标签:pid 不同 quartz john lease 配置文件 star 基础 tst
Spring是Java里非常经典的框架,由Rod Johnson创建,其已经成为Java EE行业标准,用于解决一站式服务,接下来入门学习一下。
开源的,用来简化企业级应用开发的应用开发框架,是一款轻量级的框架,一共有2200多个类。
Spring对常用的API做了封装(比如JDBC),这样就可以大大简化这些API的使用,如SpringJDBC的使用,不需要我们考虑创建连接和关闭连接。
设计有一个基本原则,即高内聚低耦合,即类的职责越单一越好,并且对类进行维护时,避免"牵一发动全身"的情况。
高内聚:类的职责需要单一
低耦合:Spring帮忙建立对象之间的依赖关系,对象之间的耦合度会大大降低,代码的可维护性大大提高。以前如果A类需要调用B类的一个方法,需要先在A类中先new一个B类的对象,然后调用B类对象的方法,如果A类不想调用B类的方法,想改成调用C类的方法,则A类中的语句需要相应的修改,耦合度就相应提高了。Spring的出现,会自动帮忙管理对象之间的依赖关系,对象通过容器和配置文件来创建,降低耦合度。
Spring可以将其他的一些框架集成进来(比如定时任务处理的Quartz,数据库连接相关的MyBatis),方便这些框架的使用。在Spring管理对象的基础上,将对象进行调用会比自己手动使用配置文件创建后调用更加的方便。
Spring容器是Spring框架中的一个核心模块,用于管理对象,所谓容器就是用来创建管理对象并建立对象之间依赖关系的,以前学习的Tomcat就是一种容器,其有初始化和销毁对象方法。
启动Spring容器分为如下几步,前提是Maven的项目:
(1)导包:使用pom.xml导入spring-mvc的包
1 <!-- 导入spring-webmvc的jar包 --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> 5 <version>4.2.3.RELEASE</version> 6 </dependency>
(2)添加Spring启动时读取的配置文件,一般名为applicationContext.xml,本次使用myApplicationContext.xml来处理。

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org /schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd"> </beans>
(3)启动容器
本次使用一个测试类来完成启动。

1 package test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 public class TestSpring { 8 @Test 9 public void testStartSpring() { 10 //测试启动Spring容器 11 String[] path= new String[]{"myApplicationContext.xml"}; 12 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path); 13 System.out.println(ac); 14 } 15 }
启动结果,正常启动并打印出对象,并显示启动时间。

Spring容器创建对象有三种方式,用的多的就是第一种方式,创建对象需要在myApplicationContext.xml配置bean属性,让Spring帮忙创建,配置在xml中的属性相当于配方,Spring根据配方来创建对应的对象。
(1)使用无参数构造器创建
(2)使用静态工厂方法创建
(3)使用实例化对象工厂方法创建
配置文件内容
bean id:需独一无二,bean的名字。
class属性:创建对象对应的类
factory-method:类的静态工厂方法,如Calendar类中有getInstance静态方法
factory-bean:指定一个bean的id,容器会调用该bean的实例方法来创建一个对象
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" 4 xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org /schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" 5 xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" 6 xsi:schemaLocation=" 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd 12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd 13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd"> 14 15 <!-- 使用无参数构造器 --> 16 <bean id="person" class="com.boe.Person"></bean> 17 18 <!-- 使用静态工厂方法 --> 19 <bean id="cal" class="java.util.Calendar" factory-method="getInstance"></bean> 20 21 <!-- 使用实例化对象工厂方法 --> 22 <bean id="date" factory-bean="cal" factory-method="getTime"></bean> 23 24 </beans>
测试类中内容

1 package test; 2 3 import java.util.Calendar; 4 import java.util.Date; 5 6 import org.junit.Test; 7 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 8 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 9 10 import com.boe.Person; 11 12 public class TestSpring { 13 @Test 14 public void testStartSpring() { 15 //测试启动Spring容器 16 String[] path= new String[]{"myApplicationContext.xml"}; 17 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path); 18 System.out.println(ac); 19 } 20 21 @Test 22 public void testGetInstance() { 23 String[] path= new String[]{"myApplicationContext.xml"}; 24 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path); 25 //方法1 26 Person person=ac.getBean("person",Person.class); 27 System.out.println(person); 28 //方法2 29 Calendar calendar=ac.getBean("cal",Calendar.class); 30 System.out.println(calendar); 31 //方法3 32 Date date=ac.getBean("date",Date.class); 33 System.out.println(date); 34 } 35 }
测试结果
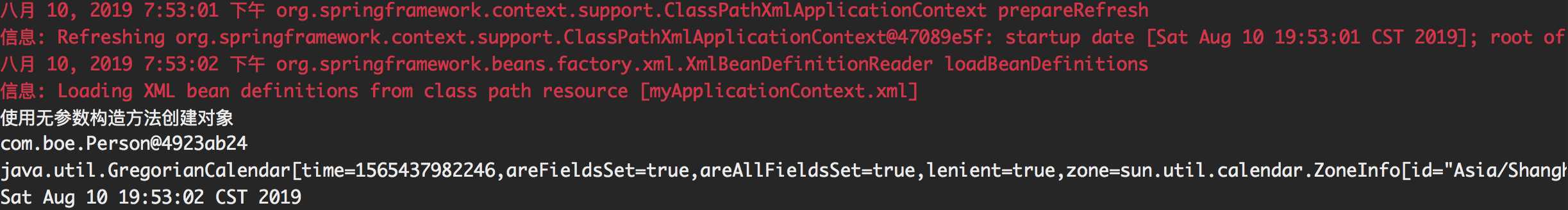
作用域:默认情况下,容器对每个bean元素只会创建一个实例对象,如果将作用域设置为prototype,则每次调用getBean方法,就会创建一个新的对象。另外作用域默认为singleton。
在上面配置文件基础上加一条配置。bean id为‘p‘的对象用于测试,分别测试scope属性为singleton和prototype。注意其他关于Person类的配置先注释,方便测试。
<!-- 测试作用域 --> <bean id="p" class="com.boe.Person" scope="singleton"></bean>
测试代码
//测试作用域 @Test public void testScope() { String[] path= new String[]{"myApplicationContext.xml"}; ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path); Person p1=ac.getBean("p",Person.class); Person p2=ac.getBean("p",Person.class); System.out.println(p1.equals(p2)); }
当scope为singleton时

