标签:文本 white 字体 盒子模型 建议 应该 搜索 宽高 超过
为了让网页元素的样式更加丰富,也为了让网页的内容和样式能拆分开,CSS由此思想而诞生
CSS是 Cascading Style Sheets 的首字母缩写,意思是层叠样式表
有了CSS,html中大部分表现样式的标签就废弃不用了,html只负责文档的结构和内容,表现形式完全交给CSS,html文档变得更加简洁。
css的定义方法是:
选择器 { 属性:值; 属性:值; 属性:值;}
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>css引入</title> <!-- 外联式:常用,内容和样式分离 --> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/001.css"> <style type="text/css"> /* 注释快捷键:Ctrl+shift+/ */ /* 嵌入式:首页一般会用可以提高性能 */ h2{ font-size: 26px; color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div>这是一个div标签</div> <h2>这是一个标题</h2> <!-- 内联式:不推荐使用 --> <p style="font-size: 14px;color: gold;">这是一个段落</p> </body> </html>
div{ font-size: 20px; color: red; }
color 设置文字的颜色,如: color:red;
font-size 设置文字的大小,如:font-size:12px;
font-family 设置文字的字体,如:font-family:‘微软雅黑‘;
font-style 设置字体是否倾斜,如:font-style:‘normal‘; 设置不倾斜,font-style:‘italic‘;设置文字倾斜
font-weight 设置文字是否加粗,如:font-weight:bold; 设置加粗 font-weight:normal 设置不加粗
line-height 设置文字的行高,设置行高相当于在每行文字的上下同时加间距, 如:line-height:24px;

font 同时设置文字的几个属性,写的顺序颠倒会有兼容问题,建议按照如下顺序写: font:是否加粗 字号/行高 字体;如: font:normal 12px/36px ‘微软雅黑‘;
text-decoration 设置文字的下划线,如:text-decoration:none; 将文字下划线去掉
text-indent 设置文字首行缩进,如:text-indent:24px; 设置文字首行缩进24px

text-align 设置文字水平对齐方式,如text-align:center 设置文字水平居中
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>文本样式</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/002.css"> </head> <body> <h2>这是标题</h2> <div>为了让网页元素的样式更加丰富,也为了让网页的内容和样式能拆分开,CSS由此思想而诞生 ,CSS是 <em>Cascading Style Sheets</em> 的首字母缩写,意思是层叠样式表。 有了CSS,html中大部分表现样式的标签就废弃不用了,html只负责文档的结构和内容,表现形式完全交给CSS,html文档变得更加简洁。<br /> 选择器是将样式和页面元素关联起来的名称,属性是希望设置的样式属性,每个属性有一个或多个值。</div> <a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度</a> </body> </html>
div{ /* fontsize默认是16px */ font-size: 26px; color: green; font-family: ‘Microsoft Yahei‘; /* font-style: italic; */ line-height: 40px; text-indent: 52px; } em{ color: pink; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; } h2{ font: normal 30px/50px ‘Microsoft Yahei‘; text-align: center; text-decoration: underline; } a{ font: normal 20px/30px ‘宋体‘; text-decoration: none; }
css颜色值主要有三种表示方法:
(1)颜色名表示,比如:red 红色,gold 金色
(2)rgb表示,比如:rgb(255,0,0)表示红色,rgb(255,255,255)为黑色
(3)16进制数值表示,比如:#ff0000 表示红色,这种可以简写成 #f00
标签选择器、id选择器、类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> /* *可以选择所有标签 */ *{ font-size: 20px; } /* 标签选择器 */ div{ color: red; } /* id选择器 */ #div1{ color: green; } /* class选择器 */ .gold{ color: gold; } .big{ font-size: 40px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="gold big">这是第一个div</div> <div class="gold big">这是第二个div</div> <div class="gold">这是第三个div</div> </body> </html>
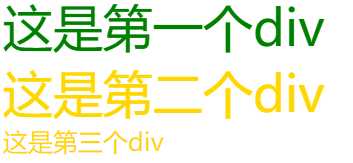
层级选择器:一般不要超过四层,否则会影响性能
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ font-size: 20px; line-height: 30px; text-indent: 40px; } .box span{ color: red; font-weight: bold; } .box em{ color: green; text-decoration: underline; font-style: normal; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"><span>层级选择器</span>主要应用在选择父元素下的子元素,或者子元素下面的子元素,可与标签元素结合使用,减少命名,同时也可以通过层级,<em>防止命名冲突</em>。层级选择器主要应用在选择父元素下的子元素,或者子元素下面的子元素,可与标签元素结合使用,减少命名,同时也可以通过层级,防止命名冲突。层级选择器主要应用在选择父元素下的子元素,或者子元素下面的子元素,可与标签元素结合使用,减少命名,同时也可以通过层级,防止命名冲突。 </div> <div class="box2"><span>层级选择器</span>主要应用在选择父元素下的子元素,或者子元素下面的子元素,可与标签元素结合使用,减少命名,同时也可以通过层级,防止命名冲突。</div> </body> </html>
组选择器:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ font-size: 20px; font-style: initial; } .box1{ color: blue; } .box2{ color: green; } .box3{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1">多个选择器,如果有同样的样式设置,可以使用组选择器。</div> <div class="box2">多个选择器,如果有同样的样式设置,可以使用组选择器。</div> <div class="box3">多个选择器,如果有同样的样式设置,可以使用组选择器。</div> </body> </html>

