标签:差距 cap determine tac tput nal ict ati exe
本节主要用于机器学习入门,介绍两个简单的分类模型:
决策树和随机森林
不涉及内部原理,仅仅介绍基础的调用方法
1. How Models Work
以简单的决策树为例
This step of capturing patterns from data is called fitting or training the model
The data used to train the data is called the trainning data
After the model has been fit, you can apply it to new data to predict prices of additional homes
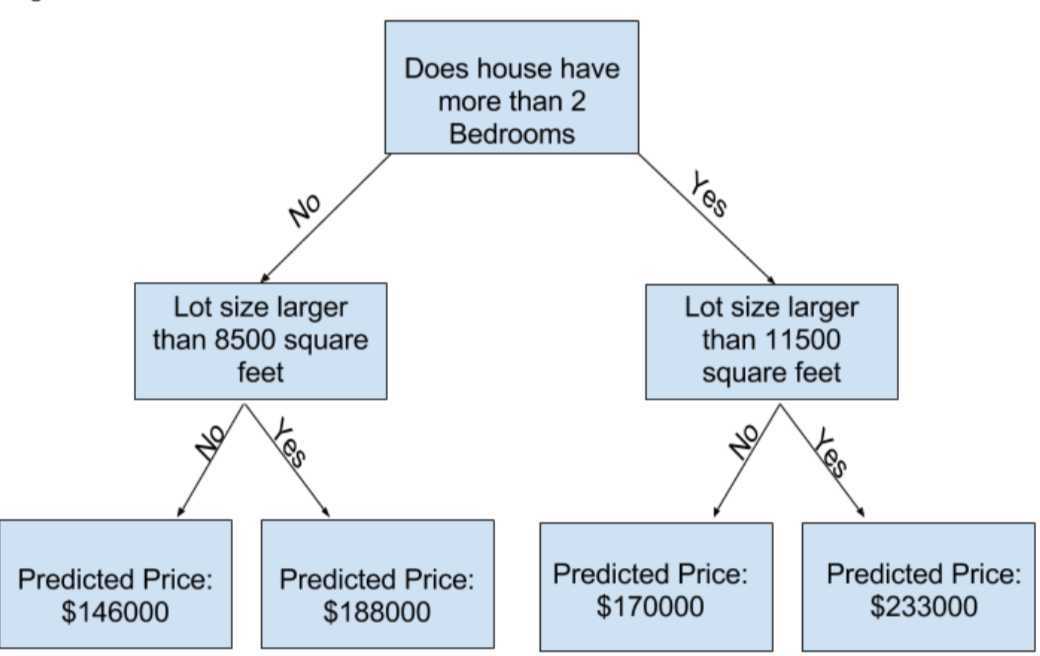
2.Basic Data Exploration
使用pandas中的describle()来探究数据:
melbourne_file_path = ‘../input/melbourne-housing-snapshot/melb_data.csv‘
melbourne_data = pd.read_csv(melbourne_file_path)
melbourne.describe()
output:
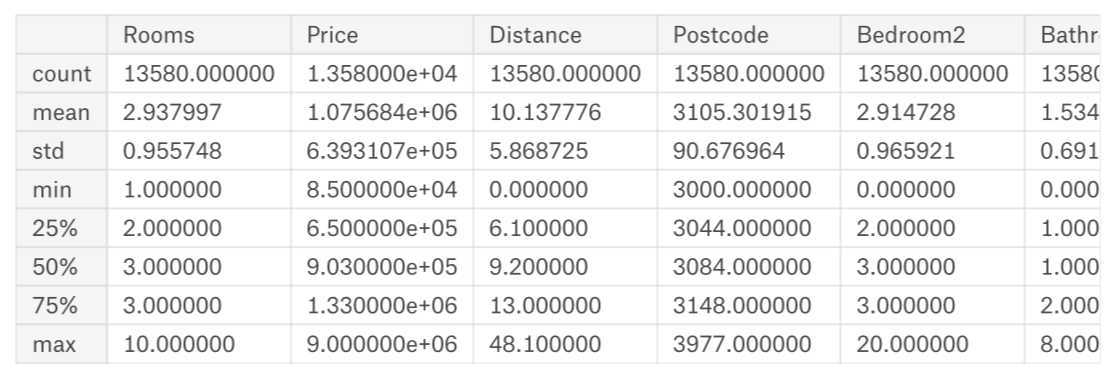
注:数值含义
count: 非缺失值的数量
mean: 平均值
std: 标准偏差,它度量值在数值上的分布情况
min、25%、50%、75%、max: 将每一列按照从lowest到highest排序,最小值是min, 1/4位置上,大于25%而小于50%是25%
3.Your First Machine Learning Model
import pandas as pd
melbourne_file_path = ‘ ../input/melbourne-housing-snapshot/melb_data.csv‘
melbourne_data = pd.read_csv(melbourne_file_path)
方法:使用dot-notation来挑选prediction target
melbourne_features = [‘Rooms‘, ‘Bathroom‘, ‘Landsize‘, ‘Lattitude‘, ‘Longtitude‘]
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]
查看数据是否加载正确:
X.head()
探究数据基本特性:
我们使用scikit-learn来创造模型,scikit-learn教程如下:
具体的原理可以根据需要自己探究
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/supervised_learning.html#supervised-learning
构建模型步骤:
What type of model will it be? A decision tree? Some other type of model? Some other parameters of the model type are specified too.
