标签:拼接 高效 enc 单个字符 xxx str 对象存储 操作系统 查看
目录
能够高速读写的缓冲流,能够转换编码的转换流,能够持久化存储对象的序列化流等等,这些功能强大的流,都是在基本的流对象基础之上创建而来的,就像穿上铠甲的武士一样,相当于是对基本流对象的一种增强。
缓冲流,也叫高效流,是对4个基本的 FileXxx流的增强,所以也是4个流,按照数据类型分类:
BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStreamBufferedReader,BufferedWriter
使用步骤(重点):
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo01BufferedOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递要输出数据的目的地
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("itcast-code\\a.txt");
// 2. 创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream对象,提高写入的效率
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
// 3. 调用BufferedOutputStream对象的方法,write写入数据
bos.write("我把数据写入到内部缓冲区中".getBytes());
// 4. 调用flush方法,刷新缓冲区
bos.flush();
// 5. 释放资源
bos.close();
}
}使用步骤(重点):
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo02BufferedInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建FileInputStream对象,构造方法中绑定读取的数据源
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("itcast-code\\a.txt");
// 2. 创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
// 3. 调用BufferedInputStream中的方法,read,读取文件
// 一次读取一个字节的方式
/*
int len = 0; // 记录每次读取字节的有效个数
while ((len = bis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)len);
}
*/
// 一次读取多个字节的方式
int len = 0; // 记录每次读取字节的有效个数
// 用来缓冲读取的字节
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
// 读取到文件末尾时,返回-1
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
}
}import java.io.*;
/*
使用缓冲流完成
文件复制练习:一读一写
明确:
数据源:
数据的目的地:
文件复制的步骤:
1. 创建字节缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流对象。
2. 创建字节缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流对像.
3. 使用字节缓冲输入流中的方法,read,读取文件。
4. 使用字节缓冲输出流中的方法 writer,把读取到的数据写入到内部缓冲区中。
5. 释放资源(会先把缓冲区中的数据,刷新到文件中)
*/
public class Demo03CopuFIle {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 1. 创建字节缓冲输入流对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\孙忠杰\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\3.jpeg"));
// 2. 创建字节缓冲输出流对象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\3.jpeg"));
// 3. 调用 read方法,读取文件
// 一次读取一个字节的方式
/*int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read()) != -1) {
// 调用 write方法,写入数据
bos.write(len);
}*/
// 使用字节数组缓冲一次读取到的多个字节
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
// 5. 释放资源
bos.close();
bis.close();
// 结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("文件复制耗费:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
}
}使用步骤:
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo04BufferedWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (// 1. 创建字符缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输出流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("itcast-code\\b.txt"));) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 2. 调用字符缓冲输出流对象中的方法,writer,把数据写入到内存缓冲区中
bw.write("我爱学习java,耶耶耶!");
// 使用特有的方法,newLine(),换行
bw.newLine();
}
// 3. 调用字符缓冲输出流对象中的方法,flush,把内存缓冲区中的数据,刷新到文件中
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
// 4. 释放资源
// bw.close();
}
}使用步骤:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo05BufferedReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建字符缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输入流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("itcast-code\\b.txt"));
/*
在不知道文本中有多少行时,使用while循环
while的结束条件,读取到 null时结束
*/
// 2. 使用字符缓冲输入流对象中的方法,read / readLine,读取文本
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
// 3. 释放资源
br.close();
}
}import java.io.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/*
练习:
对文本的内容进行排序
按照(1,2,3,4...)顺序排序
分析:
1. 创建一个HashMap集合对象
key:存储每行的文本序号(1,2,3...)
value:存储每行的文本
2. 创建字符缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输入流对象
3. 创建字符缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输出流对象
4. 调用字符缓冲输入流中的方法,readLine,逐行读取文本
5. 对读取到的文本进行切割,获取行中的序号和文本内容
6. 把切割好的序号和文本内容存储到HashMap集合中(key是有序的,会自动排序1,2,3..)
