标签:col 包装 抽象 使用 bool 基本数据 字符串 消息 子类
一、面向对象的特征?
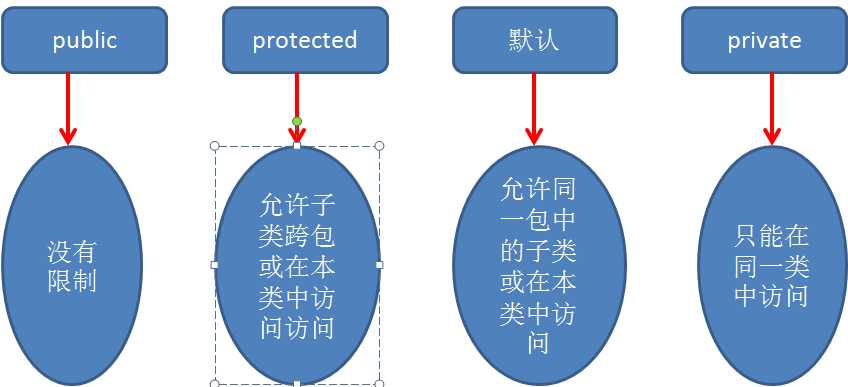
二、访问修饰符的区别?
三、Java中的基本类型有哪些?
Java中有八大基本类型:byte short int long float doble char boolean
其余都是引用类型
四、short s1 = 1; s1 = s1 + 1;有错吗?short s1 = 1; s1 += 1;有错吗?
short s1 = 1; s1 = s1 + 1; 因为1时int类型,s1位short类型,在使用时,不能将int转换为int类型,所以不对。
short s1 = 1; s1 += 1; 因为1时int类型,s1位short类型,在使用时,s1发生了强制类型的转换,相当于 s1 = (short)(s1+1);
五、关于基本类型与它们的包装类型?
示例一:
Integer a = new Integer(3);
Integer b = 3;// 将3自动装箱成Integer类型
int c = 3;
System.out.println(a == b); // false 两个引用没有引用同一对象
System.out.println(a == c); // true a自动拆箱成int类型再和c比较
System.out.println(b == c); // true b自动拆箱成int类型再和c比较
示例二:
Integer f1 = 100;
Integer f2 = 100;
Integer f3 = 150;
Integer f4 = 150;
System.out.println(f1 == f2);
System.out.println(f3 == f4);//整型字面量的值在-128到127之间,如果超过,则会new新的Integer对象。
六、简单解释内存中的栈(stack)、堆(heap)和方法区(method area)的用法。
Java虚拟机中内存空间的分配图:
基本数据类型的变、一个对象的引用、方法调用的时候 都是保存在JVM中的栈空间。
通过new关键字、构造器创建的对象则放在堆空间,堆是垃圾收集器管理的主要区域。
String str = new String("hello");
str 在栈空间中
new创建出来的字符串独享放在堆空间中
"hello"这个字面量放在方法区中
标签:col 包装 抽象 使用 bool 基本数据 字符串 消息 子类
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/in-the-game-of-thrones/p/11375211.html