDeclaredMethods() | 获得该类所有方法 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| isAnnotation() | 如果是注解类型则返回true |
| isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) | 如果是指定类型注解类型则返回true |
| isAnonymousClass() | 如果是匿名类则返回true |
| isArray() | 如果是一个数组类则返回true |
| isEnum() | 如果是枚举类则返回true |
| isInstance(Object obj) | 如果obj是该类的实例则返回true |
| isInterface() | 如果是接口类则返回true |
| isLocalClass() | 如果是局部类则返回true |
| isMemberClass() | 如果是内部类则返回true |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| equals(Object obj) | 属性与obj相等则返回true |
| get(Object obj) | 获得obj中对应的属性值 |
| set(Object obj, Object value) | 设置obj中对应属性值 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| invoke(Object obj, Object... args) | 传递object对象及参数调用该对象对应的方法 |
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| newInstance(Object... initargs) | 根据传递的参数创建类的对象 |
对象.getClass()多用于对象的获取字节码的方式
类名.class多用于参数的传递
class.forName("全类名")多用于配置文件,将类名定义在配置文件中。读取文件,加载类。
注意:在运行期间,一个类,只有一个Class对象产生。
e.g.
class Person {
String name;
Integer age;
Person() {
}
Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz1 = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Class clazz2 = Person.class;
Class clazz3 = new Person().getClass();
System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz2); // true
System.out.println(clazz2 == clazz3); // true
System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz3); // true
}
}| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getConstructor(Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类中与参数类型匹配的公有构造方法 |
| getConstructors() | 获得该类的所有公有构造方法 |
| getDeclaredConstructor(Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类中与参数类型匹配的构造方法 |
| getDeclaredConstructors() | 获得该类所有构造方法 |
获取构造器后可执行操作
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| newInstance(Object... initargs) | 根据传递的参数创建类的对象 |
class Person {
String name;
Integer age;
Person() {
}
private Person(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Constructor<?>[] cons = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> con : cons) {
System.out.println(con);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Constructor<?> con = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
System.out.println(con);
Person p = (Person) con.newInstance("zsy", 20);
System.out.println(p);
}
}运行结果
public Test.Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer)
--------
public Test.Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer)
Person [name=zs, age=20]class Person {
String name;
Integer age;
Person() {
}
private Person(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Constructor<?>[] cons = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> con : cons) {
System.out.println(con);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Constructor<?> con = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(con);
Person p = (Person) con.newInstance("zs");
System.out.println(p);
}
}运行结果
public Test.Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer)
private Test.Person(java.lang.String)
Test.Person()
--------
private Test.Person(java.lang.String)
抛出java.lang.IllegalAccessException会发现在使用私有构造器时会报异常
class Person {
String name;
Integer age;
Person() {
}
private Person(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Constructor<?>[] cons = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> con : cons) {
System.out.println(con);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Constructor<?> con = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(con);
con.setAccessible(true);
Person p = (Person) con.newInstance("zs");
System.out.println(p);
}
}运行结果
public Test.Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer)
private Test.Person(java.lang.String)
Test.Person()
--------
private Test.Person(java.lang.String)
Person [name=zs, age=null]class Person {
String name;
Integer age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Constructor<?> con = clazz.getConstructor();
System.out.println(con); // public Test.Person()
Person p = (Person) con.newInstance();
System.out.println(p); // Person [name=null, age=null]
}
}获取无参构造器时,可以简化为
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
System.out.println(p); // Person [name=null, age=null]
}
}| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getField(String name) | 获得某个公有的属性对象 |
| getFields() | 获得所有公有的属性对象 |
| getDeclaredField(String name) | 获得某个属性对象 |
| getDeclaredFields() | 获得所有属性对象 |
获取字段后可执行操作
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| get(Object obj) | 获得obj中对应的属性值 |
| set(Object obj, Object value) | 设置obj中对应属性值 |
直接调用 clazz.getField("字段名称")
class Person {
public String name;
public Integer age;
protected String a;
String b;
private String c;
Person() {
}
Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Field name = clazz.getField("name");
Field age = clazz.getField("age");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println("--------");
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
name.set(p, "zs");
System.out.println(name.get(p));
}
}运行结果:
public java.lang.String Test.Person.name
public java.lang.Integer Test.Person.age
--------
public java.lang.String Test.Person.name
public java.lang.Integer Test.Person.age
--------
zsclass Person {
public String name;
public Integer age;
protected String a;
String b;
private String c;
Person() {
}
Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
Field a = clazz.getDeclaredField("a");
Field b = clazz.getDeclaredField("b");
Field c = clazz.getDeclaredField("c");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println("--------");
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
name.set(p, "zs");
System.out.println(name.get(p));
a.set(p, "a");
System.out.println(a.get(p));
b.set(p, "b");
System.out.println(b.get(p));
c.set(p, "c");
System.out.println(c.get(p));
}
}运行结果:
public java.lang.String Test.Person.name
public java.lang.Integer Test.Person.age
protected java.lang.String Test.Person.a
java.lang.String Test.Person.b
private java.lang.String Test.Person.c
--------
public java.lang.String Test.Person.name
public java.lang.Integer Test.Person.age
protected java.lang.String Test.Person.a
java.lang.String Test.Person.b
private java.lang.String Test.Person.c
--------
zs
a
b
抛出java.lang.IllegalAccessException会发现在调用和设置私有字段时会报异常
class Person {
private String c;
Person() {