7. 遍历HashMap集合,获取每一个键值对
8. 把每一个键值对,拼接成一个文本行
9. 把拼接好的文本行,使用字符缓冲输入流的方法write,写入文件中
10. 释放资源
*/
public class Demo06Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建HashMap集合,key:序号,value:文本内容
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// 2. 创建字符缓冲输入流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("itcast-code\\in.txt"));
// 3. 创建字符缓冲输入流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("itcast-code\\out.txt"));
// 4. 使用字符缓冲输入流中的方法,readLine方法,读取文本内容
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 5. 对读取到的字符串进行切割,key:序号,value:文本内容
String[] arr = line.split("\\.");
// 6. 把切割好的字符串放入到HashMap集合中
map.put(arr[0], arr[1]);
}
// 7. 遍历HashMap集合,获取键值对
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
// 遍历Set集合的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = entrySet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
// 8. 对键值对进行拼接
line = key + "." + value;
// 9. 使用字符缓冲输出流对象,输出到文件中
bw.write(line);
// 换行
bw.newLine();
}
// 10. 释放资源
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}在IDEA中,使用FileReader读取项目中的文本文件。由于IDEA的设置,都是默认的UTF-8编码,所以没有任何问题。但是当读取Windows系统中创建的文本文件时,由于Windows系统的默认是GBK,就会出现乱码。
// 乱码问题
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\ideaproject\\itcast-code\\a.txt");
int len = 0;
while ((len = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)len);
}
fr.close();
}
}
/*
输出结果:
???????磡
*/charset 将要写入流中的字符编码成字节。(编码:把能看懂的 --> 看不懂的)使用步骤:
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Demo01OutputStreamWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// write_utf_8();
write_gbk();
}
private static void write_gbk() throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("itcast-code\\gbk.txt"), "gbk");
osw.write("你好"); // 3个字节
osw.flush();
osw.close();
}
private static void write_utf_8() throws IOException {
// 1. 创建OutputStreamWriter对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流对象和指定编码表名称
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("itcast-code\\utf_8.txt"), "utf-8");
// 2. 使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法,writer,把字符转换成字节,存储在缓冲区中。(编码)
osw.write("你好"); // 2个字节
// 3. 调用 flush方法,刷新数据到文件中、
osw.flush();
// 4. 释放资源
osw.close();
}
}使用步骤:
注意事项:
构造方法中传递的编码表名称要和文件的编码表相同,否则会产生乱码。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Demo03InputStreamReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// read_utf_8();
read_gbk();
}
private static void read_gbk() throws IOException{
// 1.创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流对象和指定的编码表名称
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("itcast-code\\utf_8.txt"), "gbk");