伪类选择器:常用的伪类选择器有hover,表示鼠标悬浮在元素上时的状态
伪元素选择器有before和after,它们可以通过样式在元素中插入内容。插入的内容无法被鼠标选中。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>伪类选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> .bd{ font-size: 26px; text-decoration: none; color: pink; } .bd:hover{ color: red; font-weight: bold; } .box1,.box2{ font-size: 20px; } .box1:before{ content: "加在前面"; color: purple; } .box2:after{ content: "加在后面"; color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="bd">百度搜索</a> <div class="box1">这是第一个</div> <div class="box2">这是第二个</div> </body> </html>

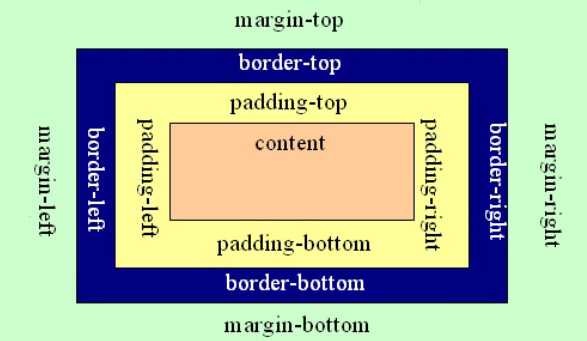
把元素叫做盒子,设置对应的样式分别为:
盒子的宽度(width)、盒子的高度(height)、盒子的边框(border)、盒子内的内容和边框之间的间距(padding)、盒子与盒子之间的间距(margin)。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>盒子模型</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1{ /*这里的宽高指的是内容的宽高,不包含内外边距和边框*/ width: 200px; height: 150px; background-color: gold; /*border-top-color:red;*/ /*border-top-width:10px;*/ /*border-top-style:solid*/ /*solid实线dashed虚线dotted点线*/ border-top: 5px solid red; border-left: 5px dashed #000; border-bottom: 5px dotted green; border-right: 5px dashed #000; /*上 右 下 左*/ /*上 左右 下*/ /*上下 左右*/ padding: 20px 30px 40px 20px; margin: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1">元素在页面中显示成一个方块,类似一个盒子,CSS盒子模型就是使用现实中盒子来做比喻,帮助我们设置元素对应的样式</div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>盒子模型做标题</title> <style type="text/css"> .news_title{ width: 400px; height: 20px; font: normal 20px/20px ‘Microsoft Yahei‘; color: #333; text-indent: 20px; border-bottom: 3px solid #666; border-top: 1px solid #f00; padding: 15px 0; } </style> </head> <body> <h3 class="news_title">新闻标题</h3> </body> </html>