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Field c = clazz.getDeclaredField("c");
System.out.println(c); // private java.lang.String Test.Person.c
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
c.setAccessible(true);
c.set(p, "c");
System.out.println(c.get(p)); // C
}
}| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| getMethod(String name, Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类某个公有的方法 |
| getMethods() | 获得该类所有公有的方法 |
| getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class...<?> parameterTypes) | 获得该类某个方法 |
| getDeclaredMethods() | 获得该类所有方法 |
获取方法后可执行操作
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| invoke(Object obj, Object... args) | 传递object对象及参数调用该对象对应的方法 |
class Person {
String name;
public void eat(String str) {
System.out.println(name + "在吃" + str);
}
public void work() {
System.out.println(name + "在工作");
}
private void walk() {
System.out.println(name + "在行走");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
p.name = "张三";
Method method = clazz.getMethod("work");
method.invoke(p); // 张三在工作
}
}类似的,使用暴力反射,忽略访问权限修饰符的安全检查
class Person {
String name;
public void eat(String str) {
System.out.println(name + "在吃" + str);
}
public void work() {
System.out.println(name + "在工作");
}
private void walk() {
System.out.println(name + "在行走");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
p.name = "张三";
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("walk");
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(p); // 张三在行走
}
}class Person {
String name;
public void eat(String str) {
System.out.println(name + "在吃" + str);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 获取字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Test.Person");
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
p.name = "张三";
Method method = clazz.getMethod("eat", String.class);
method.invoke(p, "苹果"); // 张三在吃苹果
}
}设计一个可以创建任意类的对象,执行此对象中任意方法的框架。
public class Student {
public String name = "zs";
public void study() {
System.out.println(name + "在学习");
}
public void eat(String str) {
System.out.println(name + "在吃" + str);
}
public void parents(String father, String mother) {
System.out.println(name + "的父亲是:" + father);
System.out.println(name + "的母亲是:" + mother);
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties props = new Properties();
InputStream ins = Test.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("Test/pro.properties");
props.load(ins);
ins.close();
String className = props.getProperty("className");
String methodName = props.getProperty("methodName");
String methodArgs = props.getProperty("methodArgs");
String[] argList = methodArgs.isEmpty() ? null : methodArgs.split(",");
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if(method.getName().equals(methodName)) {
method.invoke(object, argList);
}
}
}
}className=Test.Student
methodName=parents
methodArgs=ls,ww配置文件放置位置
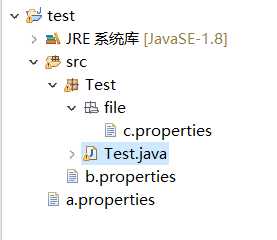
该方式必须知道文件的真实路径。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String aName = getProperties("a.properties");
String bName = getProperties("src/b.properties");
String cName = getProperties("src/Test/file/c.properties");
System.out.print(aName + "\n" + bName + "\n" + cName);
}
public static String getProperties(String path) throws Exception {
InputStream ins = new FileInputStream(path);
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(ins);
ins.close();
String className = props.getProperty("className");
return className;
}
}Class.getResourceAsStream(String path)
path 不以’/‘开头时默认是从此类所在的包下取资源
path 以’/‘开头则是从ClassPath根下(即‘/‘代表src)获取
其只是通过path构造一个绝对路径,最终还是由ClassLoader获取资源。
a.在同级目录下
有类me.class,同时在同级目录下有资源文件 myfile.properties,则应使用:me.class.getResource("myfile.properties");
b.在子目录下
com.x.y 下有类me.class,同时在子目录 com.x.y.file 下有资源文件 myfile.properties,则应使用:me.class.getResource("file/myfile.properties");
c.不在同级目录和子目录下
com.x.y 下有类me.class,同时在 com.x.file 目录下有资源文件 myfile.properties ,则应使用:me.class.getResource("/com/x/file/myfile.properties");
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//String aName = getProperties("a.properties"); // 这里a不在src下,不能获取
String bName = getProperties("../b.properties"); // 相对路径
String cName = getProperties("/Test/file/c.properties"); // 绝对路径
System.out.print(bName + "\n" + cName);
}
public static String getProperties(String path) throws Exception {
// getResource 获取资源的绝对路径
URL url = Test.class.getResource(path);
System.out.println(url);
// getResourceAsStream 获取资源的字节流
InputStream ins = Test.class.getResourceAsStream(path);
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(ins);
ins.close();
String className = props.getProperty("className");
return className;
}
}ServletContext.getResourceAsStream(String path)
默认从WebAPP根目录(即:要发布在服务器下的项目的根目录(与src同级的web文件夹下))下取资源
path是否以’/‘开头无所谓。 例:
在web项目的根目录下有myfile.xml文件,则应该使用
getServleContext().getResourceAsStream("myfile.xml");
Class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(String path)
a.不在同级目录和子目录下
com.x.y 下有类me.class,同时在 com.x.file 目录下有资源文件 myfile.properties ,则应使用:me.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("com/x/file/myfile.properties");
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//String aName = getProperties("a.properties"); // 这里a不在src下,不能获取
String bName = getProperties("b.properties");
String cName = getProperties("Test/file/c.properties");
System.out.print(bName + "\n" + cName);
}
public static String getProperties(String path) throws Exception {
// getResource 获取资源的绝对路径
URL url = Test.class.getClassLoader().getResource(path);
System.out.println(url);
// getResourceAsStream 获取资源的字节流
InputStream ins = Test.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(path);
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(ins);
ins.close();
String className = props.getProperty("className");
return className;
}
}文件必须是 key=value 的properties文件
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//String aName = getProperties("a"); // 这里a不在src下,不能获取
String bName = getProperties("b");
String cName = getProperties("Test/file/c");
System.out.print(bName + "\n" + cName);
}
public static String getProperties(String path) throws Exception {
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle(path);
String className = bundle.getString("className");
return className;
}
}标签:语言 code 父类 walk ack xml文件 head instance 设计
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xzh0717/p/11332003.html