// 2.使用InputStreamReadr中的方法,read,读取文件。
int len = 0; // 记录读取到字符的有效个数
// 使用字符数组缓冲读取到的多个字符
char[] cs = new char[1024];
while ((len = isr.read(cs)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(cs, 0, len));
}
// 3.释放资源
isr.close();
}
private static void read_utf_8() throws IOException {
// 1.创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流对象和指定的编码表名称
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("itcast-code\\utf_8.txt"));
// 2.使用InputStreamReadr中的方法,read,读取文件。
int len = 0; // 记录读取到字符的有效个数
// 使用字符数组缓冲读取到的多个字符
char[] cs = new char[1024];
while ((len = isr.read(cs)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(cs, 0, len));
}
// 3.释放资源
isr.close();
}
}import java.io.*;
/*
练习:转换文件编码
将gbk编码的文件,转换为utf-8编码的文件。
分析:
1.创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流对象和指定gbk编码
2.创建OutputStreamWriter对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流对象和指定utf-8编码
3.使用InputStreamReader对象的方法 read,读取数据到缓冲区中
4.使用OutputStreamWriter对象的方法 writer,将数据写入到文件中
5.释放资源
*/
public class Demo02Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("itcast-code\\gbk.txt"),"gbk");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("itcast-code\\utf_8.txt"), "utf-8");
int len = 0;
while ((len = isr.read()) != -1) {
osw.write(len);
}
osw.close();
isr.close();
}
}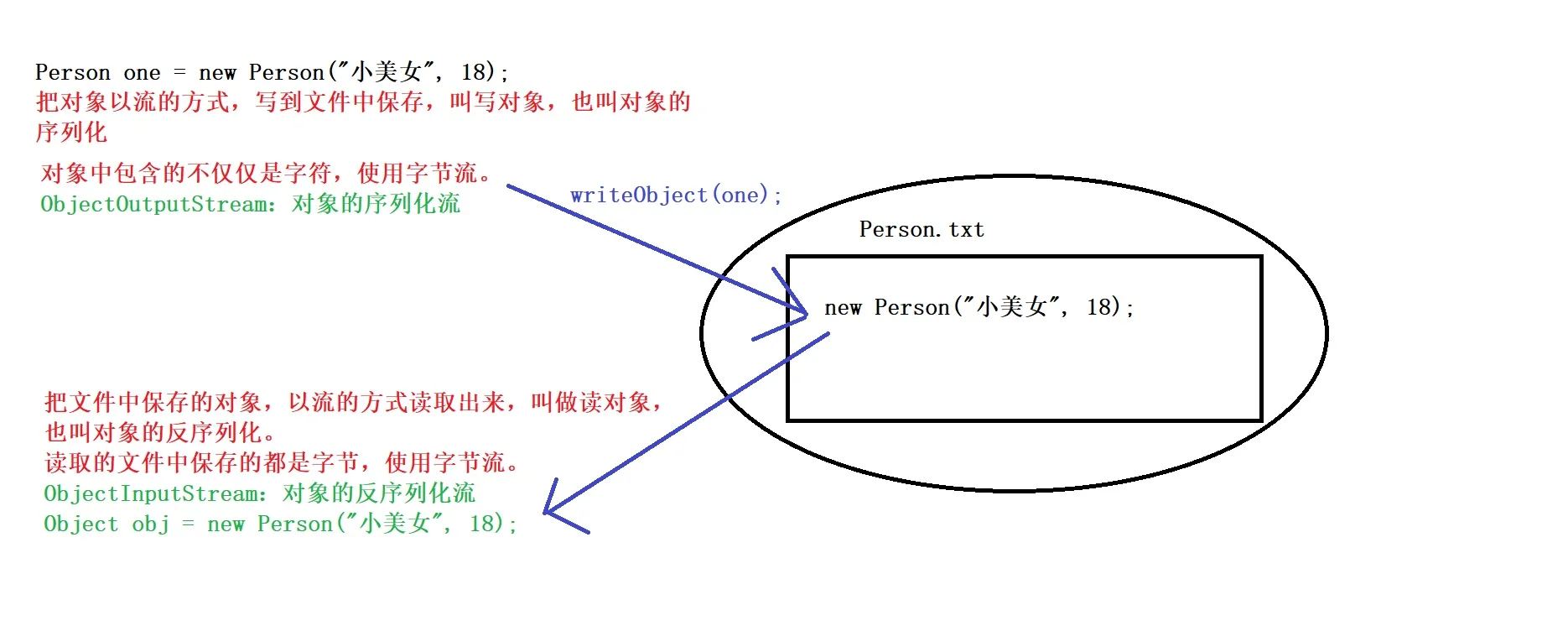
使用步骤:
import java.io.Serializable;
/*
序列化和反序列化的时候,会抛出 NotSerializableException没有序列化异常
类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。
未实现此接口的类将无法使其任何状态序列化或反序列化。
Serializable接口也叫标记型接口
要进行序列化和反序列化的类,必须实现 Serializable接口,就会给类添加一个标记
当我们进行序列化和反序列化的时候,就会检测类上是否有这个标记
有:可以序列化和反序列化
没有:就会抛出 NotSerializableException异常
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Demo01ObjectOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Person one = new Person("小美女", 18);
// 1.创建ObjectOutputSream对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("itcast-code\\person.txt"));
// 2.使用ObjectOutputstream中的方法,writerObject,将对象写入到文件中
oos.writeObject(one);
// 3.释放资源
oos.close();
}
}使用步骤:
注意事项:
readObject方法声明抛出了 ClassNotFoundException(class文件找不到异常)
当不存在对象的 class文件时抛出此异常。
反序列化的前提:
- 类必须实现 Serializable接口
- 必须存在类对应的 class文件
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class Demo03ObjectInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 1.创建ObjectInputStream对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("itcast-code\\person.txt"));
// 2.使用ObjectInputStream中的方法,readObject,读取文件中保存的对象
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