使用技巧:
(1)margin的左右值可以设为auto,可以使盒子水平居中。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin使用技巧</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 200px; height: 200px; font: normal 20px/200px ‘Microsoft Yahei‘; color: white; text-align: center; background-color: blue; margin: 0 auto; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- 设置元素水平据中 --> <div class="box">水平居中的盒子</div> </body> </html>
(2)margin负值让元素位移及边框合并
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin</title> <style type="text/css"> body{ /*body默认带有margin*/ margin: 0; } .box{ width: 202px; height: 156px; background-color: pink; margin: 50px auto 0; } .box div{ width: 200px; height: 30px; border: 1px solid green; background-color: gold; /*下面的样式可以把上面的覆盖掉*/ /*border-bottom: 0;*/ margin-top: -1px; } /*.box .b5{ border-bottom: 1px solid green; }*/ </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> <div class="b5"></div> </div> </body> </html>
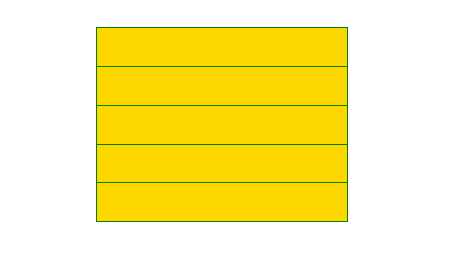
(3)外边距合并问题
当两个垂直外边距相遇时,它们将形成一个外边距。合并后的外边距的高度等于两个发生合并的外边距的高度中的较大者。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin合并问题</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2{ width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: gold; } .box1{ margin-bottom: 20px; } .box2{ margin-top: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> </body> </html>

解决方法:
a. 使用这种特性
b. 设置一边的外边距,一般只设置margin-top
c. 将元素浮动或者定位
垂直外边距特性的应用场景:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 500px; border: 1px solid #000; margin: 50px auto 0; } .box div{ margin: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <div>外边距合并指的是,当两个垂直外边距相遇时,它们将形成一个外边距。合并后的外边距的高度等于两个发生合并的外边距的高度中的较大者</div> <div>外边距合并指的是,当两个垂直外边距相遇时,它们将形成一个外边距。合并后的外边距的高度等于两个发生合并的外边距的高度中的较大者</div> <div>外边距合并指的是,当两个垂直外边距相遇时,它们将形成一个外边距。合并后的外边距的高度等于两个发生合并的外边距的高度中的较大者</div> <div>外边距合并指的是,当两个垂直外边距相遇时,它们将形成一个外边距。合并后的外边距的高度等于两个发生合并的外边距的高度中的较大者</div> </div> </body> </html>
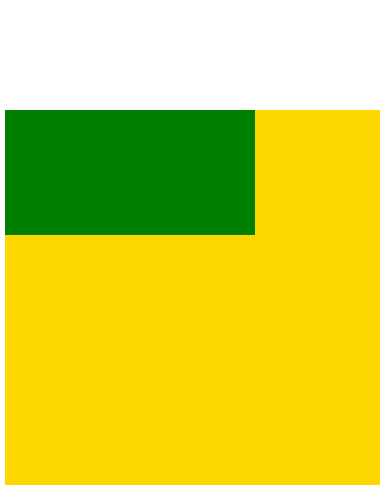
(4)margin-top塌陷
在两个盒子嵌套时候,内部的盒子设置的margin-top会加到外边的盒子上,导致内部的盒子margin-top设置失败
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin-top塌陷</title> <style type="text/css"> .con{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: gold; } .box{ width: 200px; height: 100px; background-color: green; margin-top: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="con"> <div class="box"></div> </div> </body> </html>
解决方法:
a. 外部盒子设置一个边框
b. 外部盒子设置 overflow:hidden
c. 使用伪元素类
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>margin-top塌陷</title> <style type="text/css"> .clearfix:before{ content: ‘‘; display: table; } .con{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: gold; } .box{ width: 200px; height: 100px; background-color: green; margin-top: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="con clearfix"> <div class="box"></div> </div> </body> </html>

当子元素的尺寸超过父元素的尺寸时,需要设置父元素显示溢出的子元素的方式,设置的方法是通过overflow属性来设置。
overflow的设置项:
1)visible 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。
2)hidden 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的,此属性还有清除浮动、清除margin-top塌陷的功能。
3)scroll 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容(不管是否溢出都会有滚动条)
4)auto 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。(溢出的时候才会产生滚动条)
5)inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>元素溢出</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 300px; /*如果不给高度内容会自动撑开盒子*/ height: 200px; border: 1px solid #000; margin: 50px auto 0; background-color: gold; font-size: 18px; line-height: 25px; overflow: auto; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box">当子元素的尺寸超过父元素的尺寸时,需要设置父元素显示溢出的子元素的方式,设置的方法是通过overflow属性来设置。 overflow的设置项: 1、visible 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。 2、hidden 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的,此属性还有清除浮动、清除margin-top塌陷的功能。 3、scroll 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 4、auto 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 5、inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。 </div> </body> </html>
标签:文本 white 字体 盒子模型 建议 应该 搜索 宽高 超过
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ysysyzz/p/11318771.html