当scope为prototype时

可以看出作用域为singleton时,对象只创建了一次,并且两者相等,虽然使用getBean方法两次,但是却只有一个对象,似乎对象不是getBean方法获得,这跟后面要说的延迟加载有关。
当作用域为prototype时,创建了两个对象,并且两者不相等,说明使用一个getBean方法,就创建了一个新的对象。
延迟加载:默认情况下容器启动之后,会将作用域为singleton的bean创建好,设置延迟加载容器启动之后,对作用域为singleton的bean不再创建,直到调用getBean方法才会创建,设置延迟加载需在配置文件中设置lazy-init属性。
<!-- 测试作用域 --> <bean id="p" class="com.boe.Person" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true"></bean>
测试分为以下几种情况,根据控制台输出情况得到如下结果:
(1)scope="singleton",lazy-init="false":启动容器就创建对象,并且只有一个
(2)scope="singleton",lazy-init="true":启动容器不会创建对象,直到调用getBean方法才会创建对象,并且只有一个
(3)scope="prototype",无论是否设置延迟加载,均只有在调用getBean方法才会创建对象,并且是创建多个不同的对象
对象生命周期管理可以用来更好的分配资源,其有初始化方法和销毁方法,可以在xml配置文件中对方法进行指定,只对作用域为singleton的有效。
初始化方法:Spring容器创建好bean的实例后,会调用初始化方法
销毁方法:容器关闭后会调用销毁方法,将spring容器管理的对象全部销毁
配置文件内容
1 <!-- 测试生命周期,对初始化方法和销毁方法进行配置--> 2 <bean id="message" class="com.boe.MessageService" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean> 3
MessageService类

1 package com.boe; 2 3 public class MessageService { 4 5 public MessageService() { 6 System.out.println("构造方法MessageService()执行了,完成创建对象"); 7 } 8 9 /** 10 * 做成初始化方法,希望spring容器创建好MessageService对象后,马上调用init()方法 11 * 方法:需要修改容器配置文件,让容器知道这个是MessageService的初始化方法 12 */ 13 public void init() { 14 System.out.println("初始化方法init()执行了"); 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * 做成销毁方法,配置文件也需要说明 19 */ 20 public void destroy() { 21 System.out.println("销毁方法destroy()执行了"); 22 } 23 }
测试代码
1 //测试生命周期 2 @Test 3 public void testLife() { 4 String[] path= new String[]{"myApplicationContext.xml"}; 5 AbstractApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path); 6 ac.close(); 7 }
测试结果,可以看出不设置延迟加载,singleton作用域的对象在容器启动后就创建,并随后执行了对象初始化方法,当容器关闭,就会执行销毁方法。
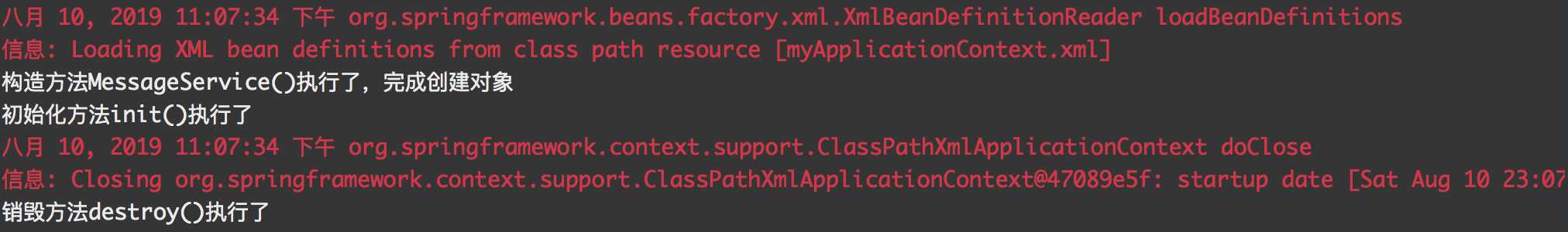
(1)Spring是一个提供一站式服务的框架,可以使用Spring容器和配置文件来创建和管理对象
(2)创建对象方式有3种方式
(3)作用域有singleton和prototype,默认为前者,设置延迟加载只对singleton有效。
(4)对象生命周期管理可以更好的分配资源
标签:pid 不同 quartz john lease 配置文件 star 基础 tst
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/youngchaolin/p/11332783.html