Person one = (Person)o;
System.out.println(one.getName()+one.getAge());
// 3.释放资源
ois.close();
}
}private static int age;
oos.writeObject(new Person("小美女", 18));
Object o = ois.readObject();
Person{name='小美女', age=0}private transient int age;
oos.writeObject(new Person("小美女", 18));
Object o = ois.readObject();
Person{name='小美女', age=0}编译器(javac.exe)会把 Person.java文件编译成生成 Person.class 文件,Person类实现了 Serializable接口,就会根据类的定义,给 Person.class文件添加一个序列号(serialVersionUID)。
修改了类的定义,那么就会给 Person.class 文件重新编译生成一个新的序列号(serialVersionUID)。
static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/*
练习:序列化集合
当我们想在文件中保存多个对象的时候,可以把多个对象存储到一个集合中
对集合进行序列化和反序列化
分析:
1.定义一个存储Person对象的ArrayList集合
2.往ArrayList集合中添加多个对象
3.创建一个序列化ObjectOutputStream对象
4.使用ObjectOutputStream对象中的 writeObject方法,对集合进行序列化
5.创建一个反序列化ObjectInputStream对象
6.使用ObjectInputStream对象中的方法 readObject方法,读取文件中保存的集合
7.把 Object类型的集合强转为 ArrayList类型
8.遍历ArrayList集合
9.释放资源
*/
public class Demo02Pracitse {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 创建集合
ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加元素
list.add(new Person("周元", 20));
list.add(new Person("夭夭", 21));
list.add(new Person("苏幼薇", 19));
// 创建序列化流对象
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("itcast-code\\list.txt"));
// 调用 writeObject方法,将集合写入
oos.writeObject(list);
// 创建反序列化流对象
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("itcast-code\\list.txt"));
// 调用 readObject方法,读取集合
Object o = ois.readObject();
// 将 Object类型强转为 Arraylist类型
ArrayList<Person> personArrayList = (ArrayList<Person>)o;
// 遍历集合
for (Person p : personArrayList) {
System.out.println(p);
}
// 释放资源
oos.close();
ois.close();
}
}注意事项:
- 如果使用继承自父类的 write方法写数据,那么查看数据的时候,会查询编码表:97 --> a。
- 如果使用自己特有的方法 print / println方法写数据,那么写的数据会原样输出:97 --> 97。
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Demo01PrintStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 1.创建PrintStream对象,构造方法中绑定输出的目的地
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("itcast-code\\print.txt");
// 2.调用父类的 write方法
ps.write(48); // 0
// 2.调用自己的 print / println 方法
ps.println();
ps.println(97); // 97
// 3.释放资源
ps.close();
}
}import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Demo02PrintStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("itcast-code\\print.txt");
// 在控制台输出
System.out.println("我在控制台输出,哈哈哈");
// 改变输出流的流向
System.setOut(ps);
// 这条语句在文件中原样输出
System.out.println("我在print.txt中输出,呵呵呵");
ps.close();
}
}标签:拼接 高效 enc 单个字符 xxx str 对象存储 操作系统 查看
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/blog-S/p/11487469.html