标签:any des 时间 public 返回 max submit 中断 blocking
java.util.concurrent
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService
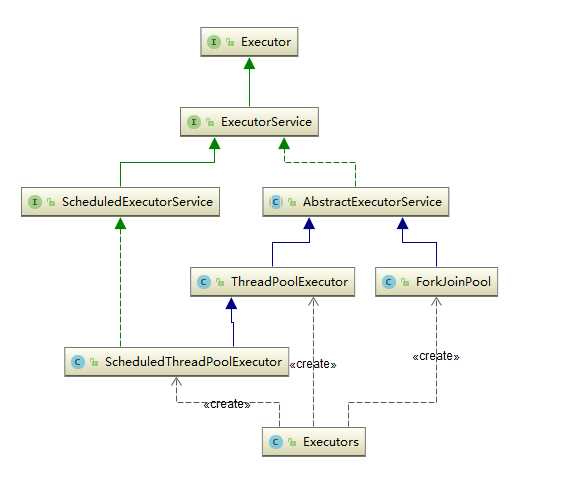
三种ThreadPoolExecutor实现类:
ExecutorService?newCachedThreadPool():
无界线程池,如果有可用线程,当线程池调用execute, 将重用之前的构造函数。
如果没有现有的线程可用,那么就创建新的线程并添加到池中。
核心线程数为0,最大线程数为Integer最大值大小,超过0个的空闲线程在60秒后销毁
ExecutorService?newFixedThreadPool():
有界线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
核心线程数和最大线程数固定相等
ExecutorService?newSingleThreadExecutor():
单线程线程池,核心线程数和最大线程数均为1
每次只执行一个线程,多余的先存储到工作队列,一个一个执行,保证了线程的顺序执行。
三种线程池的构造函数:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
四种ThreadPoolExecutor构造函数:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory)
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
int corePoolSize:
核心线程数,即使空闲也仍保留在池中的线程数
int maximumPoolSize:
最大线程数(线程总数计算公式 = 核心线程数 + 非核心线程数)
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue:
阻塞队列,在执行任务之前用于保存任务的队列维护着等待执行的Runnable对象。
当所有的核心线程都在干活时,新添加的任务会被添加到这个队列中等待处理,如果队列满了,则新建非核心线程执行任务
long keepAliveTime:
保持激活时间,当线程数大于核心数时,这是多余的空闲线程在终止之前等待新任务的最大时间
TimeUnit unit:
keepAliveTime的时间单位
threadFactory:
线程工厂,主要用来创建线程
handler:
表示当拒绝处理任务时的策略当线程池已经关闭或达到饱和(最大线程和队列都已满)状态时,新提交的任务将会被拒绝。
handler:表示当拒绝处理任务时的策略,有以下四种取值:
AbortPolicyCallerRunsPolicyDiscardPolicyDiscardOldestPolicyworkQueue,它用来存放等待执行的任务。
workQueue的类型为BlockingQueue<Runnable>,通常可以取下面三种类型:
ArrayBlockingQueue:基于数组的先进先出队列,此队列创建时必须指定大小;LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表的先进先出队列,如果创建时没有指定此队列大小,则默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE;synchronousQueue:这个队列比较特殊,它不会保存提交的任务,而是将直接新建一个线程来执行新来的任务。ExecutorService接口继承了Executor接口,并声明了一些方法:submit、invokeAll、invokeAny以及shutDown等
AbstractExecutorService实现了ExecutorService接口,基本实现了ExecutorService中声明的所有方法
ThreadPoolExecutor继承了类AbstractExecutorService
ThreadPoolExecutor类中有几个非常重要的方法:execute(),submit(),shutdown(),shutdownNow()
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
提交一个线程:
es.submit(Runnble run);es.execute(Runnble run);submit和execute分别有什么区别:
execute没有返回值,如果不需要知道线程的结果就使用execute方法,性能会好很多。submit返回一个Future对象,如果想知道线程结果就使用submit提交,而且它能在主线程中通过Future的get方法捕获线程中的异常。关闭线程池:
es.shutdown();(不能够接受新的任务,它会等待所有任务执行完毕)es.shutdownNow();(不能接受新的任务,并且会去尝试终止正在执行的任务)此方法并不能保证一定会停止每个任务,可以通过Thread.interrupt来中断线程,如果中断失败,就可能无法终止线程池。ThreadPoolExecutor提供了动态调整线程池容量大小的方法:setCorePoolSize()和setMaximumPoolSize()
setCorePoolSize:设置核心池大小
setMaximumPoolSize:设置线程池最大能创建的线程数目大小
ThreadPoolExecutor封装了两个概念字段:
workerCount:表示工作线程数,最大为(2^29)-1
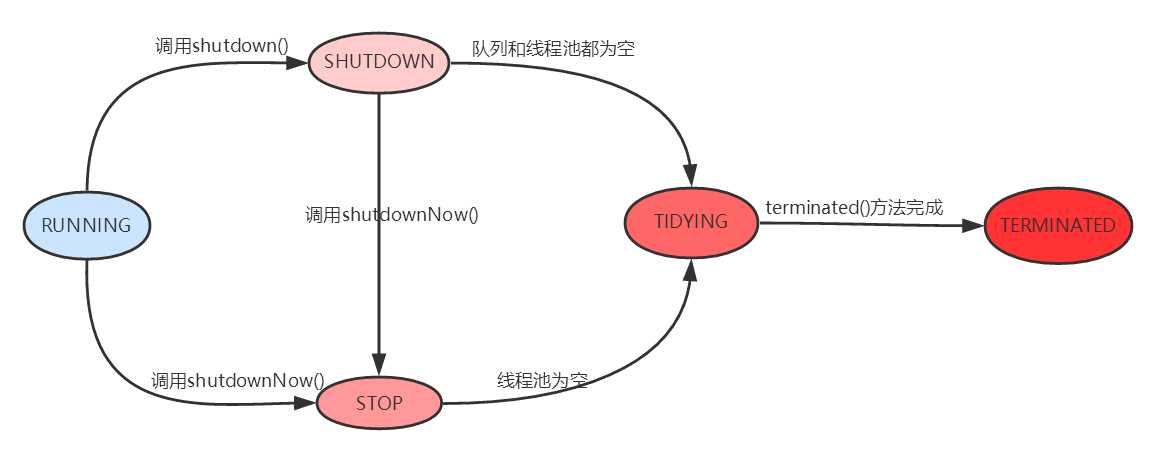
runState:提供了对池生命周期的控制,包括以下几种状态:
转换:
标签:any des 时间 public 返回 max submit 中断 blocking
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/loveer/p/11414605.html