标签:tmp ret ref 初始 栈的实现 数据 时间 while null
Stack
后进先出 使用数组实现的叫顺序栈 使用链表实现的叫链式栈
顺序栈的实现代码
// 基于数组实现的顺序栈
public class ArrayStack {
private String[] items; // 数组
private int count; // 栈中元素个数
private int n; // 栈的大小
// 初始化数组,申请一个大小为 n 的数组空间
public ArrayStack(int n) {
this.items = new String[n];
this.n = n;
this.count = 0;
}
// 入栈操作
public boolean push(String item) {
// 数组空间不够了,直接返回 false,入栈失败。
if (count == n) return false;
// 将 item 放到下标为 count 的位置,并且 count 加一
items[count] = item;
++count;
return true;
}
// 出栈操作
public String pop() {
// 栈为空,则直接返回 null
if (count == 0) return null;
// 返回下标为 count-1 的数组元素,并且栈中元素个数 count 减一
String tmp = items[count-1];
--count;
return tmp;
}
}
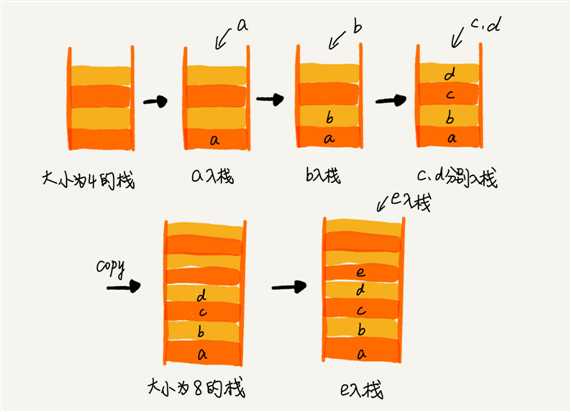
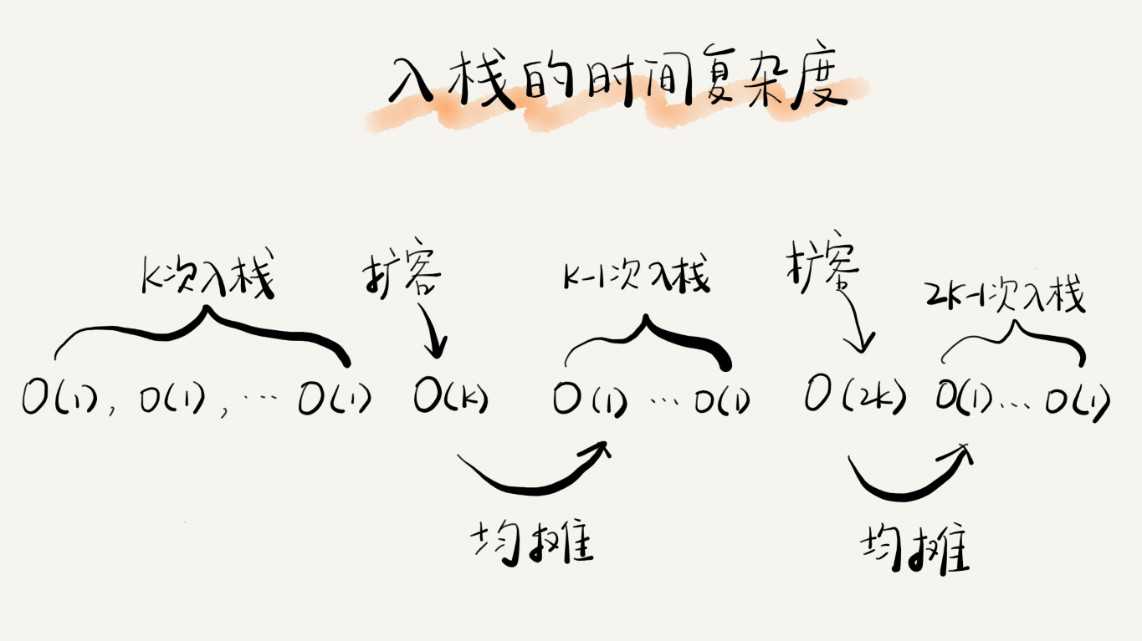
对于顺序栈 ,栈满了之后需要动态扩容 使用均摊分析法,入栈的时间复杂度为O(1)
‘(‘,‘)‘,‘{‘,‘}‘,‘[‘,‘]‘ 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
map<char,char> wordbook;
wordbook.insert(pair<char,char>(‘)‘,‘(‘));
wordbook.insert(pair<char,char>(‘]‘,‘[‘));
wordbook.insert(pair<char,char>(‘}‘,‘{‘));
stack<char> stack_first,stack_second;
//que
if(s.length()==1) return false;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
stack_first.push(s[i]);
}
//return false;
while(!stack_first.empty()){
if(stack_second.empty()){
stack_second.push(stack_first.top());
stack_first.pop();
}
if(wordbook.count(stack_second.top())){
if(wordbook[stack_second.top()]==stack_first.top()){
stack_first.pop();
stack_second.pop();
}else {
stack_second.push(stack_first.top());
stack_first.pop();
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
if(stack_second.empty()) return true;
else return false;
}
};
使用两个栈
Map:
插入数据 insert
map <char,char> Map; map.insert(pair<char,char>(a,b));
标签:tmp ret ref 初始 栈的实现 数据 时间 while null
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiwen/p/11373436.html