Capture patterns from provided data. This is the heart of modeling
Just what it sounds like
Determine how accurate the model‘s predictions are
实现:
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
melbourne_mode = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=1)
melbourne_mode.fit(X , y)
打印出开始几行:
print (X.head())
预测后的价格如下:
print (melbourne_mode.predict(X.head())
4.Model Validation
由于预测的价格和真实的价格会有差距,而差距多少,我们需要衡量
使用Mean Absolute Error
error= actual-predicted
在实际过程中,我们要将数据分成两份,一份用于训练,叫做training data, 一份用于验证叫validataion data
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
melbourne_model = DecisionTreeRegressor()
melbourne_model.fit(train_X, train_y)
val_predictions = melbourne_model.predict(val_X)
print(mean_absolute_error(val_y, val_predictions))
5.Underfitting and Overfitting
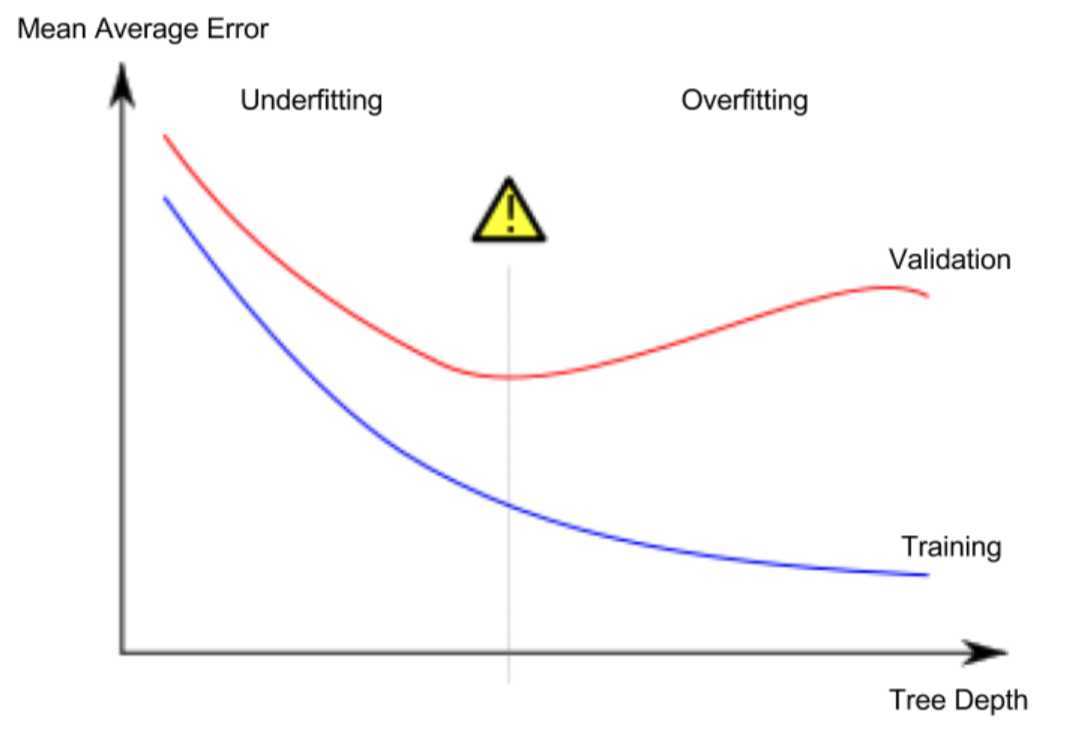
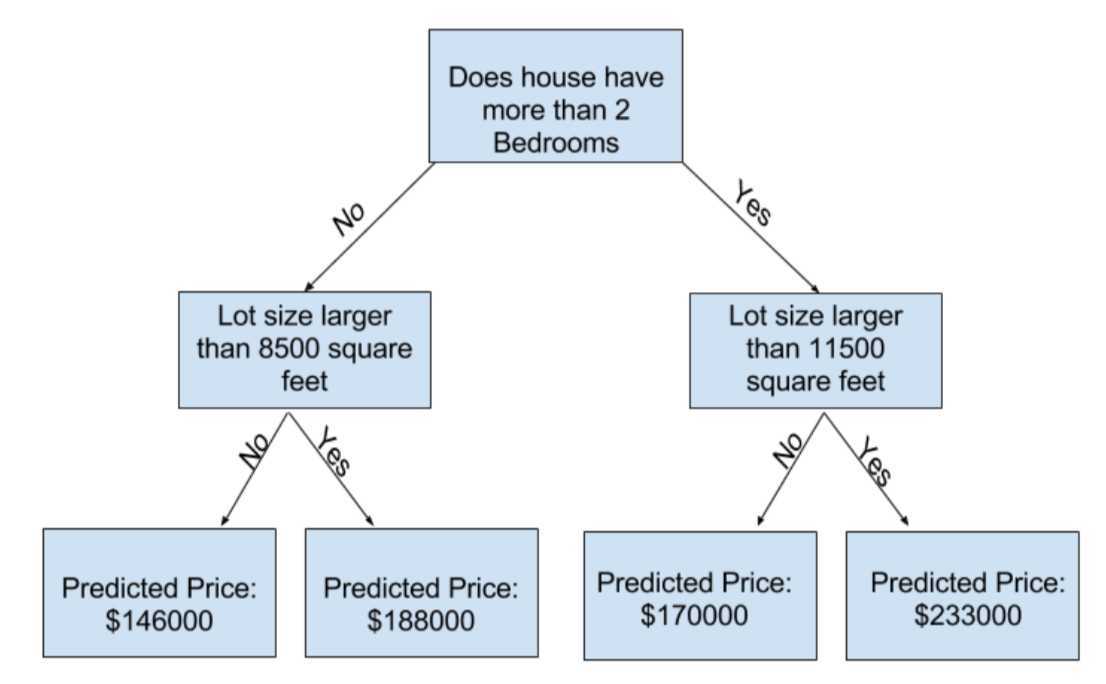
The more leaves we allow the model to make, the more we move from the underfitting area in the above graph to overfitting area.
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.tree import DecsionTreeRegressor
def get_ame(max_leaf_nodes, train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y):
model = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_leaf_nodes = max_leaf_nodes, random_state = 0)
model.fit(train_X, train_y)
preds_val = model.predict(val_X)
mae = mean_absolute_error(val_y, preds_val)
return(mae)
我可以使用循环比较选择最合适的max_leaf_nodes
for max_leaf_nodes in [5,50,500,5000]:
my_ame = get_ame(max_leaf_nodes, train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y)
print(max_leaf_nodes, my_ame)
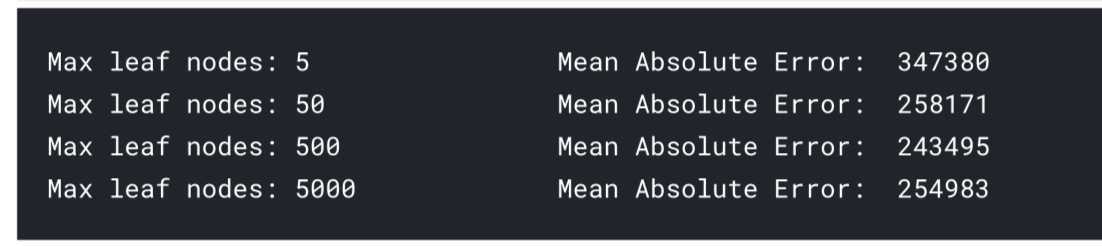
最后可以发现,当max leaf nodes 为 500时,MAE最小, 接下来我们换另外一种模型
6.Random Forests
The random forest uses many trees, and it makes a prediction by averaging the predictions of each component tree. It generally has much better predictive accuracy than a single decision tree and it works well with default parameters.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
forest_model = RandomForestRegressor(random_state=1)
forest_model.fit(train_X,train_y)
melb_preds = forest_model.predict(val_X)
print(mean_absolute_error(val_y, melb_preds))
可以发现最后的误差,相对于决策树小。
one of the best features of Random Forest models is that they generally work reasonably even without this tuning.

7.Machine Learning Competitions
标签:差距 cap determine tac tput nal ict ati exe
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhichun/p/11